Quality Standards for Diabetes Care Toolkit
... Diabetes presents a serious health challenge for New Zealand, with 8% of the adult population known to have type 2 diabetes, rising at a rate of 7–8% per annum, and 25% known to have pre-diabetes (Coppell et al 2013). According to the Virtual Diabetes Register (VDR) as at 31 December 2013 (summary a ...
... Diabetes presents a serious health challenge for New Zealand, with 8% of the adult population known to have type 2 diabetes, rising at a rate of 7–8% per annum, and 25% known to have pre-diabetes (Coppell et al 2013). According to the Virtual Diabetes Register (VDR) as at 31 December 2013 (summary a ...
ADA: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes 2017
... individual patient in mind. Individual circumstances, such as comorbid and coexisting diseases, age, education, disability, and, above all, patients’ values and preferences, must be considered and may lead to different treatment targets and strategies. Furthermore, conventional evidence hierarchies, ...
... individual patient in mind. Individual circumstances, such as comorbid and coexisting diseases, age, education, disability, and, above all, patients’ values and preferences, must be considered and may lead to different treatment targets and strategies. Furthermore, conventional evidence hierarchies, ...
standards of medical care in diabetes—2017
... individual patient in mind. Individual circumstances, such as comorbid and coexisting diseases, age, education, disability, and, above all, patients’ values and preferences, must be considered and may lead to different treatment targets and strategies. Furthermore, conventional evidence hierarchies, ...
... individual patient in mind. Individual circumstances, such as comorbid and coexisting diseases, age, education, disability, and, above all, patients’ values and preferences, must be considered and may lead to different treatment targets and strategies. Furthermore, conventional evidence hierarchies, ...
Clinical practice guidelines: Type 1 diabetes in children and adolescents
... for a period not exceeding five years, at which date the approval expires. The NHMRC expects that all guidelines will be reviewed no less than once every five years. Readers should check with the Department of Health and Ageing for any reviews or updates of these guidelines. ...
... for a period not exceeding five years, at which date the approval expires. The NHMRC expects that all guidelines will be reviewed no less than once every five years. Readers should check with the Department of Health and Ageing for any reviews or updates of these guidelines. ...
ADA: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes 2016
... must always be interpreted with the individual patient in mind. Individual circumstances, such as comorbid and coexisting diseases, age, education, disability, and, above all, patients’ values and preferences, must be considered and may lead to different treatment targets and strategies. Furthermore ...
... must always be interpreted with the individual patient in mind. Individual circumstances, such as comorbid and coexisting diseases, age, education, disability, and, above all, patients’ values and preferences, must be considered and may lead to different treatment targets and strategies. Furthermore ...
SENSORY NEURON INSULIN SIGNALING AND ITS
... helpful. It is an environment like that which makes research possible. A special thanks to Dr. Julie Christianson for advice on science and life, Dr. Mark Chertoff for help with statistical analysis, and Dr. Ken McCarson for help with pharmacological analysis. Additionally, I would like to thank the ...
... helpful. It is an environment like that which makes research possible. A special thanks to Dr. Julie Christianson for advice on science and life, Dr. Mark Chertoff for help with statistical analysis, and Dr. Ken McCarson for help with pharmacological analysis. Additionally, I would like to thank the ...
Epidemiology, Pathophysiology and Diagnosis
... research into the aetiology of the disease, and for health promotion and disease prevention programs. 4. Awareness of any change in the nature of diabetes over time. Furthermore, it will facilitate the evaluation of intervention programs. The epidemiology of IFG and IGT also needs to be considered a ...
... research into the aetiology of the disease, and for health promotion and disease prevention programs. 4. Awareness of any change in the nature of diabetes over time. Furthermore, it will facilitate the evaluation of intervention programs. The epidemiology of IFG and IGT also needs to be considered a ...
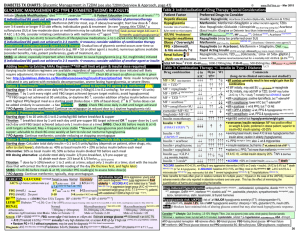
