* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nutrition and red blood cells
Survey
Document related concepts
Embryonic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Artificial cell wikipedia , lookup
Dictyostelium discoideum wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic resistance to malaria wikipedia , lookup
Stem-cell therapy wikipedia , lookup
Induced pluripotent stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Chimera (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
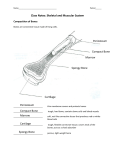
Name __________________________ Tuesday, 11-15-16 Packet # 2 - 10 7th Science - ________ AIM: Explain how specialized cells are the building blocks for multicellular organisms. Quote of the Day: “Practice doesn’t make perfect. Perfect practice makes perfect.” - Cal Ripken, Sr., Baltimore Orioles Coach and Manager Do Now - Read/annotate the text before answering the questions that follow: Cell Specialization All organisms are composed of cells. Unicellular organisms are composed of a single cell. Multicellular organisms are composed of many specialized cells. Specialized cells differ in structure (size, shape...) and function (the role they perform in the organism). The structural modifications (changes) that occur in a specialized cell prepare it to do its job in the organism. An adult human is composed of approximately 100 trillion cells and has over 200 different types of specialized cells. All of these specialized cells do a very different, very specific job. Examples of specialized cells are red blood cells (carry oxygen), skeletal muscle cells (contract to allow movement of body parts) and sperm cells (male reproductive). 1. How many cells are in an adult human? 100 trillion 2. How many different types of specialized cells are in an adult human? 200 3. Give one example of a specialized cell. Red blood cells Video, Discovery Education – Specialized Cells, 4:26. Take notes on each type of specialized cell during the video. Be prepared to discuss. Epidermis (Skin Cells) Muscle Cells Bone Cells Nerve Cells (Neurons) Red Blood Cells White Blood Cells 1 Work with a Partner – each group will be assigned one type of specialized cell. They will read/annotate the text for their specific cell and be prepared to present the following to the class: Draw the cell What does this specialized cell do? How does it do it? What is unique about this specialized cell? 1. Muscle Cells A myocyte (also known as a muscle cell) is the type of cell found in muscle tissue. Myocytes are long, tubular cells that develop from myoblasts to form muscles in a process known as myogenesis. There are various specialized forms of myocytes: cardiac, skeletal, and smooth muscle cells, with various properties. The striated cells of cardiac and skeletal muscles are referred to as muscle fibers. Cardiomyocytes are the muscle fibers that form the chambers of the heart, and have a single central nucleus. Skeletal muscle fibers help support and move the body. Smooth muscle cells control involuntary movements such as contractions in the esophagus and stomach. 2. Nerve Cells (Neurons) A neuron (also known as a[nerve cell) is an electrically excitable cell that processes and transmits information through electrical and chemical signals. These signals between neurons occur via synapses, specialized connections with other cells. Neurons can connect to each other to form neural networks. Neurons are the core components of the brain and spinal cord of the central nervous system (CNS), and of the ganglia of the peripheral nervous system (PNS). Specialized types of neurons include: sensory neurons which respond to touch, sound, light and all other stimuli affecting the cells of the sensory organs that then send signals to the spinal cord and brain, motor neurons that 2 receive signals from the brain and spinal cord to cause muscle contractions and affect glandular outputs, and interneurons which connect neurons to other neurons within the same region of the brain, or spinal cord in neural networks. 3. Red Blood Cells Red blood cells play an important role in your health by carrying fresh oxygen throughout the body. Red blood cells are round with a flattish, indented center, like doughnuts without a hole. Your healthcare provider can check on the size, shape, and health of your red blood cells using tests, such as the complete blood count screening. Hemoglobin is the protein inside red blood cells that carries oxygen. Red blood cells also remove carbon dioxide from your body, transporting it to the lungs for you to exhale. 