* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Splanchnology
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
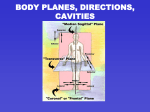
Splanchnology 一、Introduction 1 Conception : study of viscera(internal organs) 2 Organs of viscera : include the organs of the alimentary system, respiratory system, urinary system and genital system. 3 Location of viscera: thoracic,abdominal and pelvic cavity 4 Classify of visera: ·Tubular viscus : four layers →Mucosa、submucosa、muscular layer、 Serosa or adventitia ·Parenchymatous organs : 二、Reference lines Lobules 、hilum or porta and abdominal regions (一)The common used reference lines of the Thorax 1 anterior: Anterior median line Sternal line Midclavicular line Parasternal line 2 lateral: Anterior axillary line Midaxillary line Posterior axillary line 3 posterior: Scapular line Posterior median line (二)Abdominal regions:four lines and nine regions Four lines 1 Two horizontal lines :Upper horizontal plane or transpyloric plane 、 Lower horizontal plane or transtubercular plane 2 Two longitudinal lines ·Nine regions 1 Superior : Epigastric region , Right hypochondriac , Left hypochondriac 2 Middle : Umbilical region, Right lumbar region, Left lumbar region 3 Inferior: Pubic (hypogastric)region , Right inguinal region ,Left inguinal region The second chapter: Alimentary system Digestive canal : Mouth、Pharynx、Esophagus、Stomach、 Small Intestines 、Large intestines Digestive glands:Major glands(parotid ,submandibular and sublingual glands, liver and pancreas) , minor glands ( lip , cheek , tongue and wall of digestive canal) The first part: digestive canal Section one The oral cavity 一、Introduction 1 The oral vestibule 2 Oral cavity proper The space behind the 3th molar teeth on each side Lateral wall : Cheeks → opening of the parotid duct Roof : Palate palate Hard palate:anterior 2/3 soft palate:posterior 1/3 uvula palatoglossal arch palatopharyngeal arch tonsillar fossa Isthmus of fauces 二、 Oral cavity contents Teeth Tongue Salivary glands 1.Teeth 1)Two sets of teeth in man Deciduous (milk) : 20 in number Permanent : 28~32 in number 2)Morphology of teeth crown of tooth 、neck of tooth 、root of tooth Dental pulp cavity root canal of tooth Dental pulp 3)The structure of the teeth and periodontal structure: Dental tissues : dentin,enamel,cement,Cavum dentis (dental pulp) Periodeontal structure :Alveolar bone,Periodontal membranen,gums 4)The morphological classification and arrangement of the teeth classification: two Incisors one canine Molars Two premolars Three molars 2 Tongue Muscular organ covering mucosa on the surface Function: Digestive organ,Pronounce organ,Tasting organ Location Morphology Tongue muscle 1)Location: Lies partly in the floor of the mouth Partly in the lower part of the pharynx 2)Tongue morphology (1) Division : a root 、an apex and a body (2) Two surfaces: A Dorsum or superior surface papillae: vallate papillae Fungiform papillae Filiform papillae B ventral or inferior surface Frenulum of tongue , sublingual caruncle , sublingual fold; (3) Lingual tonsil 3)Tongue muscles: striated muscles (1) Intrinsic muscles Longitudinal tongue muscles Superior longitudinal muscle Inferior longitudinal muscle Horizontal tongue muscles Perpendicular tongue muscle (2) Extrinsic muscles 3 Genioglossus , Styloglossus , Hyoglossus ,Myloglossus Salivary glands (1)parotid gland: location: duct: Opening at cheek mucosa , oppsite the crown of the upper 2nd molar of maxilla (2)submandibular gland location duct: open on the sublingual caruncle (3) Sublingual gland Location Duct : major duct opens on the sublingual caruncle; minor ducts open on the sublingual fold. The second section: pharynx Location: Subdivisions nasopharynx oropharynx Laryngopharynx Pharygeal muscles 一、Location 二、Subdivision (一) Nasopharynx Location: from cranial base to the level of soft palate (二) Structures: Choanae( posterior nasal apertures ) Tubal torus Pharyngeal opening of auditory tube Pharyngeal recess Phartngeal Tonsil (二)Oropharynx Location:above the level of the soft palate and below border of the epiglottis. Structures of the superior Palatine