* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - Mrs. Abbott OPHS
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
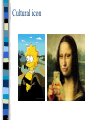
Renaissance Art Italian Early and High Renaissance Art Art and Patronage Italians were willing to spend a lot of money on art. /Art communicated social, political, and spiritual values. /Italian banking & international trade interests had the money. Public art in Florence was organized and supported by guilds. Therefore, the consumption of art was used as a form of competition for social & political status! Characteristics of Renaissance Art Realism & Expression Expulsion from the Garden Masaccio 1427 First nudes since classical times. 2. Perspective First use of linear perspective! The Trinity Masaccio 1427 3. Classicism Greco-Roman influence. Secularism. Humanism. Individualism free standing figures. Symmetry/Balance The “Classical Pose” Medici “Venus” 4. Emphasis on Individualism Batista Sforza & Federico de Montefeltre: The Duke & Dutchess of Urbino Piero della Francesca, 14651466. 5. Geometrical Arrangement of Figures The Dreyfus Madonna with the Pomegranate Leonardo da Vinci 1469 The figure as architecture! 6. Artists as Personalities/Celebrities Lives of the Most Excellent Painters, Sculptors, and Architects Giorgio Vasari 1550 Early Renaissance The First Three Hall-of-Famers Masaccio 1401-1428 Founder of early Renaissance Painting Painted human figure as a real human being (3D) Used perspective Consistent source of light (accurate shadows) The Tribute Money #2 Donatello 1386-1466 The sculptor’s Masaccio David (1430-32) – First free standing, life-size nude since Classical period – Contrapposto – Sense of Underlying skeletal structure The Penitent Magdalene (Donatello) Real gaunt “Speak, speak or the plague take you!” #3 Boticelli 1482 Rebirth of Classical mythology Fully Pagan THE BIRTH OF VENUS The Italian Renaissance Leonardo Michelangelo Raphael Da Vinci Vitruvian Man (1490) Classical Orders of architecture Da Vinci Mona Lisa (15031517?) Perspective, Anatomy, Composition Da Vinci: Mona Lisa (1503-1517?) Did you know that Leonardo da Vinci worked on his masterpiece, the Mona Lisa, for over 10 years? He wanted to make her perfect and to create depth in the landscape behind her. da Vinci continued to paint translucent layers of color over and over in order to create the perfection that we now know as the Mona Lisa. His work remains a masterpiece today because of his dedication to creating perfection in his art. He never gave up on reviewing his art to make it better! Cultural icon Cultural icon The Last Supper Emotions Response The Last Supper Leonardo sought a greater detail and luminosity than could be achieved with traditional fresco. He painted The Last Supper on a dry wall rather than on wet plaster, so it is not a true fresco. He used a double layer of dried plaster over a stone wall, he added an undercoat of white lead to enhance the brightness of the oil and tempera that was applied on top. These techniques were important for Leonardo's desire to work slowly on the painting, giving him sufficient time to develop the gradual shading or chiaroscuro that was essential in his style. The Last Supper The Last Supper in 1495 and completed it in 1498 One story goes that a prior from the monastery complained to Leonardo about the delay, enraging him. He wrote to the head of the monastery, explaining he had been struggling to find the perfect villainous face for Judas, and that if he could not find a face corresponding with what he had in mind, he would use the features of the prior who complained. The Last Supper Because the painting was on a thin exterior wall, the effects of humidity were felt more keenly, and the paint failed to properly adhere to the wall. Because of the method used, soon after the painting was completed on February 9, 1498 it began to deteriorate. Leonardo, later in his life, is said to have regretted "never having completed a single work". Michelangelo David (based on the biblical hero) Michelangelo Buonarotti 1504 Marble The David The sculpture include unusually large head and hands. No one is really sure why…take a moment to observe the details of his face the veins in his hands, and remember, this statue was carved out of marble! Michelangelo: The Sistine Chapel Michelangelo: The Sistine Chapel Michelangelo: The Sistine Chapel Michelangelo: The Sistine Chapel The Last Judgment Michelangelo: The Sistine Chapel The Delphic Sibyl on the Sistine Chapel ceiling Raphael School of Athens 1510 Raphael: School of Athens 1510 •Raphael was one of the great masters of the later Italian Renaissance. He is famous for his skill at artistic techniques like foreshortening and perspective. •Foreshortening means adjusting a figure into non-realistic proportions to give the impression that certain parts of the body are closer to the viewer. For example, a subject's hands are the same size, but if the subject is standing sideways, then the more distant hand is painted smaller so it appears further away. •Perspective is a similar form of illustration where more distant objects are painted smaller, and the edges of all objects are angled towards a single point on the horizon - the vanishing point. Our eyes perceive space around us this way, so recreating the effect makes the painting feel real. Da Vinci Raphael Michelangelo Michelangelo Raphael and Michelangelo were rivals, but when Rafael saw part of the finished Sistine Chapel ceiling he added Michelangelo into the painting as a tribute. Plato: looks to the heavens [or the IDEAL realm]. Aristotle: looks to this earth [the here and now]. Pythagoras Ptolemy Euclid