* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download World War II - SJS AP World History
German military administration in occupied France during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Forced labor of Germans in the Soviet Union wikipedia , lookup
Nazi views on Catholicism wikipedia , lookup
Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
German–Soviet Axis talks wikipedia , lookup
Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere wikipedia , lookup
India in World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Appeasement wikipedia , lookup
European theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
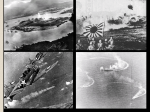
WORLD WAR II World War II – Big Picture In contrast to the disorganized beginning of World War I, World War II was provoked by deliberate aggressions of Germany, Japan, and Italy. The failures of the Western policy of appeasement encouraged the Axis Powers’ militaristic expansions. The most deadly conflict in history, World War II, resulted in the rise of the United States and the Soviet Union to world supremacy and competition. Western European hegemony came to an end. Independence movements in Africa and Asia succeeded in the decades after the war. WWII Era Timeline Causes of World War II Officially started in 1939 after decade of aggression Grievances from World War I’s aftermath Economic havoc resulted in militarist responses from Japan, Germany and Italy. Japan attacked Manchuria (Mukden Incident) in 1931; little response from politicians in the West Japan had gradual militarism while Germany’s was abrupt ○ Adolf Hitler promised to restore Germany’s once- impressive economic and military place in Europe and to eliminate the Communist threat within its borders. In alliance with Italy, Germany assisted the fascist takeover of Spain Old and New Causes of WWII China vs. Japan China looking stronger - Chiang Kai-shek uniting/defeating warlords Nationalist (Guomindang) party pose a threat to Japan’s ambitions Afraid Chinese would retake Manchuria By the late 1930s interaction between the new totalitarian states of Germany, Italy, and Japan and Western democracies. Unchecked aggression led to yet more aggression. ○ This lesson was taught most clearly at Munich. Aggression of Axis powers went unchecked – appeasement why? Failure to unite… Nationalism plus Red Scare of Soviets prevented early alliance Each government disagreement on how to respond Some actually felt guilty about Versailles League of Nations a failure Italy & Japan merely left the League after censured Axis/Fascist leaders laughed at treaties Methods of delaying intervention of enemy Old and New Causes of WWII Germany - Weimar Republic weak - blamed for Versailles Great Depression made life look worse Adolf Hitler takes advantage through the political and ideological leader of the National Socialist Party. Nazis made a ton of promises ○ Put German people back to work ○ Ignore orders of Versailles ○ Turn back Communist push ○ Enslave Slavic peoples Unchecked Aggression in Europe & Pacific US, Britain, France appeasement of Hitler Sacrifice small nations to protect themselves Fear of another world war Want to focus on welfare states, not military states Japan first to attack - invaded China from Manchukuo Japanese moderate political leaders silenced ○ Fear of assassination from military officers Rape of Nanjing(Nanking) - horrific treatment of Chinese civilians - 1937 ○ Symbolic beginning of horrific war of suffering Japan and China in war for Asia far before 1941 Unchecked Aggression in Europe & Pacific Japan, Germany, Italy did not coordinate attacks Germany needs to attack Soviet Union – wrote in Mein Kampf “lebensraum” living space Signs Non-Aggression Agreement with Soviets ○ Buys time, splits Poland, Later invades USSR from Poland British/France declare war once Poland is attacked Prepared for another trench warfare, unfortunately Hitler doesn't play fair Main Theaters of World War II Philippe Petain Blitzkrieg, Hitler’s Strategy Hitler's victories stunningly fast West's reluctance to arm/react decisively War shifts once Germans get stuck in Russian winter Anglo-American, Soviet alliance has more #s, industry, technology Nazi Blitzkrieg, Stalemate, and the Long Retreat Blitzkrieg - lightning fast war Coordinate tanks, mechanized troop carriers, fighter aircraft/bombers Penetrate deep into nation - hit capital hard Severely punished civilian population that didn't surrender In months, French defeated, British pushed back across the Channel ○ Phony War before France….Sitzkrieg Sep 39-May 40 Why did France lose so quickly? Gov't couldn't agree on what to do - left vs. right argued Weapons painfully outdated Civilian population demoralized Only the French capital of Vichy in South exists – A puppet government of the Nazisʹ regime The Conduct of a Second Global War Battle of Britain - holds off Hitler Strong leadership of Churchill/war cabinet Radar detection discovered Nazi flight plans Bravery of Britain's Royal Family High morale of citizens Efficient use of their Air Force Land invasion called off, can't fight off British Navy But Germany had taken over W. Europe, Scandinavia, Mediterranean, N. Africa Conquered areas must provide ○ War materials, soldiers, slave labor Hitler turns on USSR Soviets easily pushed out of Finland, Poland, Baltic states, but then winter Soviets don’t surrender – “body for bullet?” Just kept retreating eastward Nazi mass killings inspire guerilla warfare behind front lines Stopped at Moscow, Leningrad, Stalingrad Fought most severe battles - Stalingrad Momentum shifts - Germany on the run 