* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Pericardium and external features of Heart
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Congenital heart defect wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
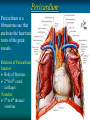
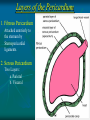
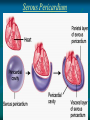
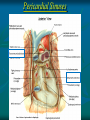
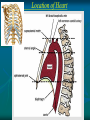
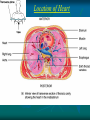
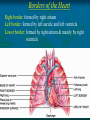
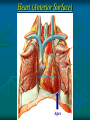
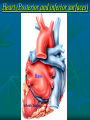
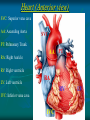
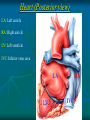
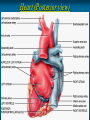
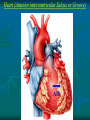
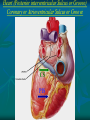
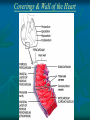
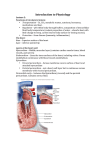
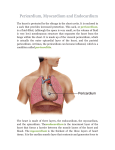
Pericardium and External features of Heart Dr. Sama ul Haque Objectives • Define pericardium. • Differentiate between fibrous and serous pericardium. • Define pericardial sinuses. • Identify the borders and surfaces of the heart. • Describe the structure of the heart Pericardium Pericardium is a fibroserous sac that encloses the heart and roots of the great vessels. Relations of Pericardium: Anterior: Body of Sternum 2nd to 6th costal cartilages Posterior: 5th to 8th thoracic vertebrae Layers of the Pericardium 1. Fibrous Pericardium Attached anteriorly to the sternum by Sternopericardial ligaments. 2. Serous Pericardium Two Layers: a. Parietal b. Visceral Serous Pericardium Pericardial Sinuses Nerve supply of the Pericardium 1. Fibrous Pericardium and Parietal layer of serous Pericardium: By Phrenic nerves 2. Visceral layer of Serous Pericardium: By Sympathetic trunk and vagus nerves Location of Heart Angle of Louis Location of Heart Borders of the Heart Right border: formed by right atrium Left border: formed by left auricle and left ventricle Lower border: formed by right atrium & mainly by right ventricle Surfaces of the Heart Sternocostal surface (Anterior surface): Mainly formed by right atrium and right ventricle. Diaphragmatic surface (Inferior surface): Mainly formed by right and left ventricles. Small portion is formed by right atrium. Base (Posterior surface): Mainly formed by left atrium. Apex: formed by left ventricle Heart (Anterior Surface) Anterior Surface Apex Heart (Posterior and inferior surfaces) Base Inferior Surface Heart (Anterior view) SVC: Superior vena cava AA: Ascending Aorta SVC PT: Pulmonary Trunk RA: Right Auricle AA PT RV: Right ventricle LV: Left ventricle RA RV IVC: Inferior vena cava IVC LV Heart (Posterior view) LA: Left auricle RA: Right auricle LV: Left ventricle IVC: Inferior vena cava LA LV RA IVC Heart (Posterior view) Heart (Anterior interventricular Sulcus or Groove) AIS Heart (Posterior interventricular Sulcus or Groove) Coronary or Atrioventricular Sulcus or Groove CS PIS Coverings & Wall of the Heart Thank You