* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Comets, Asteroids & Meteoroids
Planet Nine wikipedia , lookup
Heliosphere wikipedia , lookup
Scattered disc wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
Sample-return mission wikipedia , lookup
Tunguska event wikipedia , lookup
Chelyabinsk meteor wikipedia , lookup
Halley's Comet wikipedia , lookup
Comet Shoemaker–Levy 9 wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Comet Hale–Bopp wikipedia , lookup
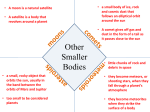
Comets, Asteroids & Meteoroids Ch 21.5 Comets • Small, icy body that orbits the Sun. • Parts of a comet: – Nucleus – Coma – Tails – http://www.classzone.com/books/earth_scienc e/terc/content/visualizations/es2706/es2706p age01.cfm Anatomy of a comet • Nucleus – Frozen water, frozen CO, frozen CO2, formaldehyde & dust – Evaporates as it nears the sun & flows outward • Coma – Outflowing gas & dust – Appears bright because of gases & dust reflecting the sunlight • Tails – Dust tail = dust swept from nucleus – Plasma tail = solar wind sweeps it outward, so it always points away from sun Comet orbits • Long-period orbits – Longer than 200 years – Comet Hale-Bopp (2400 years; passed by in 1997) • Short-period orbits – Shorter than 200 years – Comet Halley (76 year orbit) What happens to comets? • 3 things that destroy them: – Collision with planet or sun – Erosion (loses ice & dust with each orbit) – Breaking into pieces Asteroids • • • • • Orbiting rocks Minor planets 250,000 asteroids whose orbit we know Orbits vary in shape & size Most are in asteroid belt at 2.1-3.3 AU from sun Asteroids • Largest & also first discovered = Ceres • 1000 km diameter Trojan asteroids • In Jupiter’s orbit around Sun • Leading or trailing Jupiter Meteors • Meteor = bright streak of light • Meteoroid = the debris itself • Meteorite = piece that reaches the ground • http://www.classzone.com/books/earth_sci ence/terc/content/visualizations/es2707/es 2707page01.cfm Awesome meteor facts: • Traveling at 11 km/sec • Heats up, melts & vaporizes = glow that we see • 8 – 10 meteors can be seen each hour on a regular night Meteor Showers • Times when the numbers of meteors rises to 15-100 /hour • These are predictable ~ 10x/year as Earth crosses orbit of meteoroids Meteorites • Rare • Chances of being struck by a meteorite more massive than 0.1 kg are 1:10 billion * • * p 346 Astronomy by John D. Fix Types of meteorites • Stony – Rocky material • Metallic – Iron & nickel • Stony-iron – Rocky material, iron & nickel