tonsil Tonsil recess Epiglottic vallecula (三)Laryngopharynx ·Location : between the superior border of the epiglottis and the inferior border of the sixth cervical verterbra ·Piriform recess The third section: esophagus 一、Location and subdivision of esophagus ·Begin at C6 inferior border, extend from pharynx to stomach, about 25cm long. ·Subdivisions: Cervical part,Thoracic part, Abdominal part 二、Narrows of esophagus 1 At its commencement, 15cm from the incisor 2 Cross part of left and right bronchus, 25cm 3 Passes(pierces) through the diaphragm 三、Structure of esophagus Muscular layer: Upper end: striated muscles Middle part: mixture of striated and smooth muscles Lower end:smooth muscles The fourth section: stomach The location The parts of stomach The musculature and inner surface 一、Location of stomach: Left hypochondriac region and Epigastric region 二、The parts of stomach Two orifices: Cardiac orifice pyloric orifice Four parts: Cardiac part Pyloric part:Pyloric antrum,Pyloric canal Body Fundus Two curvatures :greater and lesser One incisure:Angular incisure 三、 The musculature and inner surface Mucosa or mucous membrane : Pyloric valve submucous Muscle layer: Three layers Outer longitudinal layer Inner oblique layer: pyloric sphincter Middle circular muscular layer serosa The fifth section: the small intestine Conception : between pylorus and cecum Subdivisions: Duodenum Jejunum ileum 5~7m in long: Flexures Duodenojejunal flexure Suspensory muscle of duodeunm(ligament of Treitz) 一、Duodenum Location: 25cm, between pylorus and jejunum; Subdivision: Upper part: Descending part: major duodenal papilla Horizontal part: Ascending part: 二、Jejunum and ileum jejunum Length: Caliber: ileum upper 2/5 greater lower 3/5 lesser Fold of mucous member: much and higher less and lower Blood supply: less much Lymph lymphatic follicles : solitary aggregated The sixth section: large intestine Features of the colon Colic bands Haustra of colon Epiploic appendices Subdivision: caecum Colon Rectum 一、Caecum Location: ileocaecal the right iliac fossa valves 二、Vermiform appendix 1 Attachment : spring from the posteromedial wall of the caecum, below the end of the ileum 2 3 4 Several Positions : ■ Behind or in front of the terminal part of the ileum ■ Below or behind the caecum ■ Below the brim of the lesser pelvis McBurney’ point ( surface projection of the root of the appendix) : opposite junction of the lateral and middle thirds of the line joining the anterior superior iliac spine to the umbilicus. How to find the appendix : three colic bands converge on the root of the appendix. 三、Colon 1 Ascending colon Right colic flexure 2 Transverse colon Left colic flexure 3 Descending colon; 4 Sigmoid colon 四、Rectum 1 Location: 2 Feature:sacral flexure and perineal flexure 5 Structures:ampulla of rectum , transverse folds of rectum 五、Anal canal 1 Morphology Anal columns Anal valves Anal sinuses Dentate line Anal pecten 2 Sphinter muscles internal anal sphincter externus anal sphincter The seventh section: liver (hepar) ·Location ·Lobes and ligaments ·The gallbladder and biliary ducts 一、Location and shape Shape: Wedge-shape Location Upper and right parts of the abdominal cavity below the right half of the diaphragm and extend to the left midline for about 3cm. 二、Lobes of liver and morphological features ■Superior (diaphragmatic) surface: Left and right lobes by the falciform lig. ■Inferior (visceral) surface H shape sulcus Left longitudinal fissures : anterior, posterior Right longitudianl fissures: anterior, posterior Horizontal fissures: Porta hepatis Lobes:quadrate lobe,caudate lobe, left and right lobes 三、The gallbladder and biliary ducts ·Gallbladder Fundus Body Neck→ cystic duct ·The bile duct: Right and left hepatic ducts → common hepatic duct , and cystic duct → common bile duct, and pancreatic duct → hepatopancreatic ampulla → greater duodenal papilla The eighth section: pancreas Location: between L1~2, on the posterior wall of the abdomen; Morphology and structure: Head ,(Neck) ,Body,Tail Pancreatic duct:major duodenal papilla Function:Endocrine part: Insulin, Exocrine part: Enzymes Objective: 1. To know about the definition of viscera. 