* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 14 - B-K
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
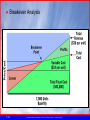
Marketing Management Chapter 14 - 2 Promotion and Pricing Strategies 1-1 Copyright © 2005 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. All rights reserved. Personal Selling ● Recent Trends in Personal Selling – Telemarketing Outbound telemarketing— calls you at your place of business Inbound telemarketing— customer calls a toll-free phone number – Relationship Selling—when a salesperson builds a mutually beneficial relationship with a customer – Consultative selling—meeting customers’ needs by listening to them, understanding and caring about their problems, paying attention to details, suggesting solutions, and following through after the sale – Team selling—joins salespeople with specialists from other functional areas of the firm to complete the selling process – Sales force automation (SFA)— uses a broad range of tools, from e-mail, telecommunications devices like pagers and cell phones, and laptop computers that automate the sales process 1-2 Copyright © 2005 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. All rights reserved. Public Relations ● Public Relations—organization’s communication and relationships with its various audiences. ● Publicity—stimulation of demand for a good, service, place, idea, person, or organization by disseminating news or obtaining favorable unpaid media presentations. 1-3 Copyright © 2005 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. All rights reserved. Promotional Strategies ● Selecting a Promotional Mix – Guidelines for allocating promotional efforts and expenditures among personal selling and advertising: What is your target market? What is the value of the product? What time frame is involved? 1-4 Copyright © 2005 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. All rights reserved. Promotional Strategies ● Pushing and Pulling Strategies – Push strategy—intended to stimulate personal selling of the good or service, thereby pushing it through the channel Cooperative advertising – Pull strategy—stimulate demand among final users, who will then exert pressure on the distribution channel to carry the good or service 1-5 Copyright © 2005 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. All rights reserved. Ethics in Promotion ● Puffery and Deception – Puffery—exaggerated claims of a product’s superiority or use of doubtful, subjective, or vague statements – Other promotional elements can also involve deception Salespeople have deceived customers with misleading information 1-6 Copyright © 2005 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. All rights reserved. Ethics in Promotion ● Promotion to Children and Teens – Risk of deception is especially great with promotion targeted to children and teens – Children not sophisticated at analyzing promotional messages 1-7 Copyright © 2005 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. All rights reserved. Ethics in Promotion ● Promotion in Public Schools and on College Campuses – Includes promotional book covers, posters, and even curriculum materials provided to today’s schools – Some schools sign contracts that give certain brands exclusive access to their students – Can generate a backlash 1-8 Copyright © 2005 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. All rights reserved. Price in the Marketing Mix ● Price— exchange value of a good or service. ● Pricing Objectives 1-9 Copyright © 2005 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. All rights reserved. Pricing Strategies ● Price Determination in Practice – Determined in two basic ways— By applying the theoretical concepts of supply and demand By completing cost-oriented analyses ● In reality, you price what the market will bear 1-10 Copyright © 2005 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. All rights reserved. Pricing Strategies ● Price Determination in Practice – Cost-based pricing—practice of adding a percentage of specific amounts (mark-up) to the base cost of a product to cover overhead costs and generate profits. 1-11 Copyright © 2005 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. All rights reserved. ● The Markup Chain for a Hardcover Book 1-12 Copyright © 2005 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. All rights reserved. Pricing Strategies ● Breakeven Analysis—pricing technique used to determine the minimum sales volume a product must generate at a certain price level to cover all costs. Breakeven point = (in units) Total Fixed Cost Contribution to Fixed Costs Per Unit Breakeven point Total Fixed Cost = 1 – Variable Cost Per Unit/Price (in dollars) 1-13 Copyright © 2005 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. All rights reserved. ● Breakeven Analysis 1-14 Copyright © 2005 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. All rights reserved. Pricing Strategies ● Skimming pricing strategy—sets an intentionally high price relative to the prices of competing products ● Penetration pricing strategy—sets a low price as a major marketing weapon ● Everyday Low Pricing and Discount Pricing—Strategy devoted to maintaining continuous low prices rather than relying on short-term price-cutting tactics ● Competitive Pricing—product priced at the general level of competing offerings 1-15 Copyright © 2005 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. All rights reserved. Consumer Perceptions of Prices ● Price-Quality Relationships – Consumers’ perceptions of product quality is closely related to price – Most marketers believe that this perceived price-quality relationship holds over a relatively wide range of prices – In other situations, marketers establish price-quality relationships with comparisons that demonstrate a product’s value at the established price ● Price is a proxy for quality 1-16 Copyright © 2005 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. All rights reserved. Consumer Perceptions of Prices ● Odd Pricing – Odd pricing (charging $39.95 or $19.98 instead of $40 or 20) – Commonly-used retail practice, as many retailers believe that consumer favor uneven amounts – Items on sale may end in a different number, e.g. 7: $17.97, $13.87. 1-17 Copyright © 2005 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. All rights reserved. Discussion ● You are to promote a new nightclub, opening in 3 months ● Objective – create a full house on opening and for two weeks thereafter ● You have $100,000 to spend – Newspaper ad - $10K per ad – Radio - $50K for 3 weeks – Flyers - $500 per 1000 4 color flyers – Personal promoters - $20 per hour – Celebrity appearance - $10K – Premiums – T-shirt $10 each ● Create a promotional campaign 1-18 Copyright © 2005 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. All rights reserved.