* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Powerpoint Notes on Meteors, Asteroids and Comets
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Impact event wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Sample-return mission wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical naming conventions wikipedia , lookup
Comet Hale–Bopp wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
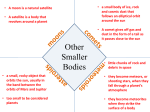
Meteoroid – a chunk of rock or dust in space. (these come from comets or asteroids) Meteor – a chunk of rock or dust that enters our atomosphere and burns up, producing a streak of light time lapse photo of meteor shower Meteorite – a meteor so large it does not completely burn up and strikes the surface. Rocky objects, most of which revolve around the sun in fairly circular orbits between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. There are more than 100,000 asteroids Most are small, but some are so large we have named them. Ceres, for example, is over 300 km across. We keep track of the biggest ones because they can get nudged out of orbit and could collide with Earth. (ie. End of dinosaurs 65 mya) Comets are a loose collection of ice, dust and small rocky particles. Comet orbits are usually highly elliptical As it nears the sun, solar energy heats up the comet and released gas and dust form a fuzzy outer layer called the coma. (the nucleus is the solid inner core) Comet means, “long haired star” in Greek. This refers to the tail which, due to solar radiation, always points away from the sun. These tails can be 100 million km long or almost the entire distance from the Earth to the Sun. Comets can come from the Kuiper Belt or the Oort cloud. They may have periodic orbits, like Halley’s comet that comes around every 76 years or, they may be disturbed by gravitational waves that send them into the inner solar system. They may collide with a planet, the sun, or swing around the sun and never return. The ESA landed a probe on a comet in 2014 More information about the Rosetta mission Actual pictures from the mission What happened to Philae?