* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Atoms, Elements, and Ions
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
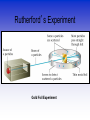
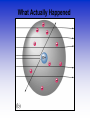
Atomic Theorists How we got to where we are now Law of Conservation of Mass • Who: Antoine Lavoisier • Matter can't be created or destroyed • When: 1785 • Where: France Law of Definite Proportions • Who: Joseph Proust • Compounds – Elements put together in fixed ratios of small whole numbers C + O2 CO2 • When: 1797 • Where: France Law of Multiple Proportions • Who: John Dalton • Two elements can form more than one compound • The subscripts of the elements in the compounds will be small whole numbers. » C + O2 CO2 » C + O2 CO • Where: England When: 1803 Who: Aristotle What: All matter is a combination of fire, air, earth or water When: 350 B.C. Where: Greece Who: Democritus •When: 400 B.C. •Where: Greece •What: Matter was made of indivisible substances he called atomos (1st talk of the atom) Who: John Dalton What: Solid Sphere Model (1st atomic theory) •Elements are made up of indivisible particles called atoms •Each element was composed of the same kind of atoms. •Different elements were composed of different kinds of atoms. •Compounds are composed of atoms in specific ratios. •Atoms are not created or destroyed in a reaction. When: 1805 Where: England Problems with Dalton’s Theory Today (issues that weren’t known about ..yet) 1.Matter is composed of indivisible particles There are electrons, protons and neutrons 2.All atoms of a particular element are identical There are isotopes 3. Different elements have different atoms 4.Atoms combine in whole number ratios 5.Atoms can’t be created or destroyed Nuclear explosions destroy matter Who: J.J. Thomson What: Atoms aren't smallest particle •Conducted experiment with a Cathode Ray Tube •Particles had a negative charge (discovered electrons) •Model = plum pudding When: 1897 Where: England Cathode Ray Tube https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XU 8nMKkzbT8 Who: Robert Millikan What: •Experiments to determine mass of electron •Conducted the oil drop experiment •Verified that electron is negatively charged; 1.6 x 10 -19 coulombs •No new model Where: America When: 1910 Millikan Oil Drop Experiment Who: Ernest Rutherford What: • Conducted Gold Foil experiment • Proved nucleus is dense, positively charged core of atom • Model = Stationary Planetary • When: 1911 • Where: America Rutherford’s Experiment • http://www.mhhe.com/physsci/chemistry/esse ntialchemistry/flash/ruther14.swf • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wzALbzTd nc8 • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XBqHkraf 8iE Rutherford’s Experiment Gold Foil Experiment Results of foil experiment if Plum Pudding model had been correct. What Actually Happened Who: Niels Bohr • What: Pulsating Planetary Model • Electrons can move between energy levels • When: 1913 • Where: Denmark There were many people involved with developing the mathematical process to determine the path of the electron. One of these men was Schroedinger. What: pulsating orbital model When: 1926 Where: Switzerland Who: James Chadwick What: • Confirmed existence of neutron • No new atomic model • When: 1932 • Where: England Atomic Theory Song • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=07yDiELe 83Y