* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Diversity Presentation November 2016
International reactions to Fitna wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Islamism wikipedia , lookup
Gender roles in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and war wikipedia , lookup
Islam and secularism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and violence wikipedia , lookup
Reception of Islam in Early Modern Europe wikipedia , lookup
Islam and modernity wikipedia , lookup
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
Soviet Orientalist studies in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Mormonism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Sikhism wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Afghanistan wikipedia , lookup
Islamic missionary activity wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Indonesia wikipedia , lookup
War against Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islamic schools and branches wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Somalia wikipedia , lookup
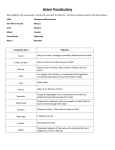
CULTURAL DIVERSITY IN THE WORKPLACE Highlights for today Types of diversity Cultural diversity challenges Islamic beliefs Cultures among us Strategies to use to on the job Dimensions of Diversity What kinds of diversity do you face in the workplace? Geographic Military Location Experience Education Work Gender Age Experience Work/thinking Style Sexual Disability Socioeconomic Orientation status Family Ethnic Race Status Religion Heritage First Communication Language Style Organizational Role and Level THE DIVERSITY CONUNDRUM AT WORK What is your workplace doing well? What areas are a struggle? Definition of culture Merriam-Webster defines culture as – 1. The beliefs, customs, arts, etc. of a particular society, group place, or time 2. A particular society that has its own beliefs, ways of life, art, etc. 3. A way of thinking, behaving, or working that exists in a place or organization (such as a business) Hidden challenges of culture Body language: Hand shaking may not be comfortable or familiar for some Muslims, particularly with the opposite gender. Some cultures view eye contact as disrespectful Gender: Respecting female supervisors Religious: Agreeing upon reasonable accommodations for faith practice at work Stumbling blocks Unknown data: Correct birthdates, names, and spelling Navigating two cultures: Maintaining the culture of origin, while assimilating to the American culture English language usage: Idioms – A slap on the wrist; against the clock Metaphors – The boss was boiling mad; the project was about to take flight Similes – As clear as a bell; as dead as a doornail Resettlement process: Flee country of origin Refugee camp placement UNHCR – United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees Screening & paperwork Resettled to another country through a resettlement agency Intense 30 day “boot camp” introduction to the country/community What is Islam? Merriam-Webster defines Islam as: “The religious faith of Muslims including belief in Allah as the sole deity and in Muhammad as his prophet.” Approximately 75 different ethnicities and nationalities with various interpretations of Islam Allah – the name used for God in Islam Muslims – The people who practice Islam Qur’an/Koran – The holy book of Islam – it contains the sacred writings revealed to Muhammad by Allah 6 Articles of faith 5 Pillars of the faith 2 Sects are the Sunni (Sunnites) and the Shi’a (Shi’ites) FAITH TERMS: CHRISTIANITY ISLAM Faith: Christianity Islam People: Christian Muslim Holy Book: Bible Koran/Qur’an Six Articles of the Muslim Faith Belief in: 1. Oneness of Allah (God) 2. Angels – now and in the afterlife 3. Holy Books – Qur’an, Torah, Bible 4. Allah’s messages – sent through prophets including Adam, Noah, Abraham, Moses, Jesus, John the Baptist, Muhammad, etc. 5. Judgment Day and the afterlife – each person is accountable for their actions during life 6. Allah’s Decree – all things happen by the will of Allah MUSLIM PREFERENCES: Diet – Halal meat (animal was slaughtered by a Muslim) may be preferred, no pork, lard, or alcohol Ramadan – a time of prayer, reflection, fasting from food and drink, refraining from smoking, and abstaining from sexual relations during daylight hours. This is a 40 day event. Prayers are directed East and typically occur on a prayer mat. Muslims are to wash their hands, face and feet before prayers. Hygiene - Many prefer to wash after using the toilet, like the bidet used in European countries. This may be done with water bottles here. Keep your hands to yourself! Do you know what you are really saying to your employee when you use these gestures? Somali Refugee Experience This 2009 photo shows a camp planned for 90,000 but sheltering more than three times that amount at the Dedaab camp on the border of Somalia and Kenya Somali culture 1. Religion – Islam 2. Values – independence, democracy, generosity; may not express their appreciation verbally 3. Communication style – open & honest; belong to clans and sub-clans; speak Somali or Arabic 4. Family life – nuclear family includes grandparents, aunts, uncles, and other relatives. The children takes their father’s last name, the wife keeps her father’s last name. Marriages have been traditionally arranged. 