* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download tissues - PBworks
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Homeostasis wikipedia , lookup
Anatomical terminology wikipedia , lookup
Chimera (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Nerve guidance conduit wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Hematopoietic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
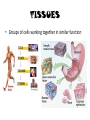
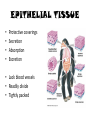
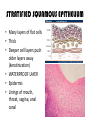
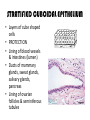
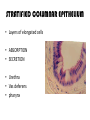
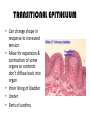
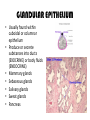
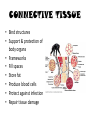
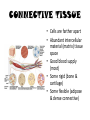
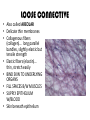
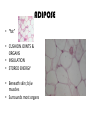
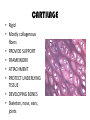
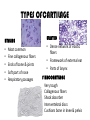
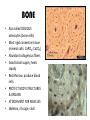
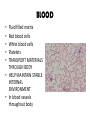
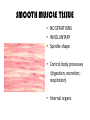
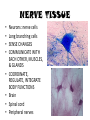
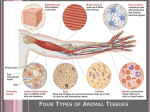
TISSUES TISSUES • Groups of cells working together in similar function 4 MAJOR TISSUE TYPES Epithelial (protection) Connective (bind organs) Muscle Nerve (movement) (communication) EPITHELIAL TISSUE • • • • Protective coverings Secretion Absorption Excretion • Lack blood vessels • Readily divide • Tightly packed 9 types of Epithelial SIMPLE SQUAMOUS SIMPLE CUBOIDAL STRATIFIED CUBOIDAL SIMPLE COLUMNAR GLANDULAR STRATIFIED SQUAMOUS PSEUDOSTRATIFIED COLUMNAR TRANSITIONAL STRATIFIED COLUMNAR SIMPLE SQUAMOUS EPITHELIUM • Single layer of thin flat cells • Allow substances to easily pass through • PROTECTION • Air sacs of lungs (alveoli) • Capillary walls • Blood & lymph vessels • Membranes that line body cavities SIMPLE CUBOIDAL EPITHELIUM • Single layer of cube shaped cells • SECRETION • ABSORPTION • Ovaries • Kidney tubules • Gland ducts (salivary, thyroid, pancreas) SIMPLE COLUMNAR EPITHELIUM • Single layer of elongated (column) shaped cells • Thick • SECRETE DIGESTIVE FLUIDS • ABSORB NUTRIENTS • Stomach • Intestines (microvilli) • Oviducts • Uterus STRATIFIED SQUAMOUS EPITHELIUM • Many layers of flat cells • Thick • Deeper cell layers push older layers away (keratinization) • WATERPROOF LAYER • Epidermis • Linings of mouth, throat, vagina, anal canal STRATIFIED CUBOIDAL EPITHELIUM • Layers of cube shaped cells • PROTECTION • Lining of blood vessels & intestines (lumen) • Ducts of mammary glands, sweat glands, salivary glands, pancreas • Lining of ovarian follicles & seminiferous tubules STRATIFIED COLUMNAR EPITHELIUM • Layers of elongated cells • ABSORPTION • SECRETION • Urethra • Vas deferens • pharynx PSEUDOSTRATIFIED COLUMNAR EPITHELIUM • Appear layered but really are a single layer (nucleus at diff locations) • Usually have cilia • MOVE DUST & MICROBES • Respiratory passages TRANSITIONAL EPITHELIUM • Can change shape in response to increased tension • Allow for expansion & contraction of some organs so contents don’t diffuse back into organ • Inner lining of bladder • Ureter • Parts of urethra GLANDULAR EPITHELIUM • Usually found within cuboidal or columnar epithelium • Produce or secrete substances into ducts (EXOCRINE) or body fluids (ENDOCRINE) • Mammary glands • Sebaceous glands • Salivary glands • Sweat glands • Pancreas CONNECTIVE TISSUE • Bind structures • Support & protection of body organs • Frameworks • Fill spaces • Store fat • Produce blood cells • Protect against infection • Repair tissue damage CONNECTIVE TISSUE • Cells are farther apart • Abundant intercellular material (matrix) tissue space • Good blood supply (most) • Some rigid (bone & cartilage) • Some flexible (adipose & dense connective) LOOSE CONNECTIVE • Also called AREOLAR • Delicate thin membranes • Collagenous fibers (collagen)… long parallel bundles, slightly elastic but tensile strength • Elastic fibers (elastin)… thin, stretch easily • BIND SKIN TO UNDERLYING ORGANS • FILL SPACES B/W MUSCLES • SUPPLY EPITHELIUM W/BLOOD • Skin beneath epithelium DENSE CONNECTIVE • Also called RETICULAR • Closely packed (very little if any matrix) • Collagen & elastin (strong) • Low blood supply; slow repair/healing • BINDS BODY PARTS TOGETHER • Ligaments & tendons ADIPOSE • “fat” • CUSHION JOINTS & ORGANS • INSULATION • STORED ENERGY • Beneath skin; b/w muscles • Surrounds most organs CARTILAGE • Rigid • Mostly collagenous fibers • PROVIDE SUPPORT • FRAMEWORK • ATTACHMENT • PROTECT UNDERLYING TISSUE • DEVELOPING BONES • Skeleton, nose, ears, joints TYPES OFCARTILAGE HYALINE • • • • • Most common Fine collagenous fibers Ends of bone & joints Soft part of nose Respiratory passages ELASTIC • Dense network of elastic fibers • Framework of external ear • Parts of larynx FIBROCARTILAGE Very tough Collagenous fibers Shock absorber Intervertebral discs Cushions bone in knee & pelvis BONE • Also called OSSEOUS osteocytes (bone cells) • Most rigid connective tissue (mineral salts: CaPO4; CaCO3) • Abundant collagenous fibers • Good blood supply; heals rapidly • Red Marrow: produce blood cells • PROTECT BODY STRUCTURES & ORGANS • ATTACHMENT FOR MUSCLES • Skeleton, rib cage, skull BLOOD • • • • • Fluid filled matrix Red blood cells White blood cells Platelets TRANSPORT MATERIALS THROUGH BODY • HELP MAINTAIN STABLE INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT • In blood vessels throughout body MUSCLE TISSUE • Contractile (elongates & shortens) • MOVES BODY PARTS SMOOTH MUSCLE SKELETAL MUSCLE CARDIAC MUSCLE SKELETAL MUSCLE TISSUE • STRIATED: long, threadlike cells w/ alternating light & dark bands • VOLUNTARY • Move head, trunk, limbs • Allow us to make facial expressions, write, walk, talk, chew, swallow, breathe • Muscle attached to bones SMOOTH MUSCLE TISSUE • NO STRIATIONS • INVOLUNTARY • Spindle-shape • Control body processes (digestion; excretion; respiration) • Internal organs CARDIAC MUSCLE TISSUE • • • • • Found only in HEART STRIATED INVOLUNTARY Cells join end to end Intercalated disks: allow nerve impulses to travel rapidly NERVE TISSUE • • • • • • • • Neurons: nerve cells Long branching cells SENSE CHANGES COMMUNICATE WITH EACH OTHER, MUSCLES, & GLANDS COORDINATE, REGULATE, INTEGRATE BODY FUNCTIONS Brain Spinal cord Peripheral nerves