* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Reliability of Goniometer
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
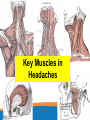
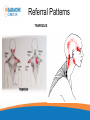
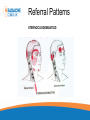
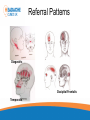
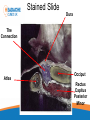
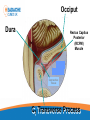
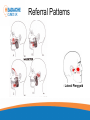
Headache Clinics UK Using a Goniometer Lynn Wilkes Cervical Range of Motion Cervical Range of Motion Reliability of Goniometer A range of studies have confirmed the goniometer, including the basic plastic one, is a valid and reliable measurement instrument for cervical spine range of motion Cervical Range of Motion Flexion and extension (A and B) the goniometer axis was positioned at the level of the seventh cervical vertebra, the fixed arm was kept parallel to the floor and, at the end of the movement, the moving arm was aligned with the earlobe Cervical Range of Motion Rotation (C): the goniometer axis was positioned at the centre of the head, the fixed arm was positioned at the centre of the head, at the sagittal suture, at the end of the movement, the moving arm was aligned with the nose; Cervical Range of Motion Lateral flexion (D): the goniometer axis was placed on the spinous process of the seventh cervical vertebra, the fixed arm was placed parallel to the floor and the moving arm was aligned with the midline of the cervical spine; Headache Clinics UK Trigger Point Therapy For Headaches Trigger Points Travell defined a TrP as “a hyperirritable spot in skeletal muscle that is associated with a hypersensitive palpable nodule in a taut band. The spot is tender when pressed and can give rise to characteristic referred pain, motor dysfunction, and autonomic phenomena.”. Trigger Points Research Travell Trigger Points—Molecular and Osteopathic Perspectives John M. McPartland, DO, MS Myofascial trigger points and sensitization: an updated pain model for tension-type headache C Fernández-de-las-Peñas1,2, ML Cuadrado2,3, CHIROPRACTIC MANAGEMENT OF MYOFASCIAL TRIGGER POINTS AND MYOFASCIAL PAIN SYNDROME: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE Howard Vernon, DC, PhD,a and Michael Schneider, DCb Myofascial trigger points in the suboccipital muscles in episodic tension - type headache Cesar Fernandez-de-las-Penasa, Contribution of Myofascial Trigger Points to Migraine Symptoms Maria Adele Giamberardino, Emmanuele Tafuri, Key Muscles in Headaches Key Muscles in Headaches Trapezius Sub Occipital Sternocleidomastoid Splenius capitis Frontalis Splenius cervicus Medial Ptyergoid Rectus capitis posterior minor Lateral Ptyergoid Rectus capitis posterior major Masseter Semispinalis capitis Temporalis Semi spinalis cervicis Referral Patterns TRAPEZIUS Referral Patterns STERNOCLEIDOMASTOID Referral Patterns Diagastric Occipital Frontalis Temporalis Referral Patterns Sub Occipital Rectus capitis posterior minor Rectus capitis posterior major Semispinalis cervicus Semi spinalis capitis Referral Patterns Sub Occipital Splenius capitis Splenius cervicus TMJ Research Leads to Discovery In addition to a new muscle of mastication, he also discovered a connective tissue bridge that attaches the rectus capitus posterior minor muscle to the dura at the atlanto – occipital junction. (it was present in all 10 cadavers) Hack GD. Anatomic relation between the rectus capitus posterior minor muscle and the dura matter. Spine 1995: 20:2484-2486 The Neuromuscular Connection • Dr. Hack stated: – Maryland Scientists speculate that the newly described muscle – dura connection may transmit forces from the neck muscles to the pain sensitive dura. Stained Slide Dura The Connection Atlas Occiput Rectus Capitus Posterior Minor Occiput Dura Rectus Capitus Posterior (RCPM) Muscle Connective Tissue C1 Transverse Process Referral Patterns Lateral Pterygoid Trigger Point Therapy Practical Mary Sanderson