* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Myo-inositol for PCOS
Epidemiology of metabolic syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Prenatal nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Menstruation wikipedia , lookup
Maternal physiological changes in pregnancy wikipedia , lookup
Menstrual cycle wikipedia , lookup
Fetal origins hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Gestational diabetes wikipedia , lookup
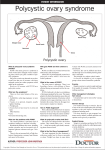
Story of poly narrated by Narendra Malhotra & Jaideep Malhotra GLOBAL RAINBOW HEALTH CARE,INDIA www.rainbowhospitals.org Declaration of conflicts of interest Sponsored & Supported by Background PCOS is an endocrine system disorder affecting women in their reproductive years. Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is the most common hormonal disorder among women of reproductive age. Infertility is one of the most common PCOS symptoms. Because the symptoms of PCOS are seemingly unrelated to one another, the condition is often overlooked and undiagnosed. EPIDEMOLOGY 20-33% of all reproductive age group have PCO 5-10% of all reproductive age group have PCOS 87% of women with oligomennorhea 26% of women with ammenorhoea 50% of them presenting with infertility 50% women with recurrent miscarriages SYMPTOMS PCOS is a syndrome disease defined by a collection of signs and symptoms. The symptoms of PCOS that one patient experiences can be very different from the symptoms of another patient. If there are two or more of the following symptoms, then a thorough checkup is needed to determine the PCOS treatment: Irregular or missing menstrual periods Infertility Excess or unwanted body or facial hair growth Thinning hair on the scalp Weight problems, often including weight gain around the waist Skin problems, including skin tags, darkening skin and acne HEALTH RISKS There are several health risks associated with PCOS like Type 2 diabetes Infertility High cholesterol Elevated lipids Sleep apnea Liver disease Abnormal uterine bleeding Increased risk of endometrial cancer, gestational diabetes, pregnancyinduced high blood pressure, heart attacks and miscarriage High blood pressure Obesity possibly leading to issues with low self-esteem and depression Metabolic syndrome Nonalcoholic fatty liver (steatohepatitis) CAUSES Probable causes for PCOS Stress Diet Genetics Pollution Excess insulin Low-grade inflammation Lazy life style and lack of excercises MECHANISM for INSULIN RESISTANCE PCOS Insulin Resistance due to poor diet, lifestyle, genetics etc High Glucose High Insulin High Androgen Hair Growth & Acne Weight Gain Low Ovulation MECHANISM for NON INSULIN RESISTANCE PCOS Pollution (toxicity of xenobiotics) -> affects embryo -> may damage a female embryo’s ovarian follicles and make them dysfunctional; unable to complete ovulation or manufacture sufficient progesterone. This damage is not apparent until after puberty. Intrauterine exposure with androgenic drugs And androgenic progesterones are Likely to be a cause of these genetically prone female Fetuses developing PCOS BABY POLY IS BORN other factors that may contribute to dysfunctional follicles Stress -> high cortisol levels ; Stress alone can cause anovulatory cycles Birth control pills -> sometimes normal ovary functions don’t resume after stopping intake of birth control pills Medications like Prozac Low grade inflammation GENETICS OF PCOS No karyotypic abnormalities found Gene studies – Candidate genes involved in steroid hormone synthesis carbohydrate metabolism genes involved in gonadotropic action Genetics and Epigenetics Underlying genetic factor Single specific gene not yet determined Many candidate genes implicated Different combinations of multiple gene polymorphisms and of environmental factors explain the heterogeneity of PCOS CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS SYMPTOMS Obesity(38%) ASSOCIATED ENDOCRINE MANIFETATIONS POSSIBLE LATE SEQUALE Androgens(29%) Diabetes mellitus(29%) Menstrual disturbance(66%) LH(40%) Cardiovascular disease Hyperandrogenism(48%) LH:FSH ratio Hyperinsulinemia Infertility (73% of anovulatory infertility) Free estradiol Low LDL Asymptomatic(20%) Fasting insulin Endometrial carcinoma Prolactin(27%) hypertension Sex hormone binding globulin DIAGNOSIS There is no definitive test for PCOS; it depends on the medical history, symptoms, and tests to rule out other possible conditions. Perform a physical and pelvic examination to look for signs of PCOS, such as swollen ovaries or a swollen clitoris. Blood tests to measure hormone levels are typically ordered, as well as thyroid function