* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Greek City States2
Thebes, Greece wikipedia , lookup
Liturgy (ancient Greece) wikipedia , lookup
Sacred Band of Thebes wikipedia , lookup
List of oracular statements from Delphi wikipedia , lookup
First Persian invasion of Greece wikipedia , lookup
Theban–Spartan War wikipedia , lookup
Athenian democracy wikipedia , lookup
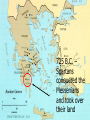
GREEK CITY-STATES KEEP IN MIND… GREECE WAS HEAVILY INFLUENCED BY IS GEOGRAPHY. The 3 main influences are: The Land Very The rugged mountains Sea (better transportation, many islands) Greeks The didn’t live on land, but around a sea Climate Outdoor lifestyle RISE OF THE POLIS The polis, AKA citystate, was made up of the city and the surrounding countryside. Citizens would gather at the agora (marketplace) or on a fortified hilltop to discuss city government. ACROPOLIS: A fortified hilltop, or the high point of the polis . Acropolis GREEK POLITICAL STRUCTURES Monarchy- rule by a king Aristocracy- rule by land-owning nobility Oligarchy- rule by a small group of powerful people - Usually merchants and artisans TYRANTS SEIZE POWER (Has good connotation) Rulers/common people clash Nobles/wealthy citizens win support of common people Seized control and ruled in interests of ordinary people ATHENS VS. SPARTA ATHENS & DEMOCRACY Idea of representative gov’t began to take root Rule by the people developed in Athens around 621 B.C. Legal Code Draco DRACO – 621 B.C. Nobleman Developed legal code based on equality of all Athenians, rich or poor Dealt harshly w/ criminals (Hammurabi) Upheld debt slavery Draconian Law SOLON – 594 B.C. Outlawed debt slavery Organized Athenians into 4 social classes according to wealth. Only top 3 could hold office All citizens could participate in the assembly no matter the class. Any citizen could bring charges against wrongdoers CLEISTHENES -500 B.C. Broke up power of nobility Organized citizens based on where they live, not by wealth Increased power of assembly (citizens could submit laws for debate) Created the Council of 500 (proposed laws and counseled the assembly- chosen by random). WHO WERE CONSIDERED CITIZENS? Free adult, male property owners born in Athens Women, slaves, & foreigners were excluded and had few rights ATHENIAN EDUCATION Boys educated to become good citizens & defend Athens Reading, math, pub. speaking Girls educated at home to become good wives & mothers VALUES OF ATHENS Athenians were very much interested in art, literature, science, math, and philosophy. Athletics also important -> Olympics Prisoners of war were used as slaves. Women didn’t go to school. Never taught to read or write. ATHENS VS. SPARTA SPARTAN GOVERNMENT Government branches had several Assembly (all citizens) Council of Elders (30 older citizens) Proposed laws to assembly 5 elected officials Carried out laws, controlled education, prosecuted court cases Two Kings Ruled over the military forces SPARTAN CULTURE Strong military power Mostly agricultural CODE OF LYCURGUS Reforms aimed at Spartan virtues Equality Created Military Fitness Austerity by Lycurgus who starved himself to death to save food for his polis This shows Spartan values of self discipline and endurance 725 B.C. – Spartans conquered the Messenians and took over their land MESSENIANS Spartans treated Messenians as slaves Called the Helots – peasants forced to stay on the land they worked Each year, the Spartans demanded half of the Helots yearly crop HELOTS By 600 B.C. the Helots outnumbered the Spartans 8 to 1 Soooo…about 500,000 Helots and only 25,000 Spartans Revolted often Krypteia (secret police) THE SPARTAN ARMY Extremely strong because of fear of revolt Spartan citizens devoted their lives to serving their army SPARTAN POWER From 600-371 B.C. the Spartans had the most powerful army in Greece However, they created little art, literature or architecture They valued duty, strength, and discipline Boys trained from age 7 SPARTAN WOMEN Received some military training Could wrestle and compete in sports Had much more freedom than other city-states Ran the family estate when husbands were at war. Couldn’t vote but had strong political voice Come back with your shield, or on it. SPARTA > EVERYTHING