1943 Soviets push west, 1944 on doorstep of Berlin Sacrifices of Soviet soldiers/women/civilians led to victory Operation Barbarossa Hitler's War Against the Jews First years of war Hitler persecuted non-Aryans Gypsies, leftist politicians, homosexuals, Jews, Polish intellectuals, communists, especially after invading Poland & Soviet Union Once war seemed lost, and on defensive “Final solution" - Wannsee Conference - 1942 - extermination camps Resources from front used or transportation, imprisonment, mass murder Shipped from all over empire to the East ○ ○ Physically fit > hard labor Women, children, ill - murdered immediately Used for scientific experiments Holocaust - 12 million killed, 6 million (50%) of them Jews Armenian genocide the root Horrific - premeditated, systematic, carried out by the state Essentially allowed by occupied countries Only really Danish & Italians resisted in any degree Allied countries refused Jewish emigrants/refugees ○ Also didn't attack railway lines or extermination camps Effect - creation of Zionist state in Israel Emigration to Palestine only option Some even made deals with Nazis to take to Palestine Anglo-American Offensives Europe American interaction Primarily supplies at first - US gov't hesitant, Roosevelt sympathetic Pearl Harbor December 7, 1941 - US enters Tank divisions and infantry join in Africa Next attacked Sicily, Italy Eventually Mussolini toppled, assassinated June 1944, Western front - invasion of Normandy Moved East to Germany, Stopped only briefly Dec 1944, at the Hitler’s last ditch effort at the “Battle of the Bulge” Hitler desperate attempt to force ending with V-1/V-2 Rockets By June 1945 US and Soviets divisive over how to divide Germany Hitler kills himself - goes down believing he was betrayed by German people The Rise and Fall of the Japanese Empire in the Pacific 1/3 of Japanese forces fight in China throughout war After Pearl Harbor, Japan takes over Asia Thailand becomes neutral, cooperates Australia and New Zealand provide support But...US on its own Took over too much, angered all of the European Allies Colonial regimes worse than European Needed natural resources, raw materials Led to resistance movements - requires even more soldiers/resources ○ ○ Main theaters of conflict islands - "island hopping“ Victories at Battle of the Coral Sea and Midway Island Joint air, sea, land assaults against Japan 1944 America begins firebombing Japanese cities ○ Guerrilla forces harassed Japanese Coordinated w/ Americans and British Destroyed wooden homes, hundreds of thousands of civilians killed Demanded unconditional surrender Atomic bombs - August 1945 ○ Threat that Japanese would fight to the death War's End & Emergence of the Superpower Standoff Wanted to avoid failed peace treaties of World War I and the results of WWII: The most destructive war in history 22 million military 34 million civilians Established United Nations More representative of world than League of Nations ○ U.S. participates Security Council made up of victors - US, France, Britain, China, USSR Though China is really represented by Taiwan, communist gov't not acknowledged Colonies and defeated powers granted membership Europe retained control of post-war global policy through 3 votes on security council Forum for negotiating international disputes World Court of Justice Human Rights organizations - food, labor, women Unsuccessful at times - large and small nations resent role ○ But...played important role in humanitarian, refugee relief Sponsored conferences to deal with social issues Child labor, women's rights, environmental protection Hot War to Cold War USSR vs. USA - no direct conflict, but tons of related global conflicts Began with how to decide post-war Europe USSR wanted territorial gains - tired of getting invaded Tehran Conference - 1944 By setting up Western front in France, USSR takes over Eastern Europe USSR doesn't pull out of many occupied lands - Iron Curtain Doesn't allow nations to "self-determine" themselves Yalta Conference – Feb.1945 (Big 3, Churchill, Roosevelt, & Stalin) Roosevelt dies April USSR gets Manchuria and northern Japanese islands Divide Germany into 4 spheres of influence Germany industry allowed to continue - needed to control Soviets USSR wants friendly gov'ts in small European nations West wants democratic gov'ts Stalin lies Yalta: Churchill, Roosevelt, & Stalin Hot War to Cold War Problems still after Potsdam Conference, July 1945 Austria divided, occupied then independent in 1956 Poland gain East Germany, but lost land to Russia USSR/USA sign separate treaties with Japan German peace treaty not even agreed upon ‘til 80s Clement Attlee, Harry Korea divided between USSR and USA Truman & Joseph Stalin European colonies returned to Europeans But...independence movements start right away China war starts Soviets aid communists US aids Nationalists Independence movements Middle East, Africa, India want independence ○ Europe fought nationalism during war, but had to revisit after Soviet Union pushes boundaries West New independent nations created in 1918 gobbled up by USSR US heavily influenced W. Europe Occupied troops, economic aid (Marshall Plan), policy manipulation Two movements roots Occupied people push for independence/decolonization World's allegiances divided between US and USSR Nationalism & Decolonization No more illusions of European dominance Destroyed by Nazis and Japanese Japanese victories over Europeans destroyed myth Pearl Harbor, Singapore, Philippines "death marches" of Europeans, Americans Harsh rule of Japanese inspired nationalism - want to control own fate Harsh total war sapped