* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Year-9-Curriculum-Overview-Spring-Half-Term-2
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Noether's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Riemann–Roch theorem wikipedia , lookup
Brouwer fixed-point theorem wikipedia , lookup
Four color theorem wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Area of a circle wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
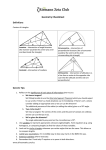
Holly Hall Academy – Maths Year 9 Spring Half Term 2 Curriculum Document 2016 Calculating Space Year 9 Conjecturing Key Unit Focuses: Key Unit Focuses: identify and apply circle definitions and properties, including: tangent, arc, sector and segment calculate arc lengths, angles and areas of sectors of circles calculate surface area of right prisms (including cylinders) calculate exactly with multiples of π know the formulae for: Pythagoras’ theorem, a² + b² = c², and apply it to find lengths in rightangled triangles in two dimensional figures Key Unit Concepts/Words: Key Unit Concepts/Words: Circle, Pi, Radius, diameter, chord, circumference, arc, tangent, sector, segment, (Right) prism, cylinder, Cross-section, Hypotenuse, Pythagoras’ theorem Congruent, congruence, Similar (shapes), similarity, Hypotenuse, Conjecture, Derive, Prove, proof, Counterexample Notation π Abbreviations of units in the metric system: km, m, cm, mm, mm2, cm2, m2, km2, mm3, cm3, km3 Notation Notation for equal lengths and parallel lines SSS, SAS, ASA, RHS The ‘implies that’ symbol () Key Assessments/Creative Outcomes: Key Assessments/Creative Outcomes: Know the vocabulary of circles Know how to find arc length Calculate the arc length of a sector when radius is given Know how to find the area of a sector Calculate the area of a sector when radius is given Calculate the angle of a sector when the arc length and radius are known Know how to find the surface area of a right prism (cylinder) Calculate the surface area of a right prism (cylinder) Calculate exactly with multiples of π Know Pythagoras’ theorem Identify the hypotenuse in a right-angled triangle Know when to apply Pythagoras’ theorem Calculate the hypotenuse of a right-angled triangle using Pythagoras’ theorem Calculate one of the shorter sides in a right-angled triangle using Pythagoras’ theorem use the basic congruence criteria for triangles (SSS, SAS, ASA, RHS) apply angle facts, triangle congruence, similarity and properties of quadrilaterals to conjecture and derive results about angles and sides, including Pythagoras’ Theorem and the fact that the base angles of an isosceles triangle are equal, and use known results to obtain simple proofs Know the criteria for triangles to be congruent (SSS, SAS, ASA, RHS) Identify congruent triangles Use known facts to form conjectures about lines and angles in geometrical situations Use known facts to derive further information in geometrical situations Test conjectures using known facts Know the structure of a simple mathematical proof Use known facts to create simple proofs Explain why the base angles in an isosceles triangle must be equal Explain the connections between Pythagorean triples Key Unit Homework: Quadratic sequences and Fibonacci Useful Websites: Useful Websites: www.mymaths.co.uk www.nrich.org www.kangaroomaths.com www.mymaths.co.uk www.nrich.org www.kangaroomaths.com Additional Assessment