* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Blood Clots - humanphys-chan
Blood sugar level wikipedia , lookup
Hemolytic-uremic syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Blood transfusion wikipedia , lookup
Schmerber v. California wikipedia , lookup
Autotransfusion wikipedia , lookup
Blood donation wikipedia , lookup
Jehovah's Witnesses and blood transfusions wikipedia , lookup
Hemorheology wikipedia , lookup
Men who have sex with men blood donor controversy wikipedia , lookup
Plateletpheresis wikipedia , lookup
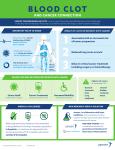
Blood Clots http://goo.gl/W0jTaQ How Do Blood Clots Form? Chemical reactions grow the blood clot o Blood contains dissolved proteins, also called clotting factors, which promote blood clots. These signal and amplify each other’s activity in massive numbers at the site of bleeding. o This results in a chain reaction where the end product is fibrin, the main protein in forming blood clots. o The fibrin formed blood clot is tougher and more durable than the platelet clump. Anti-clotting processes halt the blood clot’s growth o The platelet plug forms o After a blood clot is formed, it must be prevented from growing and spreading through the body, where it could cause damage. The body breaks down the blood clot o As the damaged tissue heals, the body breaks down the blood clot and reabsorbs it. o An enzyme called plasmin breaks down the tough fibrin strands in a blood clot. o This breaking down is called Thrombolysis or commonly called clot busting. Platelets become stimulated when they encounter a o damage blood vessel and flock to the site o http://www.anticoagulantdrugs.com/blood-clots-full-guide/ Platelets clump together and form a plug which reduces bleeding o Anti-clotting proteins like antithrmbin exist in a natural balance with clotting factors. Enzymes neutralize excess clotting factors, which prevent them from extending the blood clot farther than it should go. Blood Clots Treatments? Where? Clots can occur in veins or arteries, which are vessels that are part of the Thrombus formation http://goo.gl/Rd7wIs body’s circulatory system. prevents clots from forming. Veins carry deoxygenated blood away from the body’s organs and back to the surgically inserted and directed toward and can result in pain and swelling. the blood clot where it delievers clot- A common type of blood clot is DVT (Deep vein thrombosis), which is a type of clot that forms in the major Catheter-directed thrombolysis- a procedure in which a long tube is restrict the return of blood to the heart Pulmonary embolism http://goo.gl/0zs0k0 Clot busters- medicine tat dissolves blood clots heart. A blood clot in a vein may Anticoagulation- medicine that dissolving medication. Thrombectomy- surgical removal of a clot. veins of the leg. Sometimes a clot in a vein might be detached from its original location and travel to the lungs or heard where it can become wedged, which prevents blood flow. For lungs it is called pulmonary embolism. Removing a blood clot http://goo.gl/IccV