* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Teaching Plan 1B
Foundations of mathematics wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Ethnomathematics wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics and architecture wikipedia , lookup
Fermat's Last Theorem wikipedia , lookup
Nyquist–Shannon sampling theorem wikipedia , lookup
Central limit theorem wikipedia , lookup
Wiles's proof of Fermat's Last Theorem wikipedia , lookup
Four color theorem wikipedia , lookup
List of important publications in mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Brouwer fixed-point theorem wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental theorem of calculus wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental theorem of algebra wikipedia , lookup
Proofs of Fermat's little theorem wikipedia , lookup
Secondary School Mathematics Curriculum Improvement Study wikipedia , lookup
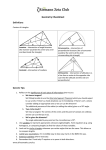
TEACHING PLAN 2B Stage 8 Learning Objectives Chapter 11 Pythagoras’ Theorem Teaching Focus Let’s Review (p.174) 1 • Teachers can ask students to • Use Pythagoras’ review the meaning of square and Theorem and its square roots. converse to solve problems • Students should recall a right-angled triangle must have • Recognize and an interior angle of 90. appreciate different proofs of Pythagoras’ • Teachers can ask students to Theorem including review the representation of a those in Ancient China number line. • Appreciate the dynamic element of mathematics knowledge through studying the story of the first crisis of mathematics • Recognize the existence of irrational numbers and surds • Explore the representations of irrational numbers in the number line Suggested No. of Periods 0.5 period Consolidation & Assessment • Worksheet 11.0 (Sets 1 & 2) • Test Bank 11.0 Special Items Additional Information • E Textbook Teaching Plan 2B Teaching Focus 11.1 Pythagoras’ Theorem and Its Proofs (pp.174 – 183) 2 • Teacher should guide students to discover the Pythagoras’ theorem by themselves by working through the Inspiring task. • Students should be able to apply the Pythagoras’ theorem to solve problems involving right-angled triangles, perimeters and areas of figures. • This section leads Students to appreciate the Pythagoras’ theorem by showing different proof of Pythagoras’ theorem. Suggested No. of Periods 3 periods Consolidation & Assessment Special Items • Additional Examples • E Textbook 11.1 – 11.3 • PowerPoint • Worksheet 11.1 Presentation (Sets 1 & 2) • Inspiring Task 11.1 • Workbook 11.1 Investigating the • Ongoing Assessment Relationship between Package: Quiz 11.1 the Three Sides of a Right-Angled Triangle • Test Bank 11.1 (p.175) • IT-Lessons Using Sketchpad to Explore the Lengths of Sides of a Right-angled Triangle (p.325) (include e-Figure Gallery) • Animations of Great Mathematicians (Pythagoras of Samos) • Flash Demonstrations • Inspiring Task 11.2 Exploring the Proof by Calculating the Area of a Trapezium (pp.180 181) Additional Information New Progress in Junior Mathematics 2B Learning Objectives Learning Objectives Teaching Focus 11.2 Applications of Pythagoras’ Theorem (pp.184 – 189) Suggested No. of Periods 3 • This section introduces the converse of Pythagoras’ theorem. • Students should be able to determine whether a triangle contains a right angle. • Students should be able to apply the converse of Pythagoras’ theorem to solve problems. Special Items 3 periods • Additional Examples • E Textbook 11.4 11.6 • PowerPoint Presentation • Worksheet 11.2 (Sets 1 & 2) • Workbook 11.2 • Ongoing Assessment Package: Quiz 11.2 • Test Bank 11.2 3 periods • Additional Examples • E Textbook 11.7 – 11.8 • PowerPoint • Worksheet 11.3 Presentation (Sets 1 & 2) • Workbook 11.3 • Ongoing Assessment Package: Quiz 11.3 • Test Bank 11.3 • Students should be able to apply the Pythagoras’ theorem to solve the real-life problems and problems involving directions. 11.3 Converse of Pythagoras’ Theorem and Its Applications (pp.189 – 194) Consolidation & Assessment Additional Information Teaching Plan 2B Teaching Focus 11.4 Surds and Irrational Numbers (pp.194 – 196) Suggested No. of Periods 2 periods • Students should be able to represent surds on a number line. • Teachers could introduce the history of the discovery of 2 caused the first crisis of mathematics. 4 Enrichment Mathematics – How Did Pythagoras Prove the Pythagoras’ Theorem (p.205) • This enrichment leads students to explore the method of proving the Pythagoras’ theorem. 0.5 period Total: 12 periods Consolidation & Assessment Special Items • Additional Examples • E Textbook 11.9 – 11.10 • PowerPoint • Worksheet 11.4 Presentation (Sets 1 & 2) • Inspiring Task 11.3 • Workbook 11.4 Surds and Irrational • Ongoing Assessment Numbers (p.194) Package: Quiz 11.4 • Test Bank 11.4 • I.T. Worksheets • Flash demonstrations • TSA Supplementary Exercises 11 • Ongoing Assessment Package: Formative Assessment 11 • Open-ended Questions Additional Information New Progress in Junior Mathematics 2B Learning Objectives