3 Red blood cells are made inside your bones, in the bone marrow. They typically live for about 120 days, and then they die. Nutrition and red blood cells Foods rich in iron help you maintain healthy red blood cells. Vitamins are also necessary to build healthy red blood cells. These include vitamin E, found in foods such as dark green vegetables, nuts and seeds, mango, and avocados; vitamins B2, B12, and B3, found in foods such as eggs, whole grains, and bananas; and folate, available in fortified cereals, dried beans and lentils, orange juice, and green leafy vegetables. 4. White Blood Cells White blood cells are an important component of your blood system, which is also made up of red blood cells, platelets, and plasma. 4 Although your white blood cells account for only about 1% of your blood, their impact is significant. White blood cells, also called leukocytes, are essential for good health and protection against illness and disease. Think of white blood cells as your immunity cells. In a sense, they are continually at war. They flow through your bloodstream to battle viruses, bacteria, and other foreign invaders that threaten your health. When your body is in distress and a particular area is under attack, white blood cells rush in to help destroy the harmful substance and prevent illness. White blood cells are made inside the bone marrow and stored in your blood and lymphatic tissues. Because some white blood cells have a short lifespan of one to three days, your bone marrow is constantly making them. 5. Bone Cells Bone cells, which are found within the bone tissue, make up the skeletons of vertebrates. There are different types of bone tissue in a bone, made up of various types of bone cells: there is the cortical bone, which is the compact tissue of the hard outer part (cortex) of the bone; the cancellous bone, which is the spongy tissue inside of the compact cortex; and the subchondral tissue, which is the smooth tissue at the end of each bone.Bone cells all work together inside of the bones to help keep up the skeletal system. The bone cells do many things for the skeletal system, such as the development of new bones and continual bone remodeling (the maintenance of bones and the regulation of minerals in the body). Types of bone cell include osteoclasts, which break down bone tissue; osteoblasts, which build new bone tissue; osteocytes, which hold up the bone together; and lining cells, which protect the bone. There are four main categories of bone cells which include: 1. osteoclasts, which destroy bones 2. osteoblasts, which build bones 3. osteocytes, which hold the bone together 4. lining cells, which protect the bone. 5 6. Xylem Xylem Xylem is an interesting part of a plant in that it is its "woody" material. One reason it is "woody" is to provide support throughout the entire plant, as with a tree. One interesting tidbit about xylem is that when you cut down a tree and look at the tree trunk's "rings", you can see the old xylem tissue that encompassed the tree. Every xylem ring constitutes a year that a tree was alive. The primary role of xylem is to provide nutrients and water for a plant. A plant achieves this by absorbing water and nutrients through the plant's roots, where it transports these goods throughout the plant by xylem. Since xylem is connected throughout the plant by its "vessels," it easily passes the nutrients and water quickly and efficiently like a human's blood vessels. It should be mentioned that xylem operates from the bottom up. This means that it starts from the roots where it acquires water and nutrients. Xylem then "progresses" up throughout the rest of the plant to regions such as the leaves and the branches. 6 Xylem 7. Leaf Epidermis You may have heard at some point that your skin is the largest organ in your body. Besides being large, your skin is very important because it protects everything underneath it from disease, temperature, and other physical damage that may occur. Much like your skin, a plant has a tissue system, a group of cells that works together for a very specific function, that forms the first line of defense against physical damage and disease. This tissue system is called the dermal tissue system, and it is the plant's outer protective coating. The dermal system itself consists of a layer of tightly packed cells called the epidermis. On most plant stems and leaves, the epidermis is covered with a waxy coating called the cuticle, which helps prevent water loss through the epidermis. Structure Plant epidermis is unique because it is actually two different layers of cells: the upper epidermis and the lower epidermis. Sandwiched in between these two layers are two other important tissue systems - the vascular tissue system and the ground tissue system. The vascular tissue system provides water and nutrient transport from the roots to other parts of the plant. The ground tissue system, also called the mesophyll, is specialized for photosynthesis, the process by which the plant converts sunlight into usable chemical energy. 7 Notes ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 8