* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Spring Final Review Guide
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal lineage marker wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic resistance to malaria wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to genetics wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
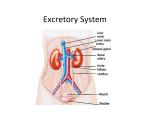
Biology Cumulative Final Review Topics 2008-2009 I. Test Topics A. Chapter 1 and Scientific Method B. Chapter 2 Biochemistry C. Chapter 7 Cells and mitosis D. Energy Unit 1. Ch. 8 photosynthesis 2. Ch. 9 cell respiration 3. Ch. 8&9 3. Ch. 3-2 E. Ch. 12 DNA & RNA F. Ch. 13 Genetic engineering G. Chapter 11 Genetics H. Chapter 15 Evolution I. Chapter 16 Populations J. Chapter 17. 1 Fossil Record K. Chapter 3, 4, 5 Ecology L. Chapter 18 classification M. Chapter 35 Nervous system N. Chapter 36 Skeletal, muscle, integumentary O. Chapter 37 Circulatory and respiratory P. Chapter 38 Digestive and Excretory Q. Chapter 40 Immune System II. Topics by Chapter Chapter 1 Scientific Method – independent, dependent, standard variables, hypothesis, conclusions, inferences, types of observations, theory Parts of a controlled experiment Characteristics of living things, homeostasis, metabolism Chapter 2 Parts of the atom, bonding: ionic, covalent, hydrogen, polar covalent Characteristics of water Acids and Bases, pH values Carbohydrates Glucose: monosaccharides, polysaccharides Amino acids as building blocks (monomers) of proteins Organic compounds as a source of energy of living things Enzymes: activation energy, catalyst, characteristics Chapter 7 Cell Theory Cell membrane structure and function Eukaryotes, prokaryote characteristics Eukaryotic cell organelles: structure and function Mitosis Levels of organization in multi-cellular organisms Energy Unit: Chapter 8, Chapter 9 and Chapter 3-2 Relate photosynthesis and cellular respiration – how they are similar and different. Word equations for photosynthesis and cellular respiration Chloroplasts: structure and function, Mitochondria: structure and function Electron transport chain-oxygen is used to pick up electrons and forms H2O Source of energy on surface of planet Food chain, food web: producer, consumers, detritivores, decomposers, autotroph, heterotroph, trohic levels, energy and food pyramids community, population energy flow in heterotrophic cells (eukaryotic cells) starts with food, then ATP then cell work Chemosynthesis ATP, ADP structure and function Chapter 12 DNA: structure, function, replication, % of base pairs, base pair rules RNA: structure, function, types Transcription, translation, codon charts Gene regulation: specialized cells (liver cells, blood cells etc.) regulate which genes are expressed because they do not need certain proteins specified by certain genes. Example: heart muscle cells do not need to make liver enzymes even though they contain the DNA to do so. Chapter 13 Genetic Engineering Restriction enzymes; see figure 13-5 on page 322 Cell Transformation: transgenic bacteria see page 327 Chapter 11 Stages of meiosis, Mendel’s law of inheritance, alleles, genes, probability using a Punnett Square, independent assortment, random mating, crossing over, incomplete dominance, codominance, Polygenetic inheritance, multiple alleles Mendel’s pea plants and P generation, F1 and F2 generation, pure breeding plants for crosses, principal of dominance, Evolution: Chapters 15, 16 and 17.1 Darwin’s theory of natural selection, inheritance of acquired characteristics, adaptations, fitness, directional selection, stabilizing selection, disruptive selection, genetic drift, temporal isolation, geographic isolation, behavior isolation genetic equilibrium, mutations, The Galapagos Island finches and how they relate to Darwin’s research, the work of James Hutton Charles Lyell and Lamarck Title of Darwin’s book, gene pool (allele frequency), speciation Ecology: Chapter 3, 4 and 5 Ecosystem organization, primary and secondary succession, compare flow of and nutrients, Nitrogen Cycle, Carbon cycle, Biomes that are in the book (basic facts) Symbiosis: mutualism. Commensalism, parasitism, Competition: limiting factors, density dependent factors, niches, niche partitioning, effect of competition on populations and individuals Populations: density, dispersion, range, growth: increase/decrease, Growth curves: J curve/ logistics, S curve, carrying capacity, growth beyond Carrying capacity Classification Chapter 18 Cladograms see pages 452 and 453 Homo sapiens on the only living member of the gene Body Systems Chapters Chapter 35: Nervous System The central nervous system is made up primarily of the brain and spinal columne The parts of the brain: 1. cerebrum: learning, intelligence and judgment 2. Cerebellum: coordinates and balances the actions of the Muscles 3. Brain stem: connects the brain and the spinal cord Neurons are the basic unit of the nervous system: See figure 35-5 on page 897. Know the parts of a neuron and their function The resting potential of a neuron means that the concentration of Na ions is greater outside the cell than inside When an impulse reaches the end of a neuron neurotransmitters are released See figure 35-8 page 900 Sensory receptors are found in many places, those sensitive to chemicals are found in the nose and taste buds of the tongue, which is why we smell smells and taste food. Homeostasis is maintained several ways: 1.regulating body temperature using a negative feedback loop Chapter 36: Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Integumentary system includes: skin, hair and nails A muscle contraction is when the thin filaments in the muscle fiber slide over the thick filaments. Pg 928 Chapter 37: Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Pathway of blood flow through the heart: study diagram 37-2 pg. 944 Red blood cells transport oxygen. If you don’t have enough red blood cell you will have trouble getting oxygen to your cells Air is forced into your lungs when your diaphragm contracts Chapter 38: Digestive and Excretory systems The parts of the excretory system includes: the kidneys, the ureter and the urinary bladder Collection of urine study figure 38-17 and read 987 Kidneys help maintain homeostasis by controlling what leaves the body and what is reabsorbed: for example if there is too much salt in the blood the kidneys respond by return less salt to the blood. Chapter 40: The Immune System and Disease The germ theory of disease states that disease is caused by microorganisms. Infectious diseases are caused by pathogens. Pathogens are disease causing agents, examples are viruses, bacteria some protists and some worms Vaccines provide protection against the disease by stimulating the body To make specific antibodies. Defense against disease is divided in nonspecific and specific defenses Nonspecific defenses include: skin, mucus, sweat and tears. The most important is the skin. Specific include the humoral immunity and cell-mediated immunity. Humoral immunity uses antibodies pg. 1038 Cell-mediated immunity uses helper T cells pg. 1040 HIV spreads through the body because it replicates inside of the cells of the immune system