* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ME 3-3 Notes Combined
Indoor air pollution in developing nations wikipedia , lookup
Energy development wikipedia , lookup
William Flynn Martin wikipedia , lookup
Efficient energy use wikipedia , lookup
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Australia wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
Environmental impact of electricity generation wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
United States energy law wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in British housing wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
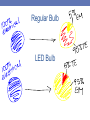
Efficiency- packet pg 37 • Efficiency- A measurement of useable energy after an energy conversion • The more efficient the conversion, the less energy is wasted • Wasted energy is energy that becomes energy forms other than the intended form Energy Efficiency Example • Regular light bulbs convert electrical energy into thermal and electromagnetic energy • Do we intend to create thermal energy? NO! • Some energy is converted to thermal though, and that is less energy that can be converted to electromagnetic energy (light!) Regular Bulb LED Bulb So which is more efficient: An LED bulb or a regular bulb? • The LED bulb • LED bulbs convert more electrical energy to electromagnetic energy • They do not “waste” as much electrical energy • Less thermal energy is created as a byproduct The Law of Conservation of Energy • A law stating that no matter how energy is transferred or transformed, it continues to exist in one form or another • In other words: • Energy is not created or destroyed, just changed from form to form ME SECTION 3.3 NOTES Handout Technology Improves Energy Conversions • In many energy conversions, energy is wasted as heat • For example: • In a “regular” light bulb, only about 5% of the electrical energy becomes electromagnetic energy Efficient Lights • LED: Light Emitting Diode • Converts almost all of the electrical energy to light energy • Used in: • Remotes, computers, signs, traffic signals, etc Efficient Cars • Burning gasoline in cars converts chemical energy into kinetic energy (mechanical, sound, thermal) • Some energy is wasted as heat from the car’s engine, tires, and breaks • Improvements have been made to increase efficiency in cars • Fuel injectors and hybrid cars both have increased the amount of kinetic energy going into the car and not into unwanted energy (like thermal energy Technology Improves the Use of Energy Resources • Much of our energy comes from fossil fuels, but these are non-renewable resources • Scientists are exploring many alternative energy sources • For example: solar energy and wind energy Solar Energy • Solar cells are used to trap electromagnetic energy from the sun and convert it to electrical energy • Solar cells produce electrical energy quietly and cleanly • The sun’s radiation (electromagnetic energy) is also used for heating (thermal energy) Wind Energy • Windmills are used to trap the kinetic energy from the wind and convert it into electrical energy Lincoln Financial Field • The combined energy created by the solar panels and wind turbines is more than 4 times the amount used during one season’s home games Energy Efficiency • Technology has improved efficiency but… Nothing is 100% energy efficient! There will always be some unwanted energy Energy Conversions and Fossil Fuels- packet pg 38 Where does earth get most of it’s energy from? 1. The sun is the major source of energy for most of Earth’s processes The Sun’s Nuclear Energy 2. On the sun, hydrogen atoms join and form helium- this process is called nuclear fusion -Electromagnetic energy is given off 3. Some of this (electromagnetic) energy reaches Earth Then what? 4. Photosynthesis then begins on earth. Plants grow, animals eat the plants. 5. When plants and animals die, dirt (sediment) slowly covers them. The energy in them is now stored and trapped within them 6. The resulting pressure along with high temperatures turns the animal and plant remains into coal (a fossil fuel!) Fossil Fuels 1. Include things like: • Coal • Petroleum • Natural gas What is fuel? 2. Fuel is a material that stores chemical potential energy • Chemical potential energy depends on… Think back…. To the Law of Conservation of Energy • Energy cannot be created or destroyed • It changes form • So where does the energy in fossil fuels come from? Energy in fossil fuels comes from… • The sun! 4. Fossil fuels can be burned to release the chemical potential energy. • (steam and heat turn turbines to produce electricity) 5. Burning fossil fuels is a process known as combustion • The (electromagnetic) energy from the sun grew the plants which provided (chemical) energy to animals. When they died they were covered in soil and compressed, forming coal and oil (chemical energy). We burn the coal (or other fossil fuels) to create other forms of energy! Energy! Problem! • Fossil fuels are non-renewable resources! • They take millions of years to form!