2. To know about the reference lines of thorax and abdominal regions. 3. To master the composition of digestive system 4.To master the structuresof the oral cavity : palatine tonsil , uvula, palatoglossal arch , palatopharyngeal arch , tonsillar fossa , Isthmus of fauces 5. To know about the classify of the deciduous and permanent teeth. 6. To master the structure of the teeth. 7. To master the locations and openings of the salivary glands. 8. To master the subdivision of pharynx . 9. To master the structures of pharynx : tubal torus ,pharyngeal opening of auditory tube, Pharyngeal recess , pharyngeal tonsil 10. To master the subdivision and three constrictions of esophagus. 11. To master the location, shape and subdivision of stomach. 12. To master the subdivision of small intestine. 13. To master the location and subdivision of duodenum. 14. To master the difference between jejunum and ileum. 15. To master the subdivision of large intestine. 16. To master the characteristics of form of colon. 17. To master the locations and structures of cecum and vermiform appendix. 18. To master the surface projection of the root of vermiform appendix. 19. To master the location and structures of rectum (sacral flexure and perineal flexure , ampulla of rectum , transverse folds of rectum ) 20. To master the location and structure of anal canal.( dentate line, anal pectin internal and external anal sphincter 21. To master the location and surface anatomy of liver. 22. To master the H-shaped group of fissures and fossae. 23. To master the lobes of liver . 24. To master the location and division of gallbladder. 25. To master the composition of bile ducts. The third chapter : the respiratory system Respiratory canal nose,pharynx, larynx,trachea,principal bronchi with their branches upper respiratory tract : nose,pharynx, larynx lower respiratory tract :trachea,principal bronchi with their branches Lungs: organ for exchange air The first section: nose 一、External nose Apex Back of nose Root of nose Alae of nose 二、Nasal cavity Nasal vestibule: limen nasi Proper nasal cavity :lateral wall Superior,middle and inferior nasal conchae Superior,middle and inferior nasal meatuses Function:Olfactory and respiratory regions 三、paranasal sinuses maxillary siuns,、frontal sinus,ethmoid sinus,sphenoidal sinus The second section: Pharynx Common channel for both alimentary system and respiratory system The third section: larynx Location:the neck of region in front of the fourth ,fifth and sixth cervical vertebrae. Structures:cartilages,joint and ligaments, Laryngeal cavity muscle 一、Laryngeal cartilages Thyroid cartilage:laryngeal prominence, superior thyroid notch, superior and inferior cornu Cricoid cartilage:lamina of cricoid cartilage , arch of cricoid cartilage Arytenoid cartilages: vocal process, muscular process Epiglottic cartilage 二、Laryngeal joints and connective membrane Cricothyroid joint Cricoarytenoid joint 三、Laryngeal ligaments and menbranes Thyrohyoid membrane Conus elasticus : superior border →vocal ligament Quadrangular membranes 四、Laryngeal muscles Open the glottis:posterior cricoarytenoid Close the glottis:transvers arytenoid,oblique arytenoid Tense and lengthen the vocal fold: posterior cricorytenoid Relax and shorten the vocal fold: thyroarytenoid 五、Laryngeal cavity ■ Two pair of folds: vestibular folds , vocal folds ■ Two fissures: rima vestibuli, fissure of glottis ■ Subdivision: three parts → Laryngeal vestibule , Intermedial cavity of larynx , Infraglottic cavity The third section: trachea and bronchi 一、Trachea Location Structure:15~30 C-shape tracheal cartilages,smooth muscle and connective tissues. Feature: Bifurcation of trachea Carina of trachea 二、Bronchi Two principal bronchus:left and right principal bronchus Structure feature of right principal bronchus Short(2~3cm) wider vertical Structure feature of left principal bronchus Long(4~5cm) finer Less vertical ■Bronchial tree Lobar bronchi→segmental bronchi→bronchioles→terminal bronchioles →alveoli The fourth section: lungs 一、Location and function of lungs Location : Situated one