* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download are found in the epidermal cells. Some plants possess stomata only
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
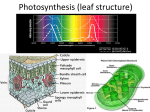
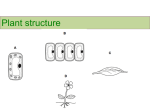
LEAF Consists of three parts: Epidermis, mesophyll and vascular bundles Epidermis A single layered cells covering the leaf surface. Consists of the upper epidermis and lower epidermis Cells in the upper epidermis do not contain chloroplasts except in the guard cells. The main function of the epidermis is to protect tissues in the inner part of the leaf. Cuticle is found on the surface of epidermal cells, including wax In some plants, crystals (a form of waste material) are found in the epidermal cells. Various forms of glands may be found in the epidermis. Generally, the lower epidermis is similar to the upper epidermis, except that the lower epidermis has more stomata. Some plants possess stomata only in the lower epidermis, while in some plants stomata are found only in the upper epidermis e.g. aquatic plants Cross section of a leaf trichomes crystals veins Epidermal surface of a leaf There are two guard cells around the stomatal pore. The guard cells are normally smaller than the surrounding epidermal cells and contain chloroplasts. The function of stomata is to regulate the exchange of gas between the inner part of leaf and the atmosphere, as well as the evaporation of water that enters the plant through the roots. Mesophyll The part which lies between the upper and lower epidermis. Mesophyll cells contain numerous chloroplasts. Photosynthesis occurs mainly in the mesophyll tissue. The mesophyll tissue usually are of two parts: i) Palisade mesophyll which usually consists of two layers of elongated parenchyma cells that are closely packed in a vertical manner. ii) Below is the spongy mesophyll that consists of irregular shaped parenchyma cells that are loosely packed, with abundant air spaces between them to allow more efficient air exchange. perforations Palisade parenchyma A large lateral vein Spongy mesophyll Vascular bundles Form the midrib and veins of various sizes in the mesophyll. Consist of xylem and phloem tissues and surrounded by thick walled parenchyma cells termed the bundle sheath The phloem transports carbohydrate manufactured by mesophyll cells to all parts of the plant, while water from the root is transported by the xylem to the leaf. In monocot leaves, the mesophyll is often not distinguished into the palisade and spongy layers. In some monocots, e.g. in the Gramineae, there are large cells with thin cell walls found on both sides of the midrib, usually in the upper epidermis, called bulliform cells. Under dry condition, the bulliform cells shrink, causing the leaf to roll, thus help reduce the rate of transpiration from the leaf. Bulliform cells (Gramineae)