* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Telecommunications and Networking
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Net neutrality law wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Computer security wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Internet protocol suite wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
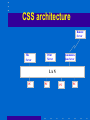
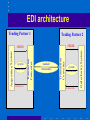
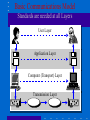
Telecommunications and Networking Network Concepts • Network – An interconnected chain, group or system • Number of possible connections on a network is N * (N-1)/2 – Where N = number of nodes (points of connections on the network) – Example, if there are 10 computers on a network, there are 10 * 9 = 90 possible connections Metcalfe’s Law • The usefulness of a network equals the square of the number of users • On a small network, a change in technology affects technology only • On a large network like the Internet, a change in technology affects social, political and economic systems Telecommunications • Telecommunications – Exchange of information in any form (voice, data, text, images, audio, video) over networks Basic concepts • Communication protocols (TCP/IP) • Data transmission methods – Asynchronous – Synchronous • Connecting – Modem and TCU – Hardwired and remote • Data transmission channels (bps) – narrow bands: 5-30 – voice bands: 1,000-9,600 – broad bands: 100,000 • Types of communication lines – simplex – half-duplex – duplex Networks • Concept – "a group of interconnected computers, workstations, or computer devices (such as printers and data storage systems).” • Network topology – bus – star – ring • Local-area networks – bus: Ethernet, carrier sense multiple access (CSMA) – ring: token passing method • Distributed data processing – "interconnects sites of one organization not only for communication of data and messages but also for the sharing of resources." Open Systems • Information systems that use common standards for hardware, software, applications and networks • Internet networking technologies are a common standard for open systems • Connectivity: – Ability of networked computers to easily access and communicate with each other and share information • Interoperability: – The ability of an open system to enable end user applications to be accomplished using different varieties of computer systems, software packages, and databases provided by a variety of interconnected networks Middleware • Any programming that serves to “glue together” two separate programs Internet2 • Next generation of the Internet • High-performance network • In use at 200 universities, scientific institutions, communications corporations The Internet • No central computer system • No governing body • No one owns it Internet Service Provider • ISP – A company that specializes in providing easy access to the Internet – For a monthly fee, you get software, user name, password and access • ISPs are connect to one another through network access points An Intranet • A network inside an organization – That uses Internet technologies (such as Web browsers and servers, TCP/IP protocols, HTML, etc.) – To provide an Internet-like environment within the organization – For information sharing, communications, collaboration and support of business processes – Protected by security measures – Can be accessed by authorized users through the Internet Extranet • Network links that use Internet technologies – To connect the Intranet of a business – With the Intranets of its customers, suppliers or other business partners GPS 1. The global positioning system (GPS) is a major technological achievement that has broad-reaching implications for business. Using the Internet, – Can find other innovative uses for GPS. – Good places to start familiarizing yourself with current accomplishments are The GPS Overview at http://www.colorado.edu/geography/gcraft/notes/gps/ gps_f.html Telecommunications network • Any arrangement where a sender transmits a message to a receiver over a channel consisting of some type of medium Types of Networks • • • • WAN LAN VPN C/S VPN VPN • Basically, a VPN is a private network that uses a public network (usually the Internet) to connect remote sites or users together. Instead of using a dedicated, real-world connection such as leased line, a VPN uses "virtual" connections routed through the Internet from the company's private network to the remote site or employee. Source: computer.Howstuffworks.com Internetwork Processors • Switch – makes connections between telecommunications circuits in a network • Router – intelligent communications processor that interconnects networks based on different protocols • Hub – a port switching communications processor • Gateway – connects networks using different communications architectures ROUTERS Routers are specialized computers that send your messages