each side with in the thorax, and separated from each other by the heart and other contents of the mediastinum. Functions 二、External feature of lungs An apex, A base, Two surface Diaphragmatic surface Medial surface:root of lung,hilum of lung Three borders 三、the lobes and bronchopulmonary segments Lobes of the lungs Left lung: two lobes Right lung: three lobes Segments of lung Tens segments The fifth section: pleura Concept: a serous membrane, that lines the inner surface of the thorax and the surface of lungs 一、The parietal pleura Costal pleura Diaphragmatic pleura Mediastinal pleura Cupula of pleura 二、The visceral pleura Pulmonary ligament 三、the pleural cavity and recesses Costodiaphragmatic recess Costomediastinal recess 四、Project of the inferior margins of lung and pleurae lungs Midclavicular line 6th rib pleurae 8th rib Midaxillary line Post. Median line 8th rib T10 spinal process 10th rib T12 spinal process The sixth section: mediastinum Concept:defined as the interval between the right and left pleural sacs. Subdivision:by the line drawn horizontally from the sternal angle the lower border of 4th thoracic vertebra. Superior mediastinum Inferior mediastinum Anterior mediastinum Middle mediastinum Posterior mediastinum Contents The fourth part: urinary system Kidney : Form urine Ureter: Convey urine Urinary bladder : Store urine to Urethra: Expel urine The first section: kidneys 一、 The Form of kidneys:bean-shaped, 10cm long , 5cm wide, 4cm thick 二、Structure of kidney Renal cortex:Renal columns Renal medulla : Renal pyramids Renal papillae Minor renal calyx Major renal calyx Renal pelvis 二、 Location and coverings (一)Location: Behind the parietal peritoneum (retroperitoneal) . Left kidney situated at level of the inferior border between T12 and L3 , but right kidney lower 1/2 vertebra (二)Coverings:from inner to outer Fibrous capsule Adipose capsule Renal fascia 三、 Renal segments and abnormal kidney ■ Five segments: according to way of artery Superior segment Superioanterior segment Anteroinferior segment Inferior segment Posterior segment ■ Abnormal kidney multilocular cyst of kidney , horseshoe kidney , double renal pevis The second section: ureters Subdivision: Abdominal segment Pelvic segment Intramural segment Constricted parts: 1 at the junction of the ureter and the renal pelvis 2 at the point where ureter crosses the superior aperture of the lesser pelvis 3 at the intramural part The third section: urinary bladder 一、Form and location of bladder Form: Apex Fundus Body Neck Location:lesser pelvis inferior to the peritoneum 二、Internal structures of bladder Inferior orifice of urethra Ureteric orifice Trigone of bladder: Interureteric ridge The fourth section: urethra Male urethra: Female urethra: Discharge of urine Feature:short、wide、straight The fifth part : The reproductive(genital) system Chapter I The male reproductive system Be divided into two parts: internal and external genital organs. 1 Internal genital organs: a.Gonads:testes b.Conveying duct: epididymes, ductus deferens,ejaculatory duct and urethra c.Accessory glands: seminal vesicle, prostate,bulbourethral gland 2 External genital organs: Penis and scrotum 一、 The internal genital organs (一) The testes 1 Location: in the scrotum 2 Shape: oval-shape. Has two extremities, two surfaces and two borders 3 Structure Content of connective tissues: • Tunica albuginea • Septula testis Gland tissue: a. Lobules testis b.Contorted semniferous tubules c.Rete testis d.Efferent ductules of testis 4 Function: (二) Epididymis 1 Morphology head body tail 2 Structure : Ductus deferens (三) Ductus deferens 1 Course 2 Division: The testicular part The funicular part:vasectomy is performed here The inguinal part The pelvic part (四)Ejaculatory duct Formed by the union of the end part of the dutus deferens and the seminal vesicle duct. (五)Spermatic cord 1 Contents:ductus deferens, testicular artery, pampeniform plexus of vein, nervous plexus, lymphatic vessels and the remnants of the vaginal process. 