* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ppt
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Propaganda in the Soviet Union wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Appeasement wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Forced labor of Germans in the Soviet Union wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
German–Soviet Axis talks wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of the Winter War wikipedia , lookup
World War II casualties wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
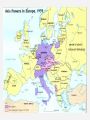
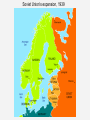
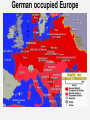
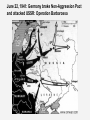
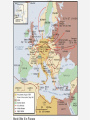
The Great Patriotic War, 1941-45 PRINCIPAL BELLIGERENTS: • Axis powers: Germany Italy Japan • Allies: British Empire United States Soviet Union France China Soviet Foreign Policy, 1934-1938 • Comintern, 1919-1943 • 1933: USA recognized USSR • W. Bullitt, US ambassador • Collective Security, 1934-1937 – Maxim M. Litvinov (1876-1951) • Narkom Foreign Affairs, 1930-38 • Jew, anti-Nazi, pro-West • Sept. 1934: USSR joined League of Nations • May 1935: France and USSR sign pact • USSR pledged to help Czechoslovakia, if France first. – March 1936: Germany remilitarized Rhineland – 1936: Germany, Italy, Japan form anti-Comintern pact Spanish Civil War, 1936-1939 • Germany and Italy supported Francisco Franco, Nationalists’ leader • West proclaimed non-intervention, but many leftists volunteered. • USSR supported Popular Front government (lost). • Seen as dress rehearsal for eastern war Appeasement and Aggression • March 1938: Anschluss (“joining”) • Austrians warmly greeted Hitler • 1938-39: Appeasement: Neville Chamberlain • Sept. 1938: Munich Agreement • Britain, France, Italy, Germany signed. • Czechoslovakia and USSR not invited. • Stalin realized West powerless or worse. Outbreak of war, 1939 • March 1939: Germany occupied Czechoslovakia • May 1939: Stalin replaced Litvinov with V. Molotov • August 23, 1939: German-Soviet Nonaggression Pact (10 years) – Secret protocol divided EE • Sept. 1, 1939: Germany invades Poland • Sept. 3, 1939: Britain and France declare war on Germany • Sept. 17, 1939: Soviet Union attacked Poland • Soviet Union imposed control over Lithuania, Estonia and Latvia • Nov. 1939-March 1940: Soviet-Finnish War or the Winter War Katyn massacre, April-May 1940 • 25,700 Polish POWs killed, 4400 at Katyn. • Germans discovered graves 1943. • NKVD Lavrenti Beria’s idea • Stalin signed • Only in 1990 admitted. Soviet Union’s expansion, 1939 Blitzkrieg: "Lightening War" • • • • • Panzer Divisions Armored vehicles motorcycles Planes Concentrated attack Blitzkrieg (cont.) • Germans quickly took France (occupied Paris on June 14, 1940) • June 22, 1940, at Rethondes (the scene of the signing of the Armistice of 1918) Franco-German Armistice was signed • Vichy France created: General HenriPhilippe Petain became head of state German occupied Europe German-Soviet War, 1941-45 • • • • Mein Kampf (My Struggle) Lebensraum (Living space) Slavs - “subhumans” Poor Soviet Army performance in “Winter war” with Finland • Possibility of Soviet attack • Hitler: “We have only to kick in the door and the whole rotten structure will come crashing down!” June 22, 1941: Germany broke Non-Aggression Pact and attacked USSR: Operation Barbarossa Numbers on the eastern front Axis powers USSR 3.9 million Troops 3.2 million (later 5 million) Troops 3600 Tanks 12-15,000 Tanks 4839 Aircrafts 11,357 (later 3540,000) Aircrafts 250,000 Killed 802,191 Killed 500,000 Wounded 3,000,000 Wounded 3,300,000 Captured Casualties 2093 Aircraft destroyed 21,200 Aircraft destroyed 2758 Tanks lost 20,500 Tanks lost The Holocaust, 1941-45 “The Final Solution” • Until 1941, Hitler and