European desire to maintain empires U.S. propagandizes notion of anti-colonialism (Guam?) Atlantic Charter of 1941 Roosevelt and Stalin persuaded Churchill to sign clause ○ Recognize "right of all people to choice the form of government" The Winning of Independence in South and Southeast Asia Indian National Congress demands independence in exchange for fighting Sir Stafford Cripps sent to India to get a deal, doesn't work Quit India movement - civil disobedience campaigns 1942 ○ Gandhi, Nehru thrown in jail- 2years! British have backing of Communists and Muslim League ○ ○ Muslim League - Muhammad Ali Jinnah - wartime support British like him, he wants separate Muslim India Nehru & Gandhi Changes after World War II Churchill loses 1945 election Labor Party ready to deal 1945-1947 - what type of India? ○ Muslims propagandize that Hindu dominated India would persecute Muslims Created Pakistan in northwest and east India Communal rioting spreads across nation To avoid civil war, Pakistan and India gain independence in 1947 Summer of violence - Hindu-Muslim and Muslim-Sikh violence ○ Led to massive refugee movement - moving to safe area India and civil disobedience inspired independence movements across globe French and American empires start to fall ○ Filipino independence comes after help during WWII, 1946 ○ Dutch Indonesia 1949 (New Guinea 1962) ○ French fight to keep colonies, Vietnam 1954. (Most Africa 1960) Liberation of Non-settler Africa Africa more dramatically affected by WWII Forced labor, Confiscation of crops/minerals Inflation/controlled markets > less money for Africans More chances to kill Europeans with European weapons Fight for freedom, return to oppression France controlled by Nazis and Vichy French (Confusion) Change in colonial policy Industrialization created in colony Rapid urbanization to take advantage of work ○ But…few jobs…millions of angry people living together Paths to independence Kwamee Nkrumah – radical African leader – British Gold Coast Establishes Convention People’s Party ○ Mass rallies, boycotts, strikes ○ Doesn’t back down regardless of threats, imprisonment By 1957, Ghana created – after decade of gradual concessions Peaceful devolution of power ○ Worked with French, tired of fighting, maintaining colonies ○ France gradually pulls out and leaves moderate leaders in place Belgian get out and run plan (1960 Congo [Zaire] & 1962 of Rwanda and Burundi) ○ No western educated elite to lead – 16 college graduates/13 million chaos Map Exercise The Struggle for the Settler Colonies Gradual withdrawal tough in settler colonies – Europeans live there Blocked nationalistic movements and concessions on part of overlords Fought attempts to turn power over African leaders forced to turn to violent, revolutionary struggles Kenya – Land Freedom Army – 1950s – guerilla warfare against British British react with violence Kenyatta forms Kenya in 1963 – British tired of fighting Algeria – French – National Liberation Front French fight back – make up for defeat in Vietnam After years of fighting Charles de Gaulle & France want to get out Huge financial drain on country ○ Secret Army Organization ○ Eventually Parisian gov’t overthrown – end of 4th Republic Settlers + Algerian sympathizers have to move to France ○ Too much hatred violence between them White Supremacy in South Africa Why did South Africa remain white dominated? Larger white settler population – Afrikaners + British Afrikaners have no nation to return to – two centuries in S. Africa White racist supremacy ideology British made concessions to Afrikaners – felt guilty after Boer War Afrikaner racism elaborate and explicit – written, detailed Gave political control to Afrikaners Afrikaner National Party Independence from Britain Establish lasting white domination Apartheid (separateness) 1948-1994 Thousands of laws to separate Best jobs for whites Africans/colored denied vote/political representation Limited educational opportunities Vigilant/brutal police force to enforce Kept populations geographically separated Nelson Mandela, anti-apartheid activist 27 years in prison until 1990 Became President of Democratic South Africa Arabs, Israelis, and the Palestinians Egypt, Syria, Iraq gained independence during Interwar Period Others all liberated by 1960s, but… Palestine because… Zionist movement gains momentum due to Holocaust International sympathy US/Britain reluctant to accept Jews Palestinian violence forces British to try and slow immigration Jews/Zionists create military – Haganah to fight British too… Deadly stalemate ○ ○ ○ Zionists want independent Jewish nation Palestinians want multi-religious nation w/ Palestinians dominating Britain just wants to get out of unsolvable situation (1947) United Nations suggests partition May 14, 1948 – Israel recognized, but all out war starts next day 1948 Arab-Israeli War - Egypt, Syria, Jordan, Lebanon and Iraq— attack (Later: Sudan, Yemen and Saudi Arabia) Jews win – 1) better weapons, 2) better prepared Led to thousands of Palestinian Arab refugees The Partition of Palestine After World War II Global Connections Were there really revolutions? Or merely transfer of power from one elite group to another w/ new nation name attached ○ Western-educated African and Asian classes merely took over Both jobs and homes ○ For the most part big landholders kept land and didn’t redistribute Exceptions – Algeria, Kenya, Zimbabwe Culturally kept many Western ideas ○ Western sciences now taught ○ Administration often conducted in English Western dominance of trade maintained ○ One of criteria for independence was protection of existing merchants/traders