* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download IG_Algebra 1_Unit 4 - allianceprincipalresources
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Location arithmetic wikipedia , lookup
Horner's method wikipedia , lookup
Vincent's theorem wikipedia , lookup
System of polynomial equations wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental theorem of algebra wikipedia , lookup
Factorization of polynomials over finite fields wikipedia , lookup
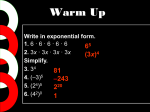
Algebra Subject:____________________ Unit Title: Monomials and Polynomials 4 Unit:_______________________ 2 (October 17th Quarter:_____________________ – December 30th) Unit Overview Unit 4: Monomials and Polynomials In this unit, students are introduced to nonlinear functions. Students first learn about polynomials and operations involving monomials and polynomials. An expression involving the division of variables is not a monomial. Monomials that are real numbers are called constants. When multiplying monomials, you can use the commutative and associative properties to group constants together and group powers with the same base together. Monomials can also be divided. To divide two powers that have the same base, subtract the exponents. To find the power of a quotient, find the power of the numerator and power of the denominator. A fraction that has a negative exponent can be rewritten as its reciprocal of the same number with the opposite, or positive power. A polynomial is a monomial or a sum (or difference) of monomials. The sum of two monomials is called a binomial, and the sum of three monomials is called a trinomial. Polynomials with more than three monomials have no special names. The degree of a polynomial is the greatest degree of any monomial in the polynomial. To find the degree of a monomial, add the exponents of all its variables. The degree of a polynomial should not be confused with the number of terms in the polynomial. Polynomials may be added and subtracted by combining like terms. If the variable parts of two terms are exactly the same, the terms are called like terms. The Distributive property is used to find the product of a monomial and a polynomial. Multiply each term of the polynomial by the monomial, using the rules for monomial multiplication. If the monomial is negative, don’t forget to apply the rules for multiplying real numbers. Some binomials have products that follow a specific pattern (e.g. square of sum or a difference and product of a sum and difference of the same two terms). 1 Math Literacy Key Vocabulary: binomial, constant, degree of a monomial, degree of a polynomial, difference of two squares, monomial, polynomial, zero product property, trinomial, standard form, leading coefficient Supporting Vocabulary: distributive property, like terms, coefficient Common Core State Standard Alignment ASSE.1a Interpret expressions that represent a quantity in terms of its context. Interpret parts of an expression, such as terms, factors, and coefficients. ASSE.2 Use the structure of an expression to identify ways to rewrite it. For example, see x4 – y4 as (x2)2 – (y2)2, thus recognizing it as a difference of squares that can be factored as (x2 – y2)(x2 + y2). A.APR.1 Understand that polynomials form a system analogous to the integers, namely, they are closed under the operations of addition, subtraction, and multiplication; add, subtract, and multiply polynomials. Sample Essential Questions • When could a nonlinear function be used to model a real-world situation? • How would you factor a cubic polynomial? • Describe the pattern formed when expanding squares and cubes of binomials? Anchor Standards/Central Concepts 10.0 Students add, subtract, multiply, and divide monomials and polynomials. Students solve multistep problems, including word problems, by using these techniques. 2 # CST Items Standard Learning Targets/ Key Concepts and Skills 10.0 Students add, subtract, multiply, and divide monomials and polynomials. Students solve multistep problems, including word problems, by using these techniques 4 2.0 Students understand and use such operations as taking the opposite, finding the reciprocal, taking a root, and raising to a fractional power. They understand and use the rules of exponents. 4 10a I can add/subtract polynomials 10b I can multiply polynomials 10c I can divide polynomials (using exponent rules) 10d I can perform operations on polynomials involving word problems 10e I can write polynomials in standard form. 10f I can solve equations involving the products of monomials and polynomials. 2a I can divide polynomials (using exponent rules) College-Ready Sample Assessment Questions The length of the rectangle above is 6 units shorter than the width. What expression can be used to represent the area? Simplify: 2(𝑥 2 + 3𝑥 + 2) − 4(𝑥 2 − 4𝑥 + 1) Simplify: 10𝑥 2 + 15𝑥 2 − 5𝑥 5𝑐 Write an expression equivalent to 𝑥 3 𝑥11 Simplify 2 83 Vertical Alignment Multiply and divide monomials 7AF2.2 Simplify numerical expressions and justify the process used 7.AF1.3 Operations on polynomials, including long division 2A.3.0 Additional Sample College-Ready Assessments Questions Sample College-Ready Assessment Questions 3 4