* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Identifying and Using Kites
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Penrose tiling wikipedia , lookup
Steinitz's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Noether's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Riemann–Roch theorem wikipedia , lookup
Brouwer fixed-point theorem wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
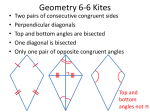
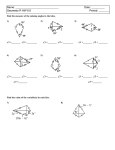
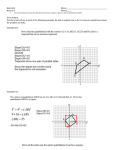
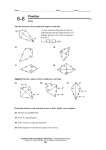
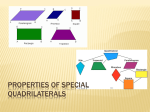
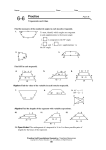
Geometry Guided Notes Kites Identifying and Using Kites Name: ______________________________ Date: __________________ Period: _____ Kite – a quadrilateral that has two pairs of consecutive congruent sides, but opposite sides are NOT congruent. Theorem – If a quadrilateral is a kite, then its diagonals are perpendicular. Theorem – If a quadrilateral is a kite, then exactly one pair of opposite angles are congruent. Vertex Angles - are the angles at the end of the longest diagonals. The longest diagonal bisects the vertex angles. The longest diagonal bisects the shortest diagonal. To find the sides of a kite given the lengths of the diagonals (half the length), use the Pythagorean theorem. The diagonals intersect at right angles. Example #1: 1. If AE = 4 and BE = 3, what is the measure of BA? 2. If AE = 3x + 1 and AC = 8x - 18, find x.