5. Health concerns – women were vulnerable of rape in their country; newborn babies are to stay home with the mother for the first 40 days, male and female circumcision practices, feelings of depression or despair as many witnessed loved ones being killed Somali culture 6. Education – refugees often have little education, a priority is given to males 7. Clothing – women do not always wear the hijab 8. Diet – halal meat, no pork, no lard 9. Potential challenges – electricity, flush toilets, telephones, and basic appliances may be a new concept; there may be conflict between differing Somali groups 10. Something to remember – they are known to easily adjust to any situation; treat them fairly and respectfully to establish their trust. They are quick to help those in need. Sudanese camp (taken January 2014) and Lost Boys of Sudan Sudanese culture 1. Religion – Islam 2. Values – freely provide assistance to family and neighbors 3. Communication style – speak Arabic along with up to one of 8 others 4. Family life – polygamy is common in Darfur; children born out of wedlock may be raised by a male relative 5. Health concerns – poor nutrition and access to healthcare in their country, physical deformities, genetic disorders, polio, war injuries, and trauma from rape and physical attack. Most have had malaria. Sudanese culture 6. Education – highly motivated learners; limited access to formal education with class sizes averaging 87 students; males were prioritized 7. Clothing – men often dress very well, women dress conservatively but in bright colors 8. Diet – grains and vegetables, no pork or alcohol 9. Potential challenges – few lived with running water or electricity, banking, money, or have driven a car 10. Something to remember – children were sometimes beaten in school if they did not speak Arabic Liberian refugee story Emmanuel Tweh, co-founder of MOWCF. I am originally from Grand Gedeh, a country in the southeastern part of Liberia. I am a first-hand witness and survivor of the 14 year war that left my country Liberia in ruins. When war broke out in Liberia, my family escaped to a country named Ivory Coast on the west side of Africa. We lived there from 1990 – 1995, until the Liberian war reached Ivory Coast. It’s there I got separated from my family and was taken to a refugee camp in Ghana by my uncle. To this day, I do not know where my parents are or if they are even alive. In 2000, my uncle who took care of after being separated from my parents died of Cholera and Malaria, and I was left all alone at the refugee camp. Life was unbearable without a family or a job. I felt like I was facing the whole world alone. In order to survive, I had to wash people’s clothes or carry people’s groceries at the market. The small amount of money I did make was hardly enough to provide for my daily meals, which consisted mostly of bread. Getting safe drinking water was a struggle. My waking thoughts were those of survival. I would start my day wondering if I would get a meal and end my day hoping for a safe place to sleep. It never felt safe in the refugee camps because security was something that was never assured. Armed robbers were always attacking the camp and the Ghana government continually raided the camp. Health needs were rarely met because people had to pay for them out of pocket. Many people died from Malaria and Cholera because they could not afford health treatment. Despite this hardship I faced, I never lost hope because I knew that my Father in Heaven was watching over me. Liberian culture Liberian culture 1. Religion – Christianity, Islam, animism, ancestral worship, witchcraft 2. Values – hospitality, politeness, respect particularly for the elders, peace, long life 3. Communication style – shaking hands, women may embrace one another 4. Family life – many were separated during the War and are presumed dead 5. Health concerns – limited health/dental care and poor nutrition, many witnessed loved ones being tortured, gang raped, and killed Liberian culture 6. Education – varies greatly with lower literacy levels 7. Clothing – varies from modern day clothing to colorful tops/skirts for women 8. Diet – rice is a staple, along with a wide variety of fruits, vegetables, and grains 9. Potential challenges – 18 cultures and 23 languages exist in Liberia; English is the official language of the government 10. Something to remember – Many have had to flee to more than one country to seek refuge; each country has a different attitude