and those of every other Internet user speeding to their destinations along thousands of pathways. • Fujitsu GeoStream R980 industrial strength router ROUTERS configuration table. A configuration table is a collection of information, including: • Information on which connections lead to particular groups of addresses • Priorities for connections to be used • Rules for handling both routine and special cases of traffic A router, then, has two separate but related jobs: • The router ensures that information doesn't go where it's not needed. This is crucial for keeping large volumes of data from clogging the connections of "innocent bystanders." • The router makes sure that information does make it to the intended destination. Distributed data processing TSS - Time Sharing Systems PC PC PC MAINFRAME CSS - Client Server Systems PC Client/Server networks • Clients: End user personal computers or networked computers • Interconnected by LANs • Servers: manage networks • Processing shared between clients and servers CSS architecture Remote Server File Server Communications Server Print Server LA N PC PC PC PC Peer-to-peer networks • Networks that connect from one PC to another PC Peer-to-peer networking enables or enhances the following scenarios: • Real-time communications (RTC) • Collaboration • Content distribution • Distributed processing • Improved Internet technologies Source: www.microsoft.com Wireless Technologies • Terrestrial microwave – Earthbound microwave systems that transmit high-speed radio signals in a line-of-sight path – Between relay systems spaced approximately 30-miles apart • Communications satellites – Satellite serves as relay stations for communications signals – Uses microwave radio signals Wireless Technologies • Cellular and PCS telephone and pager systems – Divide the geographic area into small areas or cells – Each cell has transmitter or radio relay antenna to send message from one cell to another • Wireless LANs – Radio signals within an office or building – Connect PCs to networks • Bluetooth – Short-range wireless technology – To connect PC to peripherals such as printer Bluetooth • Bluetooth is a standard developed by a group of electronics manufacturers that allows any sort of electronic equipment -- from computers and cell phones to keyboards and headphones -- to make its own connections, without wires, cables or any direct action from a user. • Bluetooth can connect up to eight devices simultaneously. With all of those devices in the same 10-meter (32-foot) radius Wireless Networks • http://www1.us.dell.com/content/topics/glo bal.aspx/solutions/en/truemobile?c=us&cs= 04&l=en&s=bsd • (see the LIVE demo on the site) Steps in wireless network source: www.dell.com EDI Concepts • EDI is a mechanism for electronic trading • EDI replaces paper flow with online transactions • EDI architecture • EDI is for trading partners • Implementation plan is a key factor • Obstacles: • – lack of transaction standardization – high start-up costs EDI third-party suppliers – AT&T, Control Data, EDS, GE, Western Union, IBM, Martin Marietta Data Systems, etc. EDI architecture Trading Partner 1 Trading Partner 2 CONFIRMATION standard transactions Transaction Converter Transaction Converter Acquisition System system transactions system transactions CONFIRMATION Order Entry System ORDER ORDER Network Topologies • Topology: structure of a network • Star: ties end user computers to a central computer • Ring: ties local computer processors together in a ring on a relatively equal basis • Bus: local processors share the same communications channel Network Architectures & Protocols • Protocol: standard set of rules and procedures for the control of communications in a network • Network Architecture: – Master plan of standard protocols, hardware, software and interfaces between end users and computer systems – Goal of promoting an open, simple, flexible, and efficient telecommunications environment OSI & TCP/IP Models • Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) Model – A seven-layer model that serves as a standard model for network architectures – Model for how messages should be transmitted between two points in a network – Each layer adds functions • Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) – A five layer telecommunications protocol used by the Internet Basic Communications Model Standards are needed at all Layers User Layer Application Layer Computer (Transport) Layer Transmission Layer Internet Telephony • Using an Internet connection to pass voice data using IP • Voice over IP (VoIP) • Skips standard long-distance phone charges VOIP (source www.fcc.gov) Bandwidth • Bandwidth – Frequency range of a telecommunications channel – Determines transmission rate – Classified in bits per second (bps) • Transmission Rates: – Narrow-band – low-speed – Broadband – high-speed Transmission Speeds Wi -Fi • Wi_fi • Wi_Max RFID • RFID & Controversy