* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Phy 2140 Exam 1 - Spring Summer 2004
Speed of gravity wikipedia , lookup
Density of states wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to gauge theory wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistivity and conductivity wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistance and conductance wikipedia , lookup
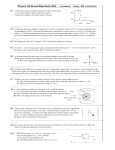
Practice Exam 1 PHY 2140 Instructions: Answer all the questions. You must show your work for credit. Write down any formula(s) used. I must be able to understand what you have done while I am grading the exam – not when you explain it to me after the exam is graded and returned. The formula sheet is on the last page of the exam. You may detach it from the rest of the exam. NOTE: This practice test is longer than an actual test would be but this gives you more practice in problem solving. 1. Three charges, each Q = 3.2 x 10-19 C, are arranged at three corners of a square of side 20 nm as shown. What is the magnitude of the electric field at D, the fourth corner of the square? +Q +Q +Q 20 nm D 2. A point charge q is located at the center of a spherical shell of radius a, which has a charge - q uniformly distributed on its surface. What is the magnitude of the electric field for a point inside the shell a distance r from the center? -q r +q a 3. An electron with a speed of 4.00 x 106 m/s moves into a uniform electric field of 500 N/C. The field is parallel to the electron’s motion. How far does the electron travel before it is brought to rest? 4. Two charges of the same magnitude and sign are placed 1.0 m apart. There is one point in space near them where the electric field is zero. Where is this point? 5. The voltage between the cathode and the screen of a television set is 22 kV. If an electron leaves the cathode with an initial speed of zero, what is its speed just before it hits the screen? 6. Two charged metal spheres are connected by a wire. Sphere A is larger than sphere B as shown. The magnitude of the electric potential of sphere A a. b. c. d. is greater than that at the surface of sphere B. A is less than that at the surface of sphere B. is the same as that at the surface of sphere B. could be greater than or less than that at the surface of sphere B, depending on the radii of the spheres. e. could be greater than or less than that at the surface of sphere B, depending on the charge on the spheres. B 7. A capacitor is connected to a battery as shown. When a dielectric is inserted between the plates of the capacitor, a. b. c. d. e. only the capacitance changes. only the voltage across the capacitor changes. only the charge on the capacitor changes. both the capacitance and the voltage change. both the capacitance and the charge change. + C 8. Find the potential at point P for the rectangular grouping of charges shown in the figure. P 8.00 C 0.200 m nm 0.350 m 8.00 C -12.0 C 9. In the figure from the previous question, how much energy would be expended to move the -12 C charge from its present location to infinity? 10. A 1.00 F capacitor is first charged by being connected across a 10.0 V battery. It is then disconnected from the battery and connected across an uncharged 2.00 F capacitor. What is the charge remaining on the 1.00 F capacitor? 11. A 200 km long high-voltage transmission line 2 cm in diameter carries a steady current of 1000 A. If the conductor is copper with a free charge density of 8.5 x 1028 electrons per cubic meter, how long does it take one electron to travel the full length of the cable? Note: one year = 31557600 seconds 12. A house is heated by a 24 kW electric furnace using resistance heating. The cost for electrical energy is $0.080/kWh. If the heating bill for January is $200, how long must the furnace have run during the month of January? 13. If the diameter of a piece of copper wire is doubled, by what factor does its resistance change? 14. What is the sum of the charges on all the capacitors in the following circuit. 5 F 8 F 3 F 12 V 15. What current flows through a 100 watt light bulb’s filament when in use? Recall that the line voltage is 120 V. 16. If the 100 watt light bulb in the previous problem has a resistance when cold ( at 20 C) of 20.0 . What is the temperature of the bulb’s filament when hot? Use = 4.5 x 10-3 C-1 for the temperature coefficient for resistivity of the filament. 17. Two small spheres of mass m = 5 g and possessing equal charge q are suspended from a common point by threads of length L = 0.3 m. What is the magnitude of the charge q if the threads make an angle = 20 with respect to the vertical? L 5g L 5g 18. Twenty grams of copper is drawn into a wire 1 mm in diameter. What is the resistance of the resulting piece of wire? Use 8900 Kg/m3 as the density of copper and = 1.7 x 10-8 m as it’s resistivity. v x f xi a t f ti A Ax Ay 2 2 v 2 v0 2ax 2 W ( F cos ) s v f vi t f ti Ay tan Ax v v x 0 t 2 KE 1 2 mv 2 Ax A cos Ay A sin 1 2 at 2 v v0 at x v0 t Fx = m ax Fy = m ay Wnet = KEf - KEi KEf +PEf = KEi + PEi W PE F ke q1 q 2 r 2 VB VA Ed C 0 energy P I 2R F E ke q0 V ke q r 1 1 1 Ceq C1 C 2 A d 1 QV 2 R E A energy R g = 9.8 m/s2 = 8.85 x 10-12 C2/Nm2 n, nano = 10-9 me = 9.11 x 10-31 Kg I nqv d A r2 q1q2 r C eq C1 C 2 Q2 2C 0 1 T T0 V 2 PE k e q I Q t R R0 1 T T0 ke ke=8.99 x 109 Nm2/C2 1 kWh = 3.60 x 106 J k, kilo = 1000 electron charge = 1.60 x 10-19 C PE qVB VA Q CV energy 1 2 C V 2 V IR P IV 1 circle, cylinder: 4 0 A r 2 ,V r 2 l 1 eV = 1.6 x 10-19 J micro = 10-6 M, mega = 106 1 hour = 3600 sec