* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Algebra 1 Unit 3: Systems of Equations
Quadratic equation wikipedia , lookup
Quartic function wikipedia , lookup
Root-finding algorithm wikipedia , lookup
Polynomial ring wikipedia , lookup
System of polynomial equations wikipedia , lookup
Polynomial greatest common divisor wikipedia , lookup
Eisenstein's criterion wikipedia , lookup
Factorization of polynomials over finite fields wikipedia , lookup
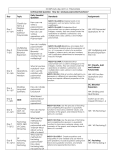
Algebra 2 Unit 3 Polynomials Enduring understanding (Big Idea): Students will understand how to factor polynomials in multiple forms, analyze polynomial functions and their graphs by identifying end behavior and roots, graph polynomial functions and inverse. Essential Questions: 1. How are factors and roots of a polynomial equation related? 2. How are a function and its inverse function related? BY THE END OF THIS UNIT: Students will know… • Behavior of Polynomial Functions • Real-World Applications of Higher-Degree Polynomials Vocabulary: • Zeroes • Binomial Expansion • Multiplicity • Relative Extrema • Concavity Unit Resources – See attached standard guides Suggested pacing time: 10 days Students will be able to… • Factor Polynomials • Describe the end behavior of polynomials • Find the inverse of functions • Know and apply the Binomial Theorem • Recognize a polynomial function in real-world situation Mathematical Practices in Focus: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving. Reason abstractly. Model with Mathematics. Use appropriate tools strategically. Look for and make use of structure. Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning. Successive pages contain an unpacking of the standards contained in the unit. Standards are listed in alphabetical and numerical order not suggested teaching order. Teachers must order the standards to form a reasonable unit for instructional purposes. Algebra 2 Unit 3 Polynomials CORE CONTENT Cluster Title: Polynomial Operations Standard A-APR.1. Understand that polynomials form a system analogous to the integers, namely, they are closed under the operations of addition, subtraction, and multiplication; add, subtract, and multiply polynomials. Concepts and Skills to Master • Add, subtract, and multiply polynomials • Synthetic Division • Remainder Theorem SUPPORTS FOR TEACHERS Critical Background Knowledge Rules of exponents Combining like terms Formulas for perimeter, area and volume of basic geometric shapes Academic Vocabulary Distributive, Closure, Synthetic Division, Quotient, Divisor, Dividend Suggested Instructional Strategies Teach various methods of adding/subtracting polynomials, including vertically and horizontally, through real-world and geometric examples and situations Teach various methods of multiplying polynomials, including the “box method” and distributive property (FOIL), through realworld and geometric examples Introduce synthetic division of a polynomial by a binomial (HONORS include when a coefficient is given for the variable in the binomial and long division) Ensure that students understand that the remainder in synthetic division equals the function evaluated at that point (Remainder Theorem) Resources Textbook Correlation: 4-4 Beginning of Chapter, 5-4 Word Problem Applications Discovery Education Video Add and Subtract Polynomials Discovery Education Video Multiply Polynomials for Volume Discovery Education Video Synthetic Division Brightstorm Video Successive pages contain an unpacking of the standards contained in the unit. Standards are listed in alphabetical and numerical order not suggested teaching order. Teachers must order the standards to form a reasonable unit for instructional purposes. Algebra 2 Unit 3 Polynomials Sample Formative Assessment Tasks Skill-based task 1. (3x3 – 4x2 + 1) – (2x + 4) Problem Task 1) The area of a rectangle can be represented by the expression 2x3 – 17x2 + 31x – 6. If the width is represented by x – 6, what expression represents the length? 2. (2x2 + 3) + 4(x – 2)2 Teacher Created Argumentation Tasks (W1-MP3&6) Divide 3x3 + 5x2 – 7x – 4 by x + 3. a) For f(x) = 3x3 + 5x2 – 7x – 4, evaluate f(-3). b) Explain the relationship between the synthetic division and f(-3)? Successive pages contain an unpacking of the standards contained in the unit. Standards are listed in alphabetical and numerical order not suggested teaching order. Teachers must order the standards to form a reasonable unit for instructional purposes. Algebra 2 Unit 3 Polynomials CORE CONTENT Cluster Title: Interpreting Functions Standard A-APR.5. Know and apply the Binomial Theorem for the expansion of (x + y)n in powers of x and y for a positive integer n, where x and y are any numbers, with coefficients determined by Pascal’s Triangle. Concepts and Skills to Master • Binomial Expansion SUPPORTS FOR TEACHERS Critical Background Knowledge • Multiplying Polynomials • Identifying Patterns Academic Vocabulary Pascal’s Triangle Suggested Instructional Strategies Have students fill out Pascal’s Triangle for the first 12 rows. Then, they should multiply (x + y) to the 6th power manually until they discover the pattern. (Start the standard with the argumentation task so they discover the pattern.) Sample Formative Assessment Tasks Skill-based task Resources Textbook Correlation: 5 – 7 5-7 Puzzle: Pyramid Power (The Binomial Theorem) 1) Expand (x + y)5. 