tests to determine how much of the thyroid hormone your body produces Fasting glucose tests to measure your blood sugar levels Lipid level tests to assess the amount of cholesterol in your blood A vaginal ultrasound A pelvic laparoscopy PCOS: Goals Identify patients with risks for or with diagnosis of PCOS Assess patients appropriately for PCOS and associated disease states Prescribe therapy to treat complaints and prevent sequelae COUNSELING OF A PCOS PATIENT Endocrine problems Metabolic problems Infertility Risk of OHSS and multiple pregnancy Pregnancy complications Long term sequel MOST IMP- Importance of life style modification Ms poly is growing at age 5-7 she is obese and overwt. She is a nice chubby girl Oooh how sweeet…… Chubby cheeks The fat appears to be baby fat No excercises Eating whenever and whatever Over feeding MISS POLY becomes 15 + CONCERNS are; Menstrual irregularities Obesity Hirsutism Acne PROTOCOLS OF MANAGEMENT IN ADOLESCENTS Counselling for weight reduction and life style modification. Carbohydrate and fat restricted diet. Diet restriction and exercise is the sheet anchor of treatment for overweight. Low glycemic index diet upto 85% will improve menstrual cycle regularity and ovulation in about six months. PCOS Treatments Polycystic ovary syndrome treatment starts with a proper diagnosis. Treatments are then chosen based on a woman's symptoms, age and future pregnancy plans. Treatment for PCOS may include: Life style changes Birth control pills to regulate menstruation Insulin-sensitizing medications Ovulation induction to treat infertility Androgen-blocking medications Topical anti-hair-growth medications Other excess hair treatments Treatments for hair loss Acne treatments Removal of other skin problems OBESITY & PCOS In a study of obese and non-obese women with PCOS, various hormones were measured with interesting results. Researchers measured blood levels of six markers, including estradiol, testosterone and androstenedione. The average levels of testosterone and androstenedione in obese PCOS women were significantly higher than those in non-obese PCOS women. This is yet another indicator that obesity can contribute significantly to hormone imbalance. PCOS disappears rapidly in most women when they reduce weight. It is difficult for most PCOS women to lose weight due to hormone imbalance. There are latest weight loss programs which works for PCOS like iSlimRx, which is a scientifically designed protocol that utilizes a combination of very specific foods at around 1000-1200 calories per day and the use of proprietary medicine drops that CHANGE THE WAY BODY PROCESSES FOOD by detoxifying liver and resetting "Hypothalamus". The hypothalamus gland moderates the thyroid, adrenals, fat storage, and more importantly, body's metabolic rate. If followed, this protocol WORKS. OBESITY AND PCOS Associated in 35-60% of cases Usually android type Raised weight: hip ratio >0.85 Increased waist circumference >90 cm Also associated with Insulin Resistance (IR)and Hyperinsulinemia But PCOS also seen in non obese women. IMPACT OF OBESITY IN REPRODUCTION Condition Associated risks Mensturation Ammenorhoea, oligomennorhoea, mennorhagia Infertility Anovualtion, poor response to infertility drugs Miscarriage Increased rate Infertility treatment Increased requirement of oral or injectable ovulation induction agent Decreased success rate of IVF Glucose intolerance Impaired glucose tolerance, type 2 DM Pregnancy Increased PIH, GDM,CS, Downs Even 7% weight reduction may lead to spontaneous resumption of menses. Moderate physical activity, 30-60 minutes per day should be goal of all patient with adolescent PCOS. M.O.A: lowers circulating free androgen and insulin levels. Increases SHBG, thereby decreases level of free testosterone. WHY ORAL CONTRACEPTIVE PILLS ? Estrogenic component of the oral contraceptive suppresses luteinising hormone and thus reduces ovarian androgen production. Estrogen also enhances hepatic production of SHBG ,thereby the level of free testosterone declines. Cyproterone acetate, Drospirenone and desogestrel can be used in combination with ethinyl estradiol. Cyproterone acetate Competitively inhibits the binding of testosterone and 5α-dihydrotestosterone to the androgen receptor. Combination of ethinyl estradiol (0.35 µg) and cyproterone acetate (2mg) is most scientific in Ideal for Hirsuit PCOS. treating hyperandrogenicity as well as maintaining the menstrual cyclicity. Dose 1 tab. daily from D1 to D21 which has to be repeated cyclically for a period of six months. also DROSPIRENONE Combination of ethinyl estradiol (30 µg) with Drospirenone (3mg), an analogue of spironolactone with unique antimineralocorticoid and antiandrogenic action has also been used. Ideal for Obese PCOS Combination of ethinyl estradiol (30 µg) with Desogestrel (20 µg) can also be used. Case studies of iSlimRx Name Doctor Age wt.after Total Starting program Weight wt.