* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electronics and Photonics Revision Sheet
Crystal radio wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
Negative resistance wikipedia , lookup
Josephson voltage standard wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
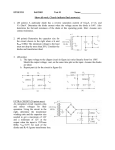
Unit 3 Electronics Revision Save the electronics revision files on the Physics VLA to your “My Documents” folder. Start the Crocodile Clips program and open the following files in order. Voltage Divider Red flags = +ve Voltage Blue flags = -ve Voltage Size of flag = relative size of Voltage Voltmeter: small black dot connected to +ve terminal. Small arrow shows direction of conventional current through device. What is the function of the two voltmeters? Label R1 and R2 in the circuit diagram above. Circle the voltmeter that reads Vout. Calculate the current flowing through each of the resistors and the battery. Check your answer by placing the mouse cursor over each component. What current flows through the voltmeter? Predict the effect on Vout if you doubled the value of R2. Check your answer by changing the value of R2 to 20k . What effect did this increased resistance have on the current through each resistor and the battery? Predict the voltage drop across each resistor if the Voltage supply were to be increased to 330V DC. The resistors can dissipate a maximum of 2W of power each before breaking. Use calculations to decide if a 330V supply is safe. Test your prediction by increasing the battery’s voltage. Potentiometer Voltage Divider A potentiometer is another name for a variable resistor. Circle Vout on the circuit diagram. Move the slider of the pot up and down. What happens to Vout? Why does the value of the 10k pot not change? Place the slider exactly in the middle. Predict wall will happen to V out if the supply voltage is increased to 12V. Adjust the circuit to check your answer. Reset the mf to 9V and ensure the slider is exactly half way. Predict what will happen if the resistance of the pot is increased to 20k . Make the change to check. Explain the observed behaviour. LDR Voltage Divider Identify Vout and the LDR. Move the light source up and down and observe the changes in LDR’s resistance. Does this LDR have a positive or negative gradient characteristic? What happens to Vout as the illumination is increased? Use the voltage divider formula to calculate V out if the LDR has a resistance of 4.5k . LED in Parallel Identify the resistor and LED which are in parallel. Start the simulation by clicking the PAUSE button. Slowly increase the resistance of the variable resistor by moving the slider to the right. What happens to the Voltage drop across the parallel part of the circuit? What is happening to the brightness of the diode? How does this relate to the current through the diode? VERY SLOWLY move the slider of the variable resistor to the LEFT. Observe what happens to the current through the diode. Stop the simulation and draw the current graph of the diode in the space above. Why did the diode blow? Move the mouse cursor over the blown diode and try to fix the problem. Amplifier You can start and stop the simulation using the pause button. The top graph plots Vin and the bottom graph plots Vout. On the circuit diagram label the component that supplies V in , the component that measure Vout and the amplifier. What is the Vin? What is the Vout? What is the voltage gain of this amplifier? Is it inverting or non-inverting? Stop and reset the simulation. Click on the signal generator symbol in the circuit diagram. Choose the PROPERTIES option at the bottom left of your screen and set the Voltage to 0.001V. Start the simulation. Describe the output signal. Phototransistor in Voltage divider Phototransistors are similar to photodiodes. What happens to the current and Vout when you slide the torch up and down? What is the effective resistance of the transistor when there is no light? How do you know? Compare the current that flows when 100% of light shines with the current for 50% of light. Is the current directly proportional to the light intensity? Electro-Optical System This system consists of a circuit containing a light source and a second circuit containing a light detector. Use two different coloured highlighters to mark the two circuits. What type of light source is used? What type of light detector is used? Adjust the variable resistor in the circuit containing the light source. What happens to the current in the left circuit as the resistance decreases? What happens to the brightness of the LED? What happens to the current of the detector circuit? Now increase the resistance and observe. Set the resistance to 1.5kΩ. Record the currents in both circuits. Adjust the resistor to double the current in the left circuit. What is the current in the detector circuit? Has the current also doubled? Are the signals that are sent by the transmission circuit replicated by the detector circuit?