* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 186,000 miles per second
Hubble Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Lovell Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Arecibo Observatory wikipedia , lookup
James Webb Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Allen Telescope Array wikipedia , lookup
Spitzer Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Optical telescope wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
CfA 1.2 m Millimeter-Wave Telescope wikipedia , lookup
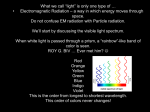
186,000 miles per second Electromagnetic Spectrum It’s not just a good idea… It’s the law! What is a light year and what does it measure? The distance light travels in a year’s time How many miles in 1 light year? 186,000 x 60 = min x 60 = hr x 24 = day x 365 = year =5.87 x 1012 miles! = 5,870,000,000,000 miles How long does it take for sunlight to reach Pluto which is 3.6 billion miles away? 3.6 x 109 mi = 1 sec = 1 min = 1 hour 186,000 mi 60 sec 60 min = 5.37 hours (.37 x 60 = 22 min) so 5 hr 22 min. How many miles to the star Sirius which is 8.7 light years away? 5.87 x 1012 miles x 8.7 = 5.1 x 1013 = 51,000,000,000,000 miles! How many miles to the Andromeda galaxy which is 2.9 million light years away? 5.87 x 1012 mi x 2.9 x 106 = 1.7 x 1019 17,000,000,000,000,000,000 miles!! And that is a NEARBY galactic neighbor!! So how do astronomers know all of this? It all starts with an understanding of the electromagnetic spectrum 1 Speed = wavelength x frequency speed or = 186,000 mi/sec 300,000 km/sec wavelength= crest to crest frequency = # of waves/sec. If you increase wavelength, then the frequency decreases If you decrease wavelength, then the frequency increases Called an inverse relationship 2 Optical Telescopes Where would be the best place to build your telescope? Why? Two purposes: gather light and magnify objects The larger the opening, the greater the light gathering ability A= ∏(r)2 So, if you double the size of the telescope, it increases its light gathering potential by ____? Refractor Reflector Multiple-Mirror Telescopes (MMT) Schmidt- reflecting mirror and refracting lens = wide angle view Charge-Coupled Devices (CCD’s) Reflecting telescope Yerkes Observatory, Wisconsin 102 cm refractor (the world’s largest refracting telescope) Hale Telescope, Mt Palomar CA mirror is 508 cm! Keck MMT: Mauna Kea, HI two telescopes work together to equal 85 meter mirror! 3 4 5 Hubble Radio Telescopes and others Utilizes different wavelengths can they be wire mesh? Wavelengths are so long Other types are infrared, gamma, x-ray Why Very Large Array: Socorro, NM Radio telescopes linked to equal a diameter of 34 kilometers!! 6