* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download SKULL – Part 1
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
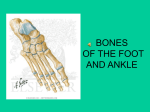
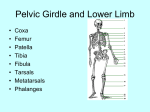
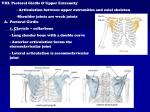
SKULL – Part 1 Cranial Bones Frontal – forehead Parietal – upper sides Temporal – lower sides Occipital – back/base Sphenoid – connects inside, wings Ethmoid – back of nasal cavity Sutures Coronal – frontal/parietal Sagittal – parietal/parietal Lambdoid – occipital/ parietal Squamous – temporal/parietal Facial Bones Maxilla – upper jaw Palatine – posterior roof of mouth Zygomatic – “cheekbones” Nasal – bridge of nose Lacrimal – medial eye socket Vomer – floor of nasal cavity Mandible – lower jaw SKULL – Part 2 Processes Zygomatic process (temporal bone) Mastoid process (temporal bone) Styloid process (temporal bone) Occipital condyles (occipital bone) External occipital protuberance (occ.) Greater wings (lateral sphenoid) Lesser wings (anterior/superior sphenoid) Pterygoid Processes (inferior sphenoid) Nasal conchae (ethmoid bone) Coronoid process (mandible) Condylar process (mandible, posterior) Interior Structures Sella turcica (sphenoid bone) “saddle” Internal auditory meatus (temporal bone) Crista galli (ethmoid bone) Openings & Depressions (other than foramina on base of skull) Mandibular fossa (temporal bone) External auditory meatus (temporal bone) Infraorbital foramen (maxilla) Supraorbital foramen (frontal bone) Mental foramen (mandible) Mandibular notch (mandible) FORAMINA OF SKULL Inferior View (from bottom) Foramen Magnum – for spinal cord Foramen Lacerum – intersection of sphenoid, temporal, and occipital Foramen Ovale – lateral to and slightly larger than Lacerum Foramen Spinosum – lateral/posterior to and smaller than Ovale Jugular Foramen – closest to Magnum, between occipital and temporal Carotid Canal – anterior/lateral to Jugular FORAMINA OF SKULL Superior View (from top, calvarium removed) Foramen Magnum – for spinal cord Foramen Lacerum – intersection of sphenoid, temporal, and occipital Foramen Ovale – lateral to and slightly larger than Lacerum Foramen Spinosum – lateral/posterior to and smaller than Ovale Foramen Rotundum – anterior sphenoid, medial to orbital fissure Orbital Fissure – slit at back of eye socket Optic Canal – between upper and lower portions of lesser wing on sphenoid bone Jugular Foramen – closest to Magnum, between occipital and temporal Carotid Canal – anterior/lateral to Jugular FETAL SKULL – FONTANELS Anterior fontanel – superior, where sagittal and coronal sutures meet Posterior fontanel – posterior, where sagittal and lambdoid sutures meet Posterolateral/Mastoid fontanel – lateral posterior, where lambdoid and squamous sutures meet Anterolateral/Sphenoidal fontanel – lateral anterior, where squamous and coronal sutures meet VERTEBRAE – general Vertebra Body – largest mass, anterior Spinous process – posterior projection Transverse process – lateral projection Vertebral foramen – hole for spinal cord to pass through Vertebral arch – ring of bone around vertebral foramen o Pedicle – between body & T.P. o Lamina – between T.P. & S.P. Articular Facets – smooth surfaces for articulation with other vertebrae ATLAS (C1) & AXIS (C2) Atlas Has no spinous process or body Anterior & Posterior arches connect Lateral Masses Superior articular facets for articulation with occipital condyles of occipital bone (skull) – allows for nodding of head Inferior articular facets for articulation with Axis (C2) Axis Dens – superior projection articulates with anterior arch of Atlas (C1) – allows for rotation of head Superior articular facets for articulation with Atlas (C1) VERTEBRAE – THREE TYPES Cervical C1-C7 Bifid (split end) spinous process (on some) Transverse foramina for blood vessels Thoracic T1-T12 Long slender spinous process Articular facets for ribs “Giraffe Head” Lumbar L1-L5 Large body Short, stubby spinous process “Moose Head” SACRUM & COCCYX Sacrum Median sacral crest (ridge down center) Lateral sacral crests (ridges down sides) Sacral foramina – holes where nerves at end of spinal cord exit Coccyx Tailbone STERNUM & RIBS Costal Cartilage Ribs do not articulate directly with sternum “True” ribs have cartilage that continues directly to sternum “False” ribs have cartilage that combines with the cartilage of true ribs to reach the sternum “Floating” ribs do not have cartilage Ribs Sternum Manubrium – superior portion Jugular notch – top of manubrium Body – main part Xiphoid process – inferior point Interesting end with bumps is the “head” end that articulates with vertebrae Plain end attaches to cartilage SCAPULA – ORIENTATION The Glenoid cavity/fossa is LATERAL o Where the head of the humerus articulates The Spine of the scapula is POSTERIOR o The lateral end of the spine is the Acromion o The anterior lateral projection is the Coracoid Process o The flat part above the spine on the posterior side is Supraspinous fossa (where the muscle Supraspinatus is located) o The flat part below the spine on the posterior side is Infraspinous fossa (where the muscle Infraspinatus is located) The anterior surface is the