and set of laws for refugees Afghan refugee experience Afghan culture 1. Religion – primarily Muslim 2. Values – tough and resilient 3. Communication style – generations of people struggling for power 4. Family life – very private large extended families, polygamy is practiced in Afghanistan, family obligations are often a priority above all else (including work) 5. Health concerns – stress disorders/high blood pressure, PTSD, land mine injuries Afghan culture 6. Education – highly varied 7. Clothing – modest to conservative 8. Diet – traditional Muslim diet 9. Potential challenges – many WAR (women at risk) who have suffered human rights abuses and may not have family in the U.S. to assist in the resettlement process 10. Something to remember – Osama Bin Laden came to assist Afghanistan during the jihad (religious war); the Taliban imposed extreme interpretations of the Islamic law with severe restrictions on women’s activities Bhutanese/Nepali refugee experience Phone charging bank – individuals pay to have their cell phone charged The wind carried the flames from hut to hut. The fire became uncontrollable. In ninety minutes 512 huts were reduced to ashes, according to the Jesuit Refugee Center Field director for Nepal, Jesuit Father Paramasivam Amalraj. Bhutanese/Nepali culture 1. Religion – Hindu, Buddhist, or Christian 2. Values – pride, high expectations for themselves and their families 3. Communication style – speak Nepali or English 4. Family life – patriarchal; extended family is part of the household 5. Health concerns – anxiety, PTSD, Depression, higher suicide risk Bhutanese/Nepali culture 6. Education – education is very important to them; academic performance has dropped; there is a shortage of qualified teachers 7. Clothing – colorful ethnic dress, traditional street clothes 8. Diet – white rice, vegetables, meat-(Hindus do not eat beef, as cows are viewed as sacred) 9. Potential challenges – Refugees may have lived in camps for decades and resettlement may very difficult as families are separated and all the comforts they have known are gone 10. Something to remember – Refugees from Nepal have one of the highest rates of acceptance from resettlement countries. Iraqi / Iraqi – Kurdish culture Iraqi / Iraqi-Kurdish culture 1. Religion – typically a more traditional Islam 2. Values – parents often struggle with socialization and dating for their children; marriages are often arranged 3. Communication style – Arabic, Kurdish; a more formal style is preferred 4. Family life – typically consists of husband, wife, children with the influence of the extended family; family is a private topic and a Kurdish male may not be comfortable discussing his family 5. Health concerns – headaches, depression, PTSD, low vaccination rate Iraqi / Iraqi-Kurdish culture 6. Education – education is valued but opportunities may have been limited by location 7. Clothing – bright clothing with mixed patterns and colors 8. Diet – vegetables and grains, homemade yogurt, tea 9. Potential challenges – potential worry of laws, regulations, and authority because of their history; there may be inconsistencies in the spelling of their names 10. Something to remember – Explain the system to provide a better understanding Hmong refugee camps Hmong culture 1. Religion – Christian, animism, and ancestral worship 2. Values – place the interest of the group, family, or clan over their own interests 3. Communication style – speak dialects of Hmong 4. Family life – a village may be located on the side of a mountain and consist of 20-40 households 5. Health concerns – limited healthcare access, major depression, anxiety, and PTSD Hmong culture 6. Education – limited opportunities, but motivated to learn 7. Clothing – colorful ethnic clothing 8. Diet – white rice, vegetables, fish, meat 9. Potential challenges – competition and rewarding individual success in the workplace opposes the Hmong values 10. Something to remember – There are alternative healing practices: herbal medicine, spiritual healing, and acupuncture/acupressure HIRING PROCESS: BE PROACTIVE 1. PPE required for the position. 2. Break time expectations (flexibility, duration, frequency) 3. Prayer practice. 4. Diversity in the workplace. EMPLOYEE HANDBOOK 1. Clear and concise explanations. 2. Keep the readability level to a minimum. 3. Use visuals where appropriate. This helps… Instill a climate of respect among all staff Invest in your employees Communicate openly Depersonalize conflict – focus on the behavior, not the individual Focus on the physical and socio-emotional well being of your employees by having safety signage, community resources (FirstLink), and EAP resources when possible RESOURCES: Center for Applied Linguistics (cal.org) Cultural Orientation Resource Center (culturalorientation.net) Religion Facts (religionfacts.org) Lutheran Social Services (lss.org) Google images *Avoid Wikipedia QUESTIONS?