* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Viruses
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
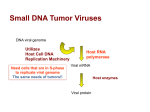
Chapter 24 VIRUSES REVIEW Characteristics of Life Cells Organization Energy use Homeostasis Growth Reproduction Protein Synthesis RNA DNA Central Dogma Viruses are _____ members of the Six-Kingdom System of Classification or Domains Not ALIVE! No ________________________________ No ________________________________ Cannot _________________ without a host Detached Fragment of a genome Infect all taxonomic levels! They are highly specific VIRAL STRUCTURE AND REPLICATION Discovery of Viruses __________________ (1904-1971) _________________________(TMV) Crystallized it not likely to be cells Described TMV as being chemical matter Virology Nobel Prize for Chemistry in 1946 Characteristics of Viruses Size Structure _____________ biological particle 17 nm to 1000 nm diameter Not cellular Nucleic acid (___________________) Protein coat or __________________ Outer __________________ (bilipids) Shape Helical icosahedrons CLASSIFICATION OF VIRUSES ____________Viruses Direct production of RNA Examples Retrovirus- use reverse transcriptase to make DNA Examples Influenza Rhabdovirus (rabies) HIV ____________________ Herpes Pox ___________ Viruses Disease causing agent, RNA with NO capsid Examples Plant disease ____________________ Abnormal protein clumps, kills host Examples Mad Cow Disease Creutzfeld-Jacob Disease Prions ___________________ Transmissible spongiform encephalopathy (TSE) Infectious agent was ______________ only change their structure 1997 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine Prions cause other proteins to change! Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease (CJD) caused by prions Connection to Alzheimer? VIRAL REPLICATION “Obligate intracellular parasite” Replication of DNA Viruses Inserts its _______ (_____________) into host’s chromosomemRNAviral proteins Replication of RNA Viruses Inserts _________- used directly as mRNA Retroviruses use “____________________________” to generate DNA to insert into host’s genome VIRAL REPLICATION Replication of Viruses that Infect Prokaryotes “__________________” Virus that infect bacteria Large and complex DNA T series Example: T4 phage The _____________Cycle Virulent 1. _____________________ 2. _____________________ 3. _____________________ 4. ____________ 5. _____________ … ___________ http://www.liquidjigsaw.com/animation/anim5. htm http://www.nature.com/nrm/journal/v1/n1/an imation/nrm1000_040a_swf_MED1.html ___________CycleTemperate 1) _____________________ 2) _____________________ 3) Integration of __________ *viral DNA integrated into host cell 4) Cell __________________ May stay ____________ for an unknown period of time THE COLD SORE! THE ORIGIN OF VIRUSES Evolved from early cells? Naked nucleic acid Developed outer protective surface The evolution of influenza… Genetic mutations Mutate quickly VIRAL DISEASES _________ of Viral Disease Intermediate host that transfers a pathogen or parasite to another organism Ex. Humans, animals, mosquitoes, ticks fleas, … Human Viral Diseases Chickenpox Shingles Viral hepatitis Acquired Immune Deficiency (AIDS) Typical animal virus Caused by HIV US since 1981 Virus closely related to a chimpanzee virus Persons die from opportunistic infections EMERGING VIRAL DISEASES _________________ Viruses Caused by new/reappearing infectious agents that typically exist in animal populations Ex. West Nile, Ebola, SARS PREVENTION AND TREATMENT Vaccines _____________– cannot replicate in host _____________– virus genetically altered Vector Control Control of animal vectors Example - Rabies vaccination for dogs Drug Therapy Acyclovir (blocks DNA Polymerase of herpes and chickenpox viruses) Viruses and Cancer Human T lymphotrophic __________ Hepatitis B ____________________ Epstein-Barr ___________________ Human papillomavirus _________________ http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hJ8x3KR75fA&f eature=related http://www.gardasil.com/tv-commercial2-forgardasil.html