(kg) (kg) lost (kg) City Shailaja S Dr.Ravi Kothari 39yrs 95 86.6 8.4kg Poona Sanobar S Dr.Deepak Patil 18yrs 73.2 62.8 10.4kg Mumbai Janavi P Dr.Jatin Shah 26yrs 99.7 93.5 6.2kg Mumbai Manju Dr.Neena Malhotra 31yrs 120 103 17kg Delhi Udipi B Dt.Aparna Karanjakr 37yrs 79.9 70.1 9.8kg U.K Ritu G Dt.Ruby Singh 49yrs 67.1 61.3 5.8kg Dubai Pankti V Dr.Malav Shah 28yrs 79 67.2 11.8kg Ahmedabad Dhwani M Dr.Kanti Bansal 25yrs 77 67.3 9.7kg Ahmedabad OUR EXPERIENCE 4 PTS IN DELHI AND AGRA RAINBOW IVF ARE ON THIS THERAPY 3 HAVE SHOWN SIGNIFICANT WT LOSS ONE HAS TO YET REPORT BACK ONE LOST 15 KGS IN 3 MONTHS AND IS NOW TAKEN FOR IVF OTHER DRUGS WHICH CAN BE ADDITION TO O.C.P. USED IN In cases of failure or where there is clinical or biochemical evidence of gross hyperandrogenicity or hyperinsulinemia, addition of metformin is recommended. Spironolactone- it has antiandrogenic effects in doses 100-200 mg daily. Finasteride - a competitive inhibitor of Type-2 5a reductase to treat hirsutism. Dose 1-5 mg/day. IMPROVEMENT OF HYPERINSULINEMIA BY INSULIN SENSITIZERS Directly sensitizing insulin receptors. Preventing neoglucogenesis. Reducing absorption of glucose from intestine. Increasing hepatic synthesis of SHBG level thereby reducing the level of bioactive free testosterone. Metformin Decreases basal hepatic glucose output in patients and lowers fasting plasma glucose concentration. It increases the uptake and oxidation of glucose by adipose tissue as well as lipogenesis. S/E- diarrhoea, nausea, vomiting ,specially initially. To avoid them metformin should be taken with meals and the dose increased gradually. Decrease in levels of leptin prevents excess estrogen formation and leads to normal restoration of HPO axis and hence ovulation. MetforminDosage 500-1500 mg daily in divided doses for six to nine months. OTHER DRUGS WHICH CAN BE USED Rosiglitazone , Pioglitazone, D chiro inositol, N acetyl cysteine. Other combinations Need a drug to LIKELY CAUSES Insulin Resistance and Hyperinsulinemia Low-grade inflammation (This can trigger insulin resistance) Heredity (researchers are looking into gene mutations) Excessive exposure to androgens in fetal life Insulin Resistance – What is It? • Inability of insulin to demonstrate its metabolic actions • It may be due to: • Decrease in affinity of insulin receptors towards insulin • Impaired signaling inside cell • Decrease in number of insulin receptors Management The first step in managing polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is getting regular exercise, eating a healthy diet, and not smoking. 1. Exercise: Bharadvajasana Running/Jogging Butterfly pose Chakki Chalanasana Management 2. Nutrition: The ideal diet plan for women with PCOS should compose of balanced meals including carbohydrates, proteins and fats Eat small meals at regular intervals and avoid large meals which would result in rise in blood glucose levels Consume fruits, vegetables, beans, legumes, whole grains, fish, lean meats, nuts and seeds Limit sugars and enriched carbohydrates Limit salt intake Avoid saturated fats Myo-inositol for PCOS Myo-inositol has shown promising results in studies of women with PCOS. It works by helping body to manage its use of insulin, restore balance to hormones, improve egg quality and help to regulate menses. It also aids in balancing appetite and moves fat from liver, which is beneficial to women who suffer from PCOS and are overweight because of it. How Does Myo-inositol for PCOS Work? Many women with PCOS struggle with insulin resistance. Inositol naturally made by the body is actually an important messenger molecule in insulin signaling. Insulin in the blood stream binds to receptors on cell walls, which sets off a biochemical cascade that leads to glucose being taken in and used by cells. Inositol is part of this reaction. Women with PCOS excrete inositol so quickly that they often do not have enough inositol to support this reaction, causing insulin resistance. Supplementing with inositol thus can reduce insulin resistance and improve the way glucose is used in the body. Role of Inositol Derivatives in PCOS INOSITOL is a polyalcohol Is a key messenger in the insulin signalling pathway Deficiency of inositol may be linked to insulin resistance Isabella R and Raffone E. Journal of Ovarian Research 2012, 5:14. MI+DCI: CLINICAL EFFICACY • MI+DCI synergistically improve insulin resistance, reduce hyperandrogenism and to induce ovulation in PCOS vs. MI alone in women with PCOS. • Improved LDL, HDL, and triglyceride levels vs. baseline values • Duration of therapy evaluated in the studies: 6 months. • DOSAGE REGIMEN: 550 mg of MI+13.8 mg of DCI (40:1 ratio) in soft gel capsule form twice a day. Nordio M, Proietti E. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2012; 16(5): 575-81. BENEFITS OF MYO-INOSITOL restores normal ovulatory activity increases fertilization rate prevents spina bifida birth defect lowers free testosterone (research has shown up to a 73% reduction) lowers total testosterone (as much as 65% reduction) lowers LH (as much as 55% reduction) lowers insulin response after meals (as much as 62% reduction) lowers DHEA-S (as much as 49% reduction) increases SHBG (as much as 92% increase) lowers androstenedione (as much as 27% reduction) lowers triglycerides (as much as 51% reduction) lowers blood pressure (minor decrease) increases peak progesterone (129% increase in one study) PROTISOL PROTEIN + INOSITOL SUPPLEMENT One of the major reason for PCOS is poor diet. Most Indian diets are low in Protein. Taking Protein supplements, especially plant protein, benefits those suffering from PCOS. PROTISOL is a unique blend of high quality imported pea protein and Inositols (Myo-Inositol & D-Chiro-inositol in ratio of 40:1). Each dosage of 20 gm contains 2 gm of Inositols. 2 doses a day meets the recommended daily dosage of 4 gm of Inositols. PCOS is associated with low 25-hydroxyvitamin D [25(OH)D] levels Increased insulin resistance, and obesity Increased androgen levels Low vitamin D in PCOS Poor follicle maturation Menstrual irregularity Poor oocyte quality MENSTRUAL IRREGULARITIES Mostly managed by OCP MPA 10 mg/day or micronized progesterone 300 mg at bedtime for 10 - 14 days effective in Rx of abnormal bleeding. If oligomenorrhoea and amenorrhoea does not respond to oral contraceptives and antiandrogen combinations, insulin sensitizing agents have to be added. A lean PCOS may also have insulin resistance and therefore if they do not respond to oral contraceptive dose, insulin sensitizing drug has to be added. COSMETIC TREATMENT Antiandrogens used in PCOS will prevent further hair growth but the hair which have already grown have to be treated by epilation, waxing, by electrolysis or laser treatments. Acne may require oral antibiotics like erythromycin and isotretinoin ointment. Acne also gets cleared in 6-9 months by use of oral contraceptive pills containing cyproterone acetate. Excessive Hair Mechanical method Laser Waxing Shaving Management 3. Dealing with acne: Acne and oily skin are primarily the result of hormonal disorders caused by androgens (male hormones). Wash face twice daily Use hypoallergenic products and mild soaps whenever possible Clean your bed sheets, especially your pillowcase weekly Avoid foods that are high in sugar or fried RESPONSE TO TREATMENT IS ASSESSED BY Resumption of menstrual cyclicity. Reduction in features of hyperandrogenicity. Improvement of biochemical parameters like reduction of free serum testosterone and normalization of fasting glucose insulin ratio. Different clinical situations Newly married not wanting conception Married wanting conception Married has one child wants spacing Secondary infertility Newer concepts in medical management Managing Mature PCOs. •Developed from articles publish from 1966 to 2006. The Metabolic Syndrome: WHO criteria IGT/IFG or type 2 diabetes Central Obesity BMI > 30 kg/m² Insulin resistance (glucose uptake below lowest quartile) METABOLIC SYNDROME Microalbuminuria UAE 20 µg min Blood pressure 160/90 mmHg Triglycerides & HDL-Ch > 150 mg/dl < 35 mg/dl Alberti & Zimmet WHO 1998 Diabetic Medicine. CONCLUSION Enigmatic,lesser understood Diagnosis can be tricky Management is age and need oriented Lifestyle modification is the crux. Fertility can be difficult. Prevention of longterm implications should be kept in mind These module have been created with the help of all my friends at FOGSI who have devoted precious time to send certain messages relevant for our day to day practice. My special thanks to: Dr.Sanjay Gupte Dr. C.N. Purandare Dr.Roza Olyai Dr.Rishma Pai Dr.Pratap Kumar Dr. Richa Singh Dr.P.K.Sekharan Dr.Sujata kar Dr.R.N.Goel Dr.Tushar Kar Dr.Anupam Gupta Dr.P.K. Shah Dr.Mandakini Parihar Dr.Abha Majumdar Dr.Sudha Prasad Dr.Maninder Ahuja Dr.Nalini Mahajan Dr. Girija Wagh Dr.Sunita Tandulwadkar Dr.Shanta Kumari Dr.Laxmi Shrikhande THANK YOU CONGRATULATIOSN UP HARYANA&DELHI ISAR FOR THIS WONDERFUL 3 DAYS