* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Outline 8
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
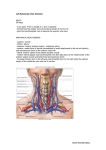
Lecture 8 (Note: Your textbook devotes very little text to the subject of surface anatomy. Instead, the book utilizes many labeled pictures. Be aware that exam questions may come from the outline or may be in the form of unlabeled pictures) Intro to Surface Anatomy Surface Anatomy is concerned with identifying body structures on the surface as they relate to _______________ structures Visual inspection – directly observing the structure and markings of surface features Palpation- Feeling with firm pressure or perceiving by sense of touch Percussion – ______________________ firmly on specific body sites to detect resonating vibrations Auscultation – listening to sounds emitted from organs Applications: Maintenance of physical fitness and medical diagnosis and treatment Fitness o Knowing where _______________ and muscle groups are located Diagnosis & Treatment o Knowing where to Record a ________________ Insert a needle or tube Listen to _________________ of internal organs Take radiographs Most of the bones of the skeleton are palpable and provide landmarks for locating other anatomical structures Exceptions: certain bones of the _____________ The effectiveness of visual inspection and palpation in studying a person’s surface anatomy is influenced by the thickness of the hypodermis, which varies in accordance with the amount of subcutaneous ______________ tissue present Head General Regions of the Head Cranial Regions _______________ Region – posterior region Frontal Region – anterior and superior region Temporal Region o ________________ region (also covered by scalp) o Attachment for the temporalis muscle, which can be palpated when jaw is repeatedly clenched o This region is often the point of entry for surgical procedures Facial Regions Orbital region that surrounds (and includes) the eye o _________________ protect from sunlight and mechanical blows o __________________ close by reflex to protect against objects moving towards the eye or visual stimuli o ___________________ prevent air-born particles from contacting the eyeball o _____________________ secretions (tears) wash away chemicals or foreign materials o _______________________ is a thin mucous membrane that covers the anterior surface of the eyeball and lines the undersurface of the eyelid; it reduces friction during blinking o ________________ is the white of the eye that gives the eye its shape o __________________ is the transparent anterior portion of the eye that refracts incoming light o _________________ is the circular, colored, muscular portion of the eye that regulates the amount of incoming light o ___________________ is the opening in the center of the iris through which light enters the eyeball the auricular region of the ear o ______________________ is the fleshy pinna of the ear that projects from the side of the head and projects sound into the external acoustic canal o __________________ is the rim of the auricle, shaped and supported by eleastic cartilage o _________________ is the inferior portion of the auricle o _________________ is the small posteriorly directed projection partially covering and protecting the the external acoustic canal the nasal region serving the respiratory system o ________________ of the nose is the point in the skull where the nasal and frontal bones unite o __________________ is the firm narrow part between the eyes o _______________ is the tip of the nose o _________________ or external nares are the paired openings into the nose o The __________________________ is the lateral depression where the ala of the nose contacts the tissues of the face o __________________ (or ala) of the nose forms the flaired outer margin of each nostril the oral region serving the digestive and respiratory systems o _____________ are upper and lower anterior borders of the mouth o __________________ is the anterior portion of the lower jaw o ___________________ is the vertical depression in the medial part of the upper lip Trunk Vital visceral organs in the trunk make the surface anatomy of this region especially important The ________________ (vertebral furrow) is visible, no matter how much adipose tissue is present The vertebral spines are ________________ One may observe the furrow or palpate the spines to determine defects of the vertebral column The _____________________ are palpable on the back The base of the spine of the scapula is level with the third thoracic vertebra and the inferior angle of the scapula is even with the seventh thoracic vertebra The medial and lateral borders are also ______________________ The triangle of auscultation is present on the back It’s the region bordered by the rhomboid major, ___________________, and latissimus dorsi At this site one can more easily hear _______________________ sounds without interference from thick muscles The palpable structures of the thorax include: the ______________________ the ______________ the costal _________________ is the lower oblique boundary of