Nazis did not agree on what to do with Jews • Emigration • Madagascar • TURNING POINT: June 1941, Operation Barbarossa • Einsatzgruppen: “Mobile Killing Groups” or “Single-task groups” • • • • Jews Communists Gypsies Poles Einsatzgruppen, 1941-42 Final Solution (cont.) • The ghettos were already sealed (1940) • Poison gas vans tested the use of gas • Auschwitz-Birkenau • Systematic annihilation of Jews and Gypsies • 1942–1944: one million killed • Anonymous slaughter • People were tortured, beaten, and executed publicly jews arrested warsaw_HU007442.jpg Map_26.06.jpg Map_26.07.jpg Overall human costs • 5.1-6.0 million Jews – 800,000 in Ghettos – 1,400,000 in open-air shootings – 2,900,000 in camps • • • • • 1.8 -1.9 million Poles 200,000-800,000 Roma & Sinti 200,000-300,000 people with disabilities 10,000-25,000 gay men 2,000 Jehovah's Witnesses pearl harbor_NA006444.jpg US enters the war • December 7, 1941: Japanese attacked Pearl Harbor • 2.5 hours later, Japanese officially declared war on the United States and Britain • Dec. 8: US Congress declared that a state of war had existed since December 7 • Dec. 9: China declared war on Japan, Germany, and Italy • Dec. 11: Germany and Italy declared war on the United States, and the US Congress voted declarations in return The Grand Alliance • BIG THREE: – Great Britain: Winston Churchill – USA: F.D. Roosevelt – USSR: Josef Stalin • Keys to victory: Agreed to: – Europe first (Hitler - greatest evil) – Postpone politics (capitalism vs. communism) – Unconditional surrender (no 1918!) yalta conf erence_BE001058.jpg But war in the east was decisive • Battle of Stalingrad: summer 1942February 2, 1943 • Hitler wanted to take the city. Why? Named after Stalin Important port on Volga river But distraction from oil reserves Battle of Stalingrad: summer 1942February 2, 1943 • • • • • • Axis powers advanced (General F. Paulus) Soviets held on Axis supplies started running out Winter came Panzer tanks useless in street fighting Soviets counterattacked (pincer movement) • Surrounded Axis forces Stalingrad: Street-to-street fighting Stalingrad • Feb. 2, 1943: Paulus surrendered (ignored Hitler) • Total Axis losses (Germans, Romanians, Italians, and Hungarians): 800,000 dead • Soviet soldiers: 1,100,000 dead • But turned the tide of the war June 6, 1944: D-Day: Battle of Normandy • Long period of preparation and planning • Largest amphibious landing in history • Five beaches: Utah Gold Juno Sword “Bloody” Omaha Significance: opened up a large second front d-day omaha beach_NA007140.jpg Yalta Conference, Feb. 1945 • Big Three • Key issue: Poland – London Poles (pre-WWII govt.) – Lublin Poles (communists) • Sovietization • Big Three agreed on “interim governmental authorities broadly representative of all democratic elements in the population . . . and the earliest possible establishment through free elections of governments responsive to the will of the people.” yalta conf erence_BE001058.jpg ENDGAME • April 25, 1945: Soviet Army first to reach Berlin • April 30: Hitler and Eva Braun committed suicide • May 8, 1945: Victory in Europe!! • War in Europe ended soviet flag over reichstag_YK004440.jpg Potsdam Conference, summer 1945 • USA: Harry S Truman • USSR: J. Stalin • Great Britain: W. Churchill, then Clement Atlee • Solved nothing • Showed sides in emerging Cold War • Truman told Stalin about the bomb End of War with Japan • August 6, 1945: Hiroshima • Killed 70,000-90,000 people, injuring another 70,000 • August 9: Nagasaki • Killed 60,000-75,000 and injured about the same number hiroshima bombed_BE042948.jpg August 14, 1945: Japan surrendered • Total deaths: • Civilians’ deaths: 40 to 52 million, including 13 to 20 million from warrelated disease and famine. • Soldiers’ deaths: 22 to 25 million, including deaths in captivity of about 5 million prisoners of war.