2) What is the fourth term in (2x – y)6? Textbook pg. 329 #24 Problem Task Teacher Created Argumentation Tasks (W1-MP3&6) 1) Fill out the first 12 rows of Pascal’s Triangle. 2) Distribute and write out the solutions to: (x + y)0, (x + y)1, (x + y)2, (x + y)3, (x + y)4, (x + y)5, and (x + y)6. 3) Explain the relationship between Pascal’s Triangle and your solutions, and apply this relationship to compute (x + y)10. 4) How do you think the answer would change if you computed (x + 5)10? Justify your answer. Successive pages contain an unpacking of the standards contained in the unit. Standards are listed in alphabetical and numerical order not suggested teaching order. Teachers must order the standards to form a reasonable unit for instructional purposes. Algebra 2 Unit 3 Polynomials CORE CONTENT Cluster Title: Interpreting Functions Standard A-SSE.2. Use the structure of an expression to identify ways to rewrite it. For example, see x4 – y4as (x2)2 –(y2)2, thus recognizing it as a difference of squares. Concepts and Skills to Master • Factoring Polynomials by Greatest Common Factor • Factoring Trinomials with and without leading coefficients • Factoring a Sum and Difference of Cubes SUPPORTS FOR TEACHERS Critical Background Knowledge • Rules for Exponents •Multiplying Polynomials • Basic Factoring Concepts (GCF, Difference of Squares, Trinomials) Academic Vocabulary Factoring, Trinomials, Greatest Common Factor, Coefficient Suggested Instructional Strategies Create factoring foldables/graphic organizers For students needing additional help, use Algebra Tiles Be sure to relate factoring to multiplying polynomials (factoring determines what multiplies to equal the polynomial) Include the sum and difference of cubes For HONORS students include problems like Resources Textbook Correlation: 4-4 4-4 Enrichment (Teacher Resources) Factoring Notes Organizer , x 4 3x 2 4 x 2 4 x 2 1 x 2x 2 x 2 1 x 9 x 3 x 3 Successive pages contain an unpacking of the standards contained in the unit. Standards are listed in alphabetical and numerical order not suggested teaching order. Teachers must order the standards to form a reasonable unit for instructional purposes. Algebra 2 Unit 3 Polynomials Sample Formative Assessment Tasks Skill-based task 1) Factor: 3x2 -48 2) Factor: x3 - 27 Problem Task A box with no top is to be made from an 8 inch by 6 inch piece of metal by cutting identical squares from each corner and turning up the sides. The volume of the box is modeled by the polynomial 4x3 – 28x2 + 48x. Factor the polynomial completely. Then use the dimensions given on the box and show that its volume is equivalent to the factorization that you obtain. Teacher Created Argumentation Tasks (W1-MP3&6) Task #1: 1) Factor x2 – 16 using the difference of squares rule. 2) Factor x2- 0x – 16 by factoring trinomials. 3) What similarities and differences do you see in the two original expressions? Explain why you got the same answer using two different methods. Task #2: Explain why you can NOT just find two numbers that add to 8 and multiply to -20 to factor 3x2 + 8x – 20. Successive pages contain an unpacking of the standards contained in the unit. Standards are listed in alphabetical and numerical order not suggested teaching order. Teachers must order the standards to form a reasonable unit for instructional purposes. Algebra 2 Unit 3 Polynomials CORE CONTENT Cluster Title: Interpreting Functions Standard A-APR.3.Identify zeroes of polynomials when suitable factorizations are available, and use the zeroes to construct a rough graph of the function defined by the polynomial. Concepts and Skills to Master • Finding zeroes of quadratics graphically • Factor trinomials and differences of squares to solve quadratics algebraically • Use the quadratic formula to solve quadratic equations • Use the roots, end behaviors, and minimum/maximum point to sketch graphs of quadratics SUPPORTS FOR TEACHERS Critical Background Knowledge • Factoring • End Behavior • Simplifying Radicals • Finding the vertex of a parabola Academic Vocabulary Zeroes, Roots, Intercepts, Vertex, Quadratic Formula Suggested