the rib cage o the costal ________________ is the location where the costal margins come together as an inverted V of the position of the xiphoid process of the sternum The important surface anatomy features of the abdomen include: the _____________ alba - A tendinous, midventral raphe from the xiphoid process to the symphysis pubis the ___________________ semilunaris - These paired and slightly curved vertical lines represent the lateral border of the rectus sheaths which enclose the rectus ____________________ muscle on each side. the ________________________- site of attachment of the fetal umbilical cord the costal _______________- lower oblique boundary of the rib cage o right costal margin is over the liver an gallbladder o left costal margin is over the stomach and spleen the _______________ crest- Highest point is opposite the body of the fourth lumbar vertebra, - needed in spinal anesthesia the ________________- can be palpated at the anterior union of the two halves of the pelvic girdle Pelvis and Perineum The crest of the ilium, the symphysis pubis, and the inguinal ligament and McBurney’s point are important pelvic landmarks The iliac crest and the symphysis pubis are both palpable The __________________ ligament extends from the anterior superior iliac spine to the symphysis pubis o It’s clinically important because hernias may occur along it o Ligament can’t be seen, but there is a groove overlying the ligament that can be seen ____________________ point is 1/3 of the distance from the right anterior superior iliac spine on a line between that spine and the umbilicus. An appendectomy is made through an incision at this point The _____________________ is the region that contains the external genitalia and the anal opening Shoulder and Upper Extremity The surface anatomy of the shoulder and upper extremity is important because of the frequent trauma to these regions. Vessels of the upper extremity are also used as pressure points and for intravenous injections or blood withdrawal. The _________________, clavicles, and humerus are palpable in the shoulder The axilla is clinically important because of the vessels, ____________, and lymph nodes located there The brachial artery is an important pressure point in the brachium. The medial cubital vein is important for the removal of ___________ or for intravenous therapy The ulna, radius, and their processes are palpable landmarks of the forearm The ______________ nerve can be palpated in the ulnar sulcus posterior to the medial epicondyls The sulcus and ulnar nerve together are referred to as the “funny bone” The knuckles, fingernails, and tendons for the extensor muscles of the forearm can be observed on the posterior aspect of the hand The anatomical ____________________ is created by two tendons pulled taut o Pulsations of the radial artery can be detected here o The two tendons include: The tendon of the __________________ pollicis brevis muscle The tendon of the extensor pollicis longus muscle Flexion creases and the __________________ eminence are important features on the anterior surface of the hand o The thenar eminence is the thickened muscular portion of the hand that forms the base of the thumb Digits have two types of joints MP joints are metacarpophalangeal joints – connecting metacarpals and phalanges Interphalangeal joints are found between the bones of individual digits DIPs are distal interphalangeal joints PIPs are proximal interphalangeal joints Buttock The massive bones and muscles in the buttock and lower extremity serve as weight-bearers and locomotors. Gluteus __________________ – forms most of the inferolateral “fleshy” part of the buttock Natal cleft- vertical separation between the buttocks Gluteal fold – inferior _______________ of the gluteus maximus Iliac crest – can be palpated The horizontal line between the iliac crests bisects the spinous process of the 4th lumbar vertebrae Injections can safely be given 5 to 7 cm inferior to the crest without much risk to the sciatic nerve Lower Extremity The thigh has three muscle groups: ________________ (quadriceps), medial (adductors), and posterior (hamstrings) The femoral triangle and popliteal fossa are clinically important surface landmarks o Femoral __________________: Depression inferior to the location of the inguinal ligament on the anteromedial surface in the upper part on the thigh Major vessels of the lower extremity and the femoral _______________ traverse this region o Popliteal Fossa: Depression on the posterior aspect of the knee joint Important due to vascular problems that occur here in the ________________, due to reduced muscle tone and inactivity The structures of the leg include the tibia and fibula, the muscles of the calf, and the saphenous veins o Great and small __________________ veins are superficial blood vessels The surface anatomy of the foot includes structures adapted to support the weight of the body, maintain balance, and function during locomotion o Lateral longitudinal arch – curvature along the ________________ side of the foot o Medial longitudinal arch – curvature along the medial side of the foot