* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download taxonomy - Zoology!
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
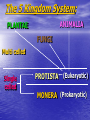
TAXONOMY The Science of Classification What is Taxonomy? It is the science of: • Describing • Identifying • and Naming organisms. • It helps scientists (like biologists) create order out of the millions of different kinds of plants, animals and other life. How many animals can you find in this rain forest scene? 29 Why is taxonomy used? • We use taxonomy in our daily lives to make order out of chaos. • An example might be: • Shopping in a grocery store. Using a Dichotomous Key • A dichotomous key is a tool that allows users to identify items or organisms in a systematic and reproducible fashion. • Dichotomous keys may be used in a variety of situations (such as for identifying rocks and minerals), as well as for identifying unknown organisms to some taxonomic level (i.e.; species, genus, family, etc.). •What makes these keys distinctive is that they are ordered in such a way that a series of choices are made that leads the user to the correct identity of the item at which they are looking. •"Dichotomous" means, "divided into two parts." Therefore, dichotomous keys always offer two choices for each step, each of which describes key characteristics of a particular organism or group of organisms. •(set up example with 4 girls/3 boys) 1. Sex female--- go to #2 Sex male--- go to #5 2. Hair color red---Sally Hair color not red--- go to #3 3. Hair color blonde---Julie Hair color black--- go to #4 4. Glasses worn---Deanna Glasses not worn---Leslie 5. Shoes high-top sneakers--- Joseph Shoes not high-tops--- go to #6 6. Hair color blonde--Michael Hair color brown--David Binomial nomenclature: • All living organisms, plant, animal and those in between, are classified down to just two names: • Genus • species • “Binomial nomenclature” roughly translates to mean “two names.” • Genus = generic; species = specific Examples of genus & species: • Homo sapien means “thinking man.” •Callenectes sapidus the blue crab means “beautiful swimmer,” Tursiops truncatus is the Atlantic bottlenose dolphin. The dolphin fish is Coryphaena hippurus Carolus Linnaeus (Carl von Linné) • He developed the modern system of taxonomic classification He published the 10th Edition of the Systema Naturae in 1758. What language to use?... • Since Linnaeus needed to be able to communicate with scientists from all over the world, he had to use a language that was familiar to most of them. • He chose Latin, because it is: • Apolitical • The root of all languages • A dead language (not spoken by anyone as a normal dialect). The 7 Levels of Classification: • Classifying organisms goes from the most general to the most specific: Kingdom – is it plant or animal? Phylum – vertebrate or invertebrate? Class Order Family Genus species How to write genus & specie: • To indicate to the reader that an organism has been identified all the way to genus & specie, it is ALWAYS written as either: 1. Genus capitalized and underlined, and specie lower case and underlined, or 2. Genus capitalized and in italics, and specie lower case and in italics. • Example: Calenectes sapidus or Calenectes sapidus The 5 Kingdom System: ANIMALIA PLANTAE FUNGI Multi celled Single celled PROTISTA (Eukaryotic) MONERA (Prokaryotic) Kingdom Characteristics: • MONERA: prokaryotic (no nuclear membrane); unicellular; ex: bacteria & blue-green algae. • PROTISTA: eukaryotic; unicelled plant and animal-like organisms; mobile & autotrophic; ex: phytoplankton. • FUNGI: sessile & heterotrophic. • PLANTAE: sessile & autotrophic. • ANIMALIA: mobile & heterotrophic. Kingdom Metaphyta: The True Plants • Plants differ from animals mainly by their ability to photosynthesize • (also known as autotrophic feeding) • They produce a simple organic sugar • Glucose (C6 H12 O6 ) from inorganic materials such as: • sunlight, water, CO2 and the nutrients phosphates and nitrates (fertilizer) • plants use chlorophyll a and b in their leaves for absorbing light, and rooted (which makes them sessile). Kingdom Metazoa: The True Animals • Animals are heterotrophic feeders because they cannot produce their own food. They need plant and animal material to make organic compounds like: • Carbohydrates– these are made by plants during photosynthesis; ex: sugar & starch. • Fats– provide the body with more than 2X as many calories per gram as do carbos. • Proteins– the main source of raw materials for the body’s muscles, blood, skin, heart and brain (amino acids). 5 Major Marine Phyla: • Porifera – the sponges; simplest multi-celled animals; body full of pores and canals. • Cnidaria – jellyfish, corals and sea anemones; have stinging cells in their tentacles called nematocysts used to capture prey. • Mollusca – clams, snails, octopus and squid; soft-bodied usually with a foot and shell. • Arthropoda – crabs, shrimp and lobster; jointed appendages with a hard exoskeleton. • Echinodermata – starfish, sand dollars, sea urchins and sea cucumbers; have spiny skin and a water vascular system.