* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Kepler*s laws of planetary motion
Scattered disc wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
Planet Nine wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
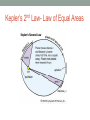
11/10/15 KEPLER’S LAWS OF PLANETARY MOTION Objective: I will summarize Kepler’s three laws of planetary motion. Early Models of the Solar System • Geocentric model- developed by Aristotle ~2,000 years ago • Earth centered, with the Sun, stars, and planets revolving around Earth • Ptolemy model- sought to better explain the geocentric model • Still had Earth as the center of the solar system • Heliocentric model- developed by Copernicus • Sun-centered solar system with planets revolving around the Sun in the same direction • Johannes Kepler- noticed a pattern in data of planetary motion • Developed 3 laws to explain the motion of orbiting object Kepler’s 1st Law- Law of Ellipses • Each planet orbits the sun in a path called an ellipse, not a circle • Shape of the ellipse determined by two points, called a focus • Eccentricity- degree of elongation of an elliptical orbit • Circular e=0 Flattened ellipse e=1 • Perihelion- point of orbit closest to the sun • Aphelion- point of orbit furthest away Kepler’s 1st Law- Law of Ellipses Kepler’s 2nd Law- Law of Equal Areas • The area through which an objects sweeps in a given period of time are equal • Describes the speed objects travel at different points in their orbit • Therefore, objects travel fastest when close to the sun, and slowest when far away from the sun Kepler’s 2nd Law- Law of Equal Areas Kepler’s 3rd Law- Law of Periods • Describes the relationship between the average distance of a planet from the sun and the planet’s orbital period • Orbital period- time required for planet to complete one orbit • Helps astronomers find out how far away planets are from the sun Kepler’s 3rd Law- Law of Periods Newton’s Law of Universal Attraction • The force of gravity exists between any two objects in the universe • Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation- force between two objects is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them • Bigger objects exert more gravity • Objects that are farther apart exert less gravity on each other than when they are close together Kepler’s Laws Haiku (Output Activity) • On your left-side page, you will create three (3) separate Haiku poems. • One poem each for: • Kepler’s 1st Law • Kepler’s 2nd Law • Kepler’s 3rd Law • Remember to include a title and color! Haiku Output Activity