* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Circulatory System
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
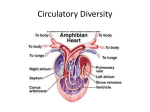
Circulatory System By: Bailey Berry Erin Parrott Circulatory System… • Moves blood to a site where it can be deoxygenated and decomposed of • Newly oxygenated blood moves to the tissue of the body Evolution of the Circulatory System • The first organisms with a simple circulatory system including tissue that helped pump the fluid were protostomes in the Lophotrochozoa • Around the Cambrian, 600 million years ago Open Circulatory System • The blood diffuses through cells • Blood does not stay in veins or vessels • Common in mollusks and arthropods (Just like Robbie!) Closed Circulatory System • The blood is within vessels of different size and thickness at all times • Is pumped by a heart through vessels (Just like Gillbert!) Evolution in the Closed System Annelids (Simplest) -Two main blood vessels (dorsal and ventral) -5 pairs of vessels (“hearts”) that connect them Vertebrates (Complex) -Animals like fish have two chambered hearts -Animals like frogs have three chambered hearts -Humans has four chambered hearts Vertebrates- Two Chambered Heart – Has an atrium and one ventricle – Muscular walls – Valve between the chambers – Blood pumps through heart then out to other organs Vertebrates- Three Chambered Heart • Two atria and on ventricle • Blood goes through a forked aorta, which leads to the lungs and other organs • Both atria empty into the ventricle Vertebrates- Four Chambered Heart • Two atria and two ventricles • Blood pumped into first atrium and oxygenized in the lungs • Then pumped through second atria and fed through second ventricle into body for use Mammalian Double Circulation • Type of blood circulation where blood flows through heart twice. • The pulmonary and systemic circulation system. Pulmonary Circulatory Systemic Circulatory • The circulation of blood through the lungs • Carries deoxygenated blood away from the heart and to the lungs • Returns from the lungs back to the heart with oxygenated blood • The circulation of blood from the heart to the body • Carries oxygenated blood away from the heart to the rest of the body • Returns to the heart with deoxygenated blood http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/118377/circulati on/33722/Embryonic-development-of-the-circulatorysystem Lymphatic System • Consists of organs, ducts, and nodes • Transports lymph • Maintains fluid balance • Absorbs lipids and transports them to the blood Disorders • Hypertension: High blood pressure • Arteriosclerosis: thickening, hardening, and loss of elasticity of the walls of the blood vessels • Rheumatic fever: systemic inflammatory disease Special Thanks To… "Closed and Open Circulatory System." Welcome to Georgia State University. Web. 04 Apr. 2011. "Double Circulation - Definition from Biology-Online.org." Life Science Reference Biology Online. Web. 05 Apr. 2011. "Evolution: Evolutionary Origin of Heart, Ucmp Berkeley, Primitive Hearts." AllExperts Questions & Answers. Web. 11 Apr. 2011. "Hemocoel - Definition of Hemocoel by the Free Online Dictionary, Thesaurus and Encyclopedia." Dictionary, Encyclopedia and Thesaurus - The Free Dictionary. Web. 04 Apr. 2011. "Lymphatic System." Patients Against Lymphoma - Lymphomation.org. Web. 05 Apr. 2011. "Rheumatic Fever — Infoplease.com." Infoplease: Encyclopedia, Almanac, Atlas, Biographies, Dictionary, Thesaurus. Free Online Reference, Research & Homework Help. — Infoplease.com. Web. 11 Apr. 2011. "The Vertebrate Animal Heart: Unevolvable, Whether Primitive or Complex." Intelligent Design and Evolution Awareness Center. Web. 05 Apr. 2011.