* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Why do things move?
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Eigenstate thermalization hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Faster-than-light wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Mass versus weight wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Work (thermodynamics) wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
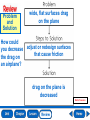
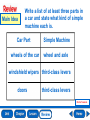
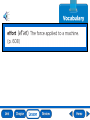
Lesson 1 Motion Lesson 2 Forces and Motion Lesson 3 Work and Energy Lesson 4 Simple Machines Why do things move? position motion frame of reference speed velocity acceleration momentum What is motion? Motion is a change in position over time. What is speed? speed = distance ÷ time bee 8 m/s giraffe 14 m/s 3 eagle 33 m/s horse 21 m/s turtle 2 m/s cheetah 33 m/s dolphin 12 m/s Speed is how fast an object’s position changes over time. What is acceleration? acceleration = change in speed ÷ time Acceleration is the change in an object’s velocity over time. What is momentum? momentum = mass x velocity The more momentum an object has, the easier it is for that object to move other objects. Main Idea Is speed or velocity more helpful to a pilot? Why? Velocity is more helpful, because it tells the pilot how fast the plane is moving and the direction it is traveling. Vocabulary _______________ is the location of an object. Position _______________ is the change in velocity over Acceleration time for an object. A group of objects from which you can measure a position or motion is a ________________. _______________ is the product of mass Momentum multiplied by velocity. momentum position acceleration frame of reference Vocabulary ________ Speed is how fast an object’s position changes over time. ________ Velocity is the measurement that combines both the speed and direction of a moving object. ________ Motion is a change in position over time. velocity motion speed Main Idea and Details How could an object accelerate while still traveling at a constant speed? Main Idea Details A car driving around a circular track is accelerating. Velocity is changing as direction changes; speed is constant. End of Lesson force friction balanced force unbalanced force action force reaction force What are forces? A force is any push or pull from one object to another. What are gravity and friction? drag gravity What is Newton’s First Law? NEWTON’S FIRST LAW An object at rest tends to stay at rest, and an object in constant motion tends to stay in motion, unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. What is Newton’s Second Law? NEWTON’S SECOND LAW The unbalanced force on an object is equal to the mass of the object multiplied by its acceleration: F=m x a. What is Newton’s Third Law? NEWTON’S THIRD LAW All forces occur in pairs, and these two forces are equal in strength an opposite in direction. Main Idea What forces are at work on a floating object? Are they balanced? The forces at work on a floating object are gravity and buoyancy. They are balanced. Vocabulary The push of the second object back on the first object is a _______________. When forces act on an object without changing its motion, it is a _______________. A _______________ is any push or pull from one object to another. reaction force force balanced force Vocabulary A force that causes an object to change its motion is an ________________. The push of the first object on the second object is an _______________. _______________ is a force that opposes the Friction motion of one object moving past another. unbalanced force friction action force Problem and Solution How could you decrease the drag on an airplane? wide, flat surfaces drag on the plane adjust or redesign surfaces that cause friction drag on the plane is decreased End of Lesson work energy potential energy kinetic energy law of conservation of energy What is work? Work is the measurement of energy used to perform a task. work = force x distance force distance What is energy? Energy is the ability to perform work or to change an object. lifting dropping throwing How can energy change? The kinetic energy of falling water is changed into electricity at a hydroelectric dam. Main Idea When is work done when you throw and catch a ball? Work is done as the ball is thrown and accelerates. Work is done when the ball is caught and is stopped. Vocabulary __________________ is the ability to perform work or Energy to change an object. _________________ Potential Energy is energy that is stored in the position, or structure of an object. __________________ is the measurement of the Work energy used to perform a task. The theory that states energy cannot be created or destroyed, it can only change form is called the ________________. __________________________. _________________ is the energy of a moving object. Kinetic energy work energy potential energy kinetic energy law of conservation of energy Infer When might kinetic energy turn into sound energy? Clues What I Know What I Infer Clap your hands. Energy cannot be created or destroyed, it can only change form. Kinetic energy turns into sound energy. End of Lesson simple machine effort load fulcrum compound machine efficiency What are simple machines? A simple machine is a machine that takes one force and changes its direction, distance, or strength. lever wheel and axle pulley inclined plane wedge screw What are levers? KEY effort output effort arm resistance arm fulcrum second-class lever first-class levers Which machines are like levers? Pulley Wheel and axle What are inclined planes? output resistance arm effort arm What are compound machines? electric winch When two or more simple machines are combined they form a compound machine. elevator counterbalance pulley Main Idea How could several pulleys help you lift a very heavy object? The pulley system could redirect your effort so that you could pull down instead of lift up. More importantly, a pulley system could multiply your effort so that you could lift the object more easily. Vocabulary ______________ is the force you apply to a Effort machine. A ______________ is a machine that takes one force and changes its direction, distance, or strength. The ______________ is the pivot point around which the bar of a lever rotates. simple machine fulcrum effort Vocabulary __________________ is the ratio of input Efficiency energy to output work, usually written as a percentage. When two or more simple machines are combined they form a __________________. The __________________ is the object moved by the output. load efficiency compound machine Main Idea Write a list of at least three parts in a car and state what kind of simple machine each is. Car Part wheels of the car Simple Machine wheel and axle windshield wipers third-class levers doors third-class levers End of Lesson