subscapular fossa HUMERUS – ORIENTATION The medial side of the humerus has the Head (proximal end) and Medial Epicondyle (medial bump, distal end) and Trochlea (rounded end, distal) The lateral side of the humerus has the Greater & Lesser Tubercles (with Intertubercular Groove between them, proximal end) and Lateral Epicondyle (lateral bump, distal end) and Capitulum (rounded end, distal), as well as the Deltoid Tuberosity (rough spot along the shaft/body) The posterior side of the humerus has the Olecranon Fossa (a deeper indentation, distal end) The anterior side of the humerus has the Coronoid Fossa (a shallower indentation, distal end) SHOULDER JOINT BONE ARTICULATIONS: Proximal humerus, scapula, clavicle The Head (rounded end) of the humerus articulates with the Glenoid cavity/fossa of the scapula The Acromial End of the clavicle is rounded and articulates with the acromion of the scapula The Sternal End of the clavicle is blunt and articulates with the manubrium of the sternum LIGAMENTS Acromioclavicular o Acromion of scapula to clavicle Coracoacromial o Coracoid process of scapula to acromion of scapula Coracoclavicular (aka Trapezoid ligament) o Coracoid process of scapula to clavicle Coracohumeral (not on model) o Coracoid process of scapula to humerus Glenohumeral (aka articular capsule ligament) o Ridge around glenoid cavity of scapula to humerus ELBOW JOINT Proximal Ulna Proximal Radius BONE ARTICULATIONS: Distal humerus, proximal radius & ulna Coronoid process of ulna articulates with coronoid fossa of humerus Olecranon process of ulna articulates with olecranon fossa of humerus Trochlear notch of ulna articulates with trochlea of humerus Articular surface of head of radius articulates with capitulum of humerus o Remember – ‘cap on head’ Radial notch of ulna articulates with side of head of radius Radial tuberosity on radius – bump just distal to head for muscle attachment WRIST & HAND Distal Radius & Ulna Each bone has a Styloid process (pointy projection – styloid = like a pen) on the lateral distal end Carpals Wrist bones You do NOT need to name them Metacarpals 5 bones of palm (I, II, III, IV, V) I is thumb side, V is pinky side Phalanges I-V same as metacarpals Proximal – closest to palm Middle – intermediate Distal – ends PELVIC BONE – ORIENTATION Each pelvic bone is made up of 3 bones: Ilium – large wing-like portion Ischium – part you sit on Pubis – front projection, forms pubic symphysis with other pelvic bone KEY LANDMARKS – use these to orient the bone into anatomical position Obturator Foramen – large hole surrounded by Ischium & Pubis Acetabulum – bowl depression (lateral) for articulation with head of femur Greater Sciatic Notch – large indent on posterior side Rough patch on Ilium is anterior, articulates with sacrum Once oriented, you can find… Anterior superior iliac spine Anterior inferior iliac spine Posterior superior iliac spine Posterior inferior iliac spine Ischial spine – bump on ischium, inferior to greater sciatic notch Iliac crest – superior ridge of ilium Ramus – bone around obturator foramen (pubis and ischium) FEMUR – ORIENTATION The medial side of the femur has the head (rounded projection, on narrower neck) and lesser trochanter (bump) on the proximal end and the medial condyle (rounded end) and epicondyle (medial bump) on the distal end The lateral side of the femur has the greater trochanter (bump) on the proximal end and the lateral condyle (rounded end) and epicondyle (lateral bump) on the distal end The intertrochanteric crest is a ridge that connects the trochanters (proximal, posterior) The intercondylar groove is the indent between the condyles (distal) Linea aspera is a rough surface along the shaft of the femur (posterior) KNEE JOINT Proximal Tibia BONE ARTICULATIONS: Distal femur, Proximal tibia & fibula The medial condyles of the femur and tibia articulate with each other The lateral condyles of the femur and tibia articulate with each other The intercondylar eminence on the tibia slides between the intercondylar groove on the femur The tibia is the medial bone of the lower leg The head of the fibula is on the lateral side of the knee joint LIGAMENTS, etc. Lateral (fibular) collateral o Lateral epicondyle of femur to head of fibula Medial (tibial) collateral o Medial epicondyle of femur to medial tibia Anterior Cruciate (ACL) o Inside of lateral condyle of femur to intercondylar eminence of tibia Posterior Cruciate (PCL) o Inside of medial condyle of femur to intercondylar eminence of tibia Patellar o Tendon of Quadriceps (anterior thigh) muscle group passes over patella to tibial tuberosity of tibia Popliteal ligaments not shown on model Medial & Lateral meniscus o Connective tissue pads between femur and tibia ANKLE & FOOT Distal Tibia & Fibula Medial malleolus – ankle bump on medial tibia Lateral malleolus – ankle bump on lateral fibula Distal tibia surface articulates with Talus (a tarsal/ankle bone) Tarsals Ankle bones Talus – articulates with Tibia Calcaneus – heel Metatarsals Foot bones (I, II, III, IV, V) I is big toe side, V is pinky side Phalanges I-V same as metatarsals Proximal – closest to foot Middle – intermediate Distal – ends