Instructional Strategies Teach factoring and quadratic formula first, and then have students discover the relationship between the solutions (especially those from factoring) and the x-intercepts of the graph using the calculator. Have students discuss how to determine the best method for solving various quadratic equations in a Paideia. Discuss the real-world implications of the roots and vertices of quadratics (connect back to Unit 1). For HONORS, extend to include completing the square and introduce x y2 Resources Textbook Correlation: 4-5, 4-6, 4-7 Chapter 4 Performance Tasks 1 and 2: Quadratic Graphs parabolas Successive pages contain an unpacking of the standards contained in the unit. Standards are listed in alphabetical and numerical order not suggested teaching order. Teachers must order the standards to form a reasonable unit for instructional purposes. Algebra 2 Unit 3 Polynomials Sample Formative Assessment Tasks Skill-based task Solve the following equations: 1) x2 + 9x = 36 2) 3x2 + 8x + 2 = 0 3) 4x2 – 25 = 0 Graph the following functions by hand or technology, labeling key points: 4) f(x) = 2x2 – 5x – 12 5) f(x) = x2 – 5x – 2 Problem Task 1) Textbook pg. 245 #39 Teacher Created Argumentation Tasks (W1-MP3&6) Paideia Seminar on Solving Quadratic Equations Successive pages contain an unpacking of the standards contained in the unit. Standards are listed in alphabetical and numerical order not suggested teaching order. Teachers must order the standards to form a reasonable unit for instructional purposes. Algebra 2 Unit 3 Polynomials CORE CONTENT Cluster Title: Functions Standard A-APR.4. Prove polynomial identities and use them to describe numerical relationships. Concepts and Skills to Master • Rational Root Theorem • Given the roots of a polynomial, write the equation of the polynomial • Find all zeroes of a function SUPPORTS FOR TEACHERS Critical Background Knowledge • Factoring • Synthetic Division • Using the calculator to find roots (graphically, using a table, and evaluating a function) Academic Vocabulary Rational Root Theorem, Root, Zeroes Suggested Instructional Strategies Focus on technology to find zeroes (HONORS, introduce the Rational Root Theorem and Descartes Rules of Signs). Discuss the rationale for synthetically dividing to create lower degree polynomials. Sample Formative Assessment Tasks Skill-based task 1) Find the roots of x – 3x + x – 3 = 0. 2) Write an equation in the least degree of a polynomial with the roots 2, 3, and -4. 3 2 Resources Textbook Correlation: 5-5 Problem Task Textbook pg. 309 #43 Teacher Created Argumentation Tasks (W1-MP3&6) Solving Higher-Order Equations Performance Task (use after solving 3rd degree equations) Successive pages contain an unpacking of the standards contained in the unit. Standards are listed in alphabetical and numerical order not suggested teaching order. Teachers must order the standards to form a reasonable unit for instructional purposes. Algebra 2 Unit 3 Polynomials CORE CONTENT Cluster Title: Functions Standard F.IF.7. Graph functions expressed symbolically and show key features of the graph, by hand in simple cases and using technology for more complicated cases. (Specifically c – Graph polynomial functions, identifying zeroes when suitable factorizations are available and showing end behavior.) Concepts and Skills to Master • Graph higher degree polynomial functions. • Identify relative extremes and concavity. SUPPORTS FOR TEACHERS Critical Background Knowledge • Graphs of functions (including intercepts, maximum and minimum values, and end behaviors) • Transformations of functions Academic Vocabulary Relative extremes, concavity Suggested Instructional Strategies • Relate everything we’ve done this unit (quadratics, solving by graphing/factoring, end behaviors, etc.) to graphing higher-order polynomials. • Show how graphs of some polynomials can have minimum and maximum values for different intervals (use graphing technology to set left bounds and right bounds). Sample Formative Assessment Tasks Skill-based task Find the relative maximum, relative minimum, and zeroes of: y = 2x3 – 23x2 + 78x – 72 Resources Textbook Correlation: 5-1, 5-2 Problem Task Textbook pg. 294 #46 Teacher Created Argumentation Tasks (W1-MP3&6) Find the zeroes and relative minimum and maximum values for y = (x + 1)4, y = (x + 3)4, and y = (x + 1)4 + 2. What are the similarities and differences between the values? Explain why this occurs based on what you have learned about transformations. Successive pages contain an unpacking of the standards contained in the unit. Standards are listed in alphabetical and numerical order not suggested teaching order. Teachers must order the standards to form a reasonable unit for instructional purposes.