* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download teachnm6
Anoxic event wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Great Lakes tectonic zone wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Supercontinent wikipedia , lookup
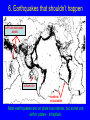
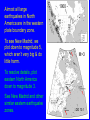
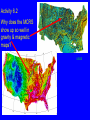
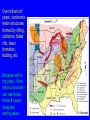
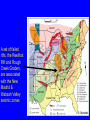
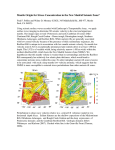
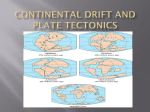
6. Earthquakes that shouldn’t happen DIFFUSE BOUNDARY ZONES INTRAPLATE NARROW BOUNDARIES Most earthquakes are on plate boundaries, but some are within plates - intraplate. Almost all large earthquakes in North America are in the western plate boundary zone. To see New Madrid, we plot down to magnitude 5, which aren’t very big & do little harm. 1900 - M>3 To resolve details, plot eastern North America down to magnitude 3. See New Madrid and other similar eastern earthquake zones. DD 10.1 Charleston, South Carolina 1886 M ~ 7 Similar to New Madrid 1811-12 Damaged buildings - especially brick & caused about 60 fatalities Similar sand blows Recovery took about five years DD 10.2 Grand Banks, Newfoundland 1933 M 7.3 Caused landslide & tsunami QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. Broke transatlantic cables Intensity pattern like 1811-12 GSC Earthquakes require -Faults to slip on - Force (stress) to cause motion of faults At plate boundaries, faults are the boundaries and plate motions provide stresses that cause motion What about within continental plates? Granite continents vs basalt oceans Continental crust is less dense, so continents are higher than ocean basins Continents float above denser mantle Continents don’t subduct, unlike oceans Continents formed earlier in Earth history and can reach ages of billions of years compared to 200 Ma oceans DD 10.3 WILSON CYCLE East African Rift Continental Oceanic lithosphere is rifting formed at Young ocean midocean ridges & destroyed at subduction zones Continental plates are rifted apart and then collide, but survive DD 10.4 Gulf of Aden, Gulf of California Andes Ocean-continent convergence Southern Europe Closing ocean Continental collision Stein & Wysession, 2003 Himalaya Zagros Global Plate Tectonics Jurassic to Present Day By L.A. Lawver, M.F. Coffin, I.W.D. Dalziel L.M. Gahagan, D.A. Campbell, and R.M. Schmitz 2001, University of Texas Institute for Geophysics February 9, 2001 Activity 6.1: Wilson cycle When does the North Atlantic rift open? When does the South Atlantic rift open? When does India collide with Eurasia? When does Arabia rift away from Africa? Some continental rifts fail to split a continent Leave “failed rift” - long valley of stretched & faulted rock that gets filled up & buried by sediments MCRS Midcontinent Rift system QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. Failed to split North America ~1.1 Ga (billion years ago) Activity 6.2 Why does the MCRS show up so well in gravity & magnetic maps? USGS Shay & Trehu, 1993 Over billions of years, continents retain structures formed by rifting, collisions, failed rifts, basin formation, faulting, etc Stresses within the plate - from various sources can reactivate these & cause intraplate earthquakes S. Marshak A set of failed rifts, the Reelfoot Rift and Rough Creek Graben, are associated with the New Madrid & Wabash Valley seismic zones S. Marshak Activity 6.3: Spot formation of the MCRS and Reeflfoot/Rough creek rifts Whitmeyer & Karlstrom 2007 Reelfoot Rift formed when supercontinent of Rodinia broke up QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. DD10.5 Meert & Torsvik, 2003