* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download angle modulation
Transmission line loudspeaker wikipedia , lookup
Spectral density wikipedia , lookup
Chirp compression wikipedia , lookup
Spectrum analyzer wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Electronic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Utility frequency wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Chirp spectrum wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
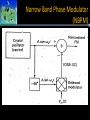
ANGLE MODULATION Angle Modulation • Introduction • Types of Angle Modulation – FM & PM • Definition – FM & PM • Signal Representation of FM & PM • Generation of PM using FM • Generation of FM using PM Angle Modulation Consider again the general carrier vc t = Vc cosωct + φc ωc t + φc represents the angle of the carrier. There are two ways of varying the angle of the carrier. a) By varying the frequency, c – Frequency Modulation. b) By varying the phase, c – Phase Modulation Frequency Modulation Phase Modulation • One of the properties of a sinusoidal wave is its phase, the offset from a reference time at which the sine wave begins. • We use the term phase shift to characterize such changes. • If phase changes after cycle k, the next sinusoidal wave will start slightly later than the time at which cycle k completes. Introduction to Angle Modulation • High degree of noise immunity by bandwidth expansion. • They are widely used in high-fidelity music broadcasting. • They are of constant envelope, which is beneficial when amplified by nonlinear amplifiers. Introduction to Angle Modulation FM and PM FREQUENCY MODULATION Frequency Modulation (FM) • Types of FM • Spectrum of FM • Transmission Bandwidth of FM • Deviation Ratio • Generation of FM • Detection of FM • Signal to Noise Ratio of FM • Pre-Emphasis & De-Emphasis in FM Types of FM • Basically 2 types of FM: – NBFM (Narrow Band Frequency Modulation) – WBFM (Wide Band Frequency Modulation) NBFM • Derivation • Difference between NBFM & AM DSB FC • Generation of NBFM WBFM • Generating WBFM from NBFM • Derivation – Bessel Function Spectrum of FM Transmission Bandwidth of FM Carson’s Rule Deviation Ratio Power in FM Generation of FM • Mainly there are 2 methods to generate FM Signal. They are: 1. Direct Method 1. Hartley Oscillator 2. Basic Reactance Modulator 2. Indirect Method 1. Amstrong Modulator (Using NB Phase Modulator) 2. Frequency Multiplier Generation of FM • Basically two methods: 1. Direct method • Build a voltage controlled oscillator (VCO) where the frequency is varied in response to an applied modulating voltage by using a voltage-variable capacitor • The main difficulty is that it is very difficult to maintain the stability of the carrier frequency of the VCO when used to generate wide-band FM. 2. Indirect method • Use a narrow-band FM modulator followed by frequency multiplier and mixer for up conversion. • Allows to decouple the problem of carrier frequency stability from the FM modulation. Edwin Howard Armstrong (1890 - †1954) Edwin Howard Armstrong received his engineering degree in 1913 at the Columbia University. He was the inventor of the following basic electronic circuits underlying all modern radio, radar, and television: Regenerative Circuit (1912) Superheterodyne Circuit (1918) Superregenerative Circuit (1922) FM System (1933). Indirect Method – Amstrong Modulator Indirect Method Narrow Band Phase Modulator (NBPM) Detection of FM • Types of FM Detectors: 1. 2. 3. 4. RL Discriminator Tuned FM Discriminator Balanced Slope Detector Centre Tuned Discriminator / Phase Discriminator / Foster – Seeley Discriminator 5. Phase Locked Loop (PLL) Demodulator 6. Ratio Detector RL Discriminator Signal to Noise Ratio of FM • Introduction to Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR) • Noise in FM – Capture Effect – FM Threshold Effect – FM Threshold Reduction – Pre-Emphasis & De-Emphasis in FM