* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Causes of Low Back Pain
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
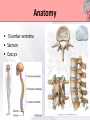
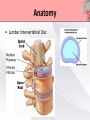
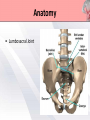
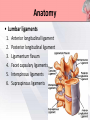
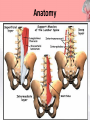
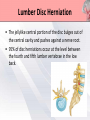
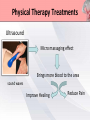
Presented by : Chathura Karunarathna DPHY 01/09/001 Content • • • • • • • • Introduction Anatomy Causes Symptoms Red and Yellow Flags Investigation Treatments Prevention Introduction • Low back pain affects over 80% of persons at some point in their life. • 90% of the time low back pain is recurrent. • The peak age of incidence of low back pain is 30 to 50 years old. • The most common cause of disability of a persons in more than 45 years. • Second most common reason for physician visit. Anatomy • 5 lumbar vertebra • Sacrum • Coccyx Anatomy • Lumbar Intervertebral Disc Anatomy • Lumbosacral Joint Anatomy • Lumbar ligaments 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Anterior longitudinal ligament Posterior longitudinal ligament Ligamentum flavum Facet capsulary ligaments Interspinous ligaments Supraspinous ligaments Anatomy Anatomy • Nerve supply Low Back Pain • Back pain is described by the length of time symptoms persist: Acute LBP • lasts less than 6 weeks Sub acute • lasts between 6 and 12 weeks LBP Chronic LBP • persists for more than 12 weeks Causes of Low Back Pain Mechanical Causes Muscle or soft tissues sprain or strain Back pain most often occurs from strained muscles and ligaments. • From improper or heavy lifting. • After a sudden awkward movement. Lumber Disc Herniation • The jellylike central portion of the disc bulges out of the central cavity and pushes against a nerve root. • 95% of disc herniations occur at the level between the fourth and fifth lumber vertebrae in the low back. Other Mechanical Causes • • • • • • Kyphosis Fractures Leg length difference Restricted hip motion Lumbar spinal stenosis Osteoporosis Causes of Low Back Pain Inflammatory Causes Ankylosing spondylitis • Ankylosing spondylitis is a form of chronic inflammation of the spine and the sacroiliac joints. • Characterized by pain and progressive stiffness in and around the spine. • Over time, chronic inflammation of the spine (spondylitis) can lead to a complete cementing together (fusion) of the lumbar vertebrae. Lumbar Spine Arthritis • Lumbar spine arthritis is most commonly seen in older patients, but can be seen in all age groups. • Patients with degenerative changes resulting in spinal stenosis (narrowing of the spinal column) may experience numbness, tingling, or weakness in the legs due to irritation of the lumbar nerve roots. Symptoms Symptoms are depend on the affected cause of lower back. Back sprain or strain • Muscle spasms, cramping, and stiffness. • Pain in the back and buttocks. Nerve-root pressure • Leg pain • Tingling, Numbness, or Weakness along the leg. • Loss of bladder and/or bowel control. Symptoms Arthritis of the spine • Usually causes pain that is worse in the back and hip region. • Starts gradually, gets worse over time. Other conditions • Fever • weight loss • Progressive weakness in the legs (cauda equina syndrome) Red Flags of Lower Back Pain • • • • • • • • • Weight loss, fever, night sweats Infection (current/recent) History of cancer Prolonged use of corticosteroids Older age Major Trauma Osteoporosis Back pain at rest Bowel or bladder dysfunction Yellow Flags of Lower Back Pain • • • • • • Environmental factors Societal factors Stressors in relationships Mental health The belief that pain is harmful or severely disabling Job dissatisfaction Yellow Flags of Lower Back Pain Investigations Method Mainly use for identify X-rays Osteoporotic fractures, Dislocations. Infection, Paget disease. Bone scan CT MRI Dexa Scan Bone tumours, Fractures, Spinal stenosis. Spinal cord, Nerve roots, Discs, Haemorrhage problems. Bone density Treatments • Although for many years there was no agreement among health professionals on how to best treat back pain. • The treatment are very specific to the cause of the low back pain. Treatments Surgical Microdiscectomy Discectomy Laminectomy Spinal fusion Disc replacement Manual Physical Therapy Back Brace TENS Ultrasound Hot or Cold packs Traction Massage Physical Therapy Treatments Back Brace • braces for the lower back are built to support abdominal muscles by restricting motion, they can take pressure off the lower back, relieving back pain and in many cases improving posture. Physical Therapy Treatments Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation • TENS is a therapy that uses low-voltage electrical current for pain relief. • The electrodes are often placed on the area of pain and creating a circuit of electrical impulses that travels along nerve fibers. Physical Therapy Treatments Ultrasound Micro massaging effect Brings more blood to the area sound waves Improve Healing Reduce Pain Physical Therapy Treatments Ice Packs Apply ice packs in every one or two hours to reduce inflammation and pain in acute stage. Hot Packs Heat therapy dilates the blood vessels of the muscles surrounding the lumbar spine. This process increases the flow of oxygen and nutrients to the muscles, helping to heal the damaged tissue. Physical Therapy Treatments Traction Increase joint space and Stretch soft tissues Increase Reduce pressure Decrease Provide Circulation on spinal cord Inflammation relaxation Treatments Other Treatments • • • • Acupuncture NSAIDs for pain relief Thrust Manipulation Yoga Outcome of Treatments Aim: To relieve symptoms and mobilise early. • Pain Control. • Manage tissue injury. • Motion in Pain-free range. • Restore Full pain free range of motion. • Restore Muscle endurance. • Restore Functional movements. • Improve propriocetion. Exercises For Lower Back Pain • The goals of performing these exercises were to reduce pain and provide lower trunk stability by actively developing the "abdominal, gluteus maximus, and hamstring muscles as well as passively stretching the hip flexors and lower back muscles. Low Back Extension Exercises Prone, or lying on your stomach on the floor or bed, is the best position in which to do extension exercises. Low Back Flexion Exercises • Pelvic tilt exercise increases the strength of the lower back muscles and help to improve full range of motion in both the pelvis and lower back vertebrae. This move loosens up any stiffness and can improve posture. More Exercises For Lower Back Prevention • • • • • • Lose any excess weight Wear flat shoes Avoid sudden movements Stop smoking Maintain healthy diet Avoid lifting heavy objects Maintain Correct Posture Standing Sitting Maintain Correct Posture Sleeping Lifting Maintain Correct Posture Driving Use Correct Body Mechanics