2 Course: extend from the upper extremity of the testis to the inguinal deep ring. (六) Seminal vesicle 1 Location:behind the urinary bladder , lateral to the ampulla ductus deferentis 2 Function (七)Prostate 1 Location:between the urinary bladder and the urogenital diaphragm. 2 Division: base, body and apex 3 Structure:gland and muscles 4 Five lobes: anterior ,left and right lobes as well as posterior lobes 5 Capusle (八)bulbourethral gland situated in the deep transverse muscle of perineum The second section: external genital organs Scrotum Penis: 一、Scrotum 1 Location:posteroinferior to the penis 2 Structure:skin, dartos 3 Function 二、Penis 1 Structures: one cavernous body of urethra two cavernous bodies of penis 2 Division: Head(glans) Body Root 3 prepuce The third section: male urethra 1 Course: 2 Subdivision: The prostatic portion The membranous portion The cavernous portion 3 Three narrows:internal urethral orfice, the membranous portion and external urethral orifice 4 Three expends:the prostatic portion, bulbous portion of urethra and navicular fossa 5 Two curvatures: the subpubic curvature and the prepubic curvature The chapter II: female genital organs Be composed of internal and external genital organs . 1.Internal genital organs include: a.gonads:ovaries b.conveying ducts:the uterine tube, uterus and vagina 2.External genital organ is termed the female pudendum collectively. The first section: internal genital organs 一、ovaries 1 Shape:a pair of oval organs.has two surfaces, two borders and two extremities. 2 Location:on the lateral wall of the pelvis. 3 Ligaments: the proper lig. of ovary, the suspensory lig. of ovary. 4 Function:produce ova and secrete female hormones. 5 Development: 二、The uterine tube 1 Location:situated on each side of uterus close to the lateral of wall of the lesser pelvis. 2 Subdivision: a. Uterine part b. Isthmus of uterine tube : legation is performed here. c. Ampulla of uterine tube: fertilization occurs here. d. Infundibulum of uterine tube 三、The uterus 1 Location: in the centrer of the pelvis, between the urinary bladder and the rectum. 2 Division: a.Fundus b.Body c.Cervix • Supravaginal part • Vaginal part 3 Interior cavity a.cavity of uterus b. Cervical canal of uterus: lower end is termed the orifice of uterus. 4 Postur : Anteversion anteflexion 5 The supporting structures of uterus: The normal position is maintained by the supporting ligaments of uterus, the pelvic diaphragm, urogenital diaphragm, vagina and neighboring connective tissues. the supporting ligaments of uterus as following: a.Broad ligament b.Round ligament c.Cardinal ligament d.Uterosacral ligament 6 The structure of uterus a.Endometrium b.Myometrium c.Perimetrium:serous coat 四、The vagina 1 Function: copulation , birth canal and passage for the menstrual flow. 2 Structure:muscular canal. The opening of the lower portion is called the vaginal orifice. The upper end forms the fornix of vagina. The second section: external organs a.mons pubis b.greater lip:skin c.lesser lip:mucosa d.vestibular fossa of vagina: e.glans of clitoris: d.hymen: e.Bulb of vestibule: f.Greater vestibular glands(barholins glands): mammae 1 Shape: Nipple, areola of breast 2 Location:between 3 -6 ribs vertically, from the parasternal line to midaxillary line transversely. 3 Structure: Mammary gland: 15-20 gland lobes and lactiferous duct. Adipose tissue 4 The suspensory ligament The section III : perineum 一、Introduction 1 Concept:diamond –shaped region of outlet of the pelvis,includes all of the soft tissue between the pubic symphysis and the coccyx. 2 Division: a.Urogenital region: b.Anal region: 3 Obstetrical perineum 二 The anal region 1 Muscles of the anal region a.Sphincter ani externus b.Levator ani c.Coccygeus 2 Superior and inferior fasciae of pelvic diaphragm 3 Ischiorectal fossa 三 The urogenital region 1 Muscles of the urogenital region superficial muscles a.Superficial transverse muscle of perineum b.Bulbocabvernosus c.ischiocaveruosus deep muscles a.Deep transverse muscle of perineum b.External sphincter of urethra (urethrovaginal sphincter) 2 The fasciae of urogenital diaphragm The superficial fascia The inferior fascia of urogenital diaphragm The urogenital diaphragm Superficial perineal space Deep perineal space