* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Igneous Rocks - My Illinois State
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Marine geology of the Cape Peninsula and False Bay wikipedia , lookup
Provenance (geology) wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Algoman orogeny wikipedia , lookup
Composition of Mars wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
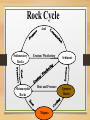
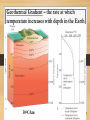
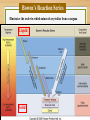
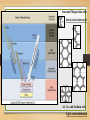
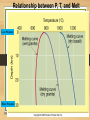
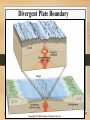
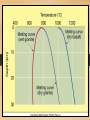
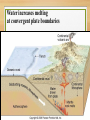
Earth Materials continued • Mineral • • • • • Naturally Occurring Inorganic Solid Chemical Composition Crystalline Shape Rock • a coherent, naturally occurring solid, consisting of an aggregate of one or more minerals, or a mass of natural glass or organic matter. Basic Rock Classifications •Igneous •Sedimentary •Metamorphic Rock Cycle And Sedimentary Rocks Metamorphic Rocks Erosion/ Weathering Heat and Pressure Magma Sediment Igneous Rocks ? Define - Freeze ? Igneous Rocks Igneous Rocks -a rock that forms when hot molten rock (magma or lava) cools and freezes solid Two types of igneous rocks • Plutonic – cools underground • Volcanic – cools above ground Factors controlling Melting 1. Temperature: Melt at [800oC and 1200oC] Source of heat [radioactive decay] Geothermal Gradient – the rate at which temperature increases with depth in the Earth 30OC/km Norman Bowen Bowen’s Reaction Series Illustrates the order in which minerals crystalize from a magma Liquid Solid Iron and Magnesium rich Dark colored minerals Al, Ca, and Sodium rich Light colored minerals Factors controlling Melting 2. Pressure: • as pressure increases, melting temperature increases • as pressure decreases, melting temperature decreases Lowering pressure causes melting in divergent margins. Relationship between P, T, and Melt Less Pressure More Pressure Divergent Plate Boundary Factors controlling Melting 3. Water content: As water content increases, melting temperature decreases Water increases melting at convergent plate boundaries Where do igneous rocks occur? Types of Molten Material 1. Magma – molten material below the Earth's surface 2. Lava – molten material above the Earth's surface Magma Composition Changes •Partial melting •Assimilation •Magma Mixing •Fractional Crystallization Partial Melting some minerals melt at a lower temperature than others. Magma Viscosity Viscosity – resistance to flow honey – high viscosity water – low viscosity Viscosity increases as silica content increases. Magma Chemistry Molten material can consist of liquid rock, mineral grains and gases (H2O, CO2, SO2). Silicon and oxygen (SiO2) make up the majority of magma 45% SiO2 - "low" silica content 75% SiO2 - "high" silica content Endmember Magma Chemistry Mafic – low SiO2 / high iron, magnesium Silicic – high SiO2 / high aluminum, calcium, sodium Igneous Rock Types Intrusive (plutonic) rock – cools and solidifies below the Earth's surface. Extrusive (volcanic) rock – cools and solidifies above the Earth's surface. Textures of Igneous Rocks Texture – overall appearance, related to size, shape, and arrangement of minerals. Texture is related to cooling history of an igneous rock, not its chemistry. Textures of Igneous Rocks 1. Aphanitic (fine grained) Earth’s surface Lava 2. Phaneritic (course grained) Magma Aphanitic Texture – Rapid Cooling Small Crystals Phaneritic Texture – Slow Cooling Large Crystals Silicic Chemical Composition Phaneritic Texture – Slow Cooling Large Crystals Granite Aphanitic Texture – Rapid Cooling Small Crystals Rhyolite Intermediate Chemical Composition Phaneritic Texture – Slow Cooling Large Crystals Diorite Aphanitic Texture – Rapid Cooling Small Crystals Andesite Mafic Chemical Composition Phaneritic Texture – Slow Cooling Large Crystals Gabbro Aphanitic Texture – Rapid Cooling Small Crystals Basalt PHANERITIC texture It means that the size of all grains in the rock are large enough to be distinguished with the unaided eye APHANITIC texture It means that not all grains in the rock are large enough to be distinguished with the unaided eye. Most of the rock is background mass. Pegmatites Ingersoll Mine Ingersoll mine, Pennington Co., South Dakota, United States One of the many adits at the old Ingersoll pegmatite. Private and Very dangerous. No Trespass. Glassy Texture - Very Rapid Cooling - No Crystal Structure Pyroclastic Texture Ash Fall Ash Flow Plutonic Structures Plutonic Structures Image courtesy of geoinfo.nmt.edu