* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Red Blood Cells
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
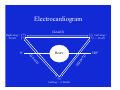
Cardiovascular System Heart Electrocardiogram • A device that records the electrical activity of the heart. • Measuring the relative electrical activity of one heart cycle. • A complete contraction and relaxation. Electrocardiogram • 3 ways to measure electrical activity: – Left wing, + right wing, right leg = Lead I – Left leg, + right wing, right leg = Lead II – Left leg, + Left wing, right leg = Lead III • Each create a triangle around heart – Einthoven’s Triangle (based on Einthoven’s law) Electrocardiogram dI I I ) a e (L Heart (-) (+) (L e a 0° I) I d (+) (+) (-) (-) Right wing = - .20 mV (Lead I) Left leg = +1.00 mV Left wing = + .30 mV 180° Electrocardiogram • Lead I – Lead II + Lead III = 0 • Lead I – Lead II = Lead III • Einthoven’s Law: – Lead I = left wing – right wing (+ .30 mV) – (- .20 mV) = + .50 mV – Lead II = left leg – right wing (+ 1.00 mV) – (- .20 mV) = + 1.20 mV – Lead III = left leg – left wing (+ 1.00 mV) – (+.30 mV) = + .70 mV Electrocardiogram • Lead I - Lead II + Lead III = 0 (+ .50 mV) – (+ 1.20 mV) + (+ .70 mV) = 0 • Lead I - Lead II = Lead III (+ .50 mV) – (+ 1.20 mV) = (+ .70 mV) Electrocardiogram Electrocardiogram Electrocardiogram Heart Output • Stroke Volume – volume of blood ejected from heart during a single systolic contraction – Only about 2/3 of volume of ventricle is pumped out with one contraction. – = End diastolic volume – End systolic volume Heart Output • Cardiac Output – amount of blood ejected from both ventricles per unit time – = Heart rate X Stroke volume • Heart rate and stroke volume negatively correlate Starling’s Law of the Heart • The more the ventricle is filled with blood during diastole (end-diastolic volume), the greater the volume of blood ejected during the systolic contraction (stroke volume). • Note - the force of contraction increases as the heart is filled with more blood. Heart contraction and Blood Pressure • More blood to ventricle with higher venous blood pressure = higher stroke volume • Higher arterial blood pressure - reduces stroke volume as semilunar valves close prematurely Blood Pressure • Blood Pressure = – Systolic over diastolic – Contracted over relaxed • Chicken blood pressure = 180 mm Hg/100 mm Hg • Turkey blood pressure = 300/250 • Human blood pressure = 120/80 Blood Pressure • Arterial pressure - Simplification “Closed system (arteries to arterioles to capillaries) Heart contracts put blood in arteries under pressure • Venous pressure due to skeletal muscles contracts - squeezing veins, gravity, “pull” of heart contractions, closed system Arterial Blood Pressure • Arteries have “elastic’ inner walls providing RESISTANCE to expansion (This is PERIPHERAL RESISTANCE) Arterial Blood Pressure • Arterial walls surrounded by smooth muscle – if muscles contract, arterial diameter ↓, arteries/arterioles constrict (VASOCONSTRICTION), resistance and B.P. ↑ – if muscles relax, arterial diameter ↑, arteries/arterioles dilate (VASODILATION), resistance and B.P. ↓ – Muscles normally do not completely relax Vascular tone Arterial Blood Pressure II • When blood is forced out of the ventricle, arterial B.P. up - Systolic B.P. • When valves close - Diastolic B.P. Arterial Blood Pressure II • Dilation/relaxation of blood vessel smooth muscles under the control of autonomic nervous system (+ hormones) – Parasympathetic nerve (part of vagus) • More nervous activity - more Acetyl choline – vasodilation – Sympathetic nerve • More nervous activity - more Norepinephrine –vasocontriction in arterioles of skin and gut, but vasodilation in arterioles of muscle. Hormones and Arterial B.P. • Renin – Angiotensin – Kidney releases renin (enzyme) – Converts Angiotensinogen (precursor produced by the liver) into Angiotensin I – ACE (lung & renal enzyme) converts Angiotensin I into Angiotensin II – Angiotensin II (I just a little) is a powerful vasoconstrictor Hormones and Arterial B.P. • Norepinephrine/Epinephrine (adrenal medulla) – at higher levels ↑ B.P. • Arginine vasotocin and Mesotocin - increase B.P. at physiological concentrations probably via increased water retention + vasoconstrictor? • Histamine (not a hormone) from basophilsvasodilator (released with inflammation) also a bronchoconstrictor (allergic reaction) Nervous Regulation of Blood Pressure • Neural receptors (largely peripheral) detect changes in arterial and venous blood pressure and blood composition (pH, CO2, 02 - hypoxia) • Brain integration of data • If Blood pressure too high - cardiac output reduced to compensate • If hemorrhage - B.P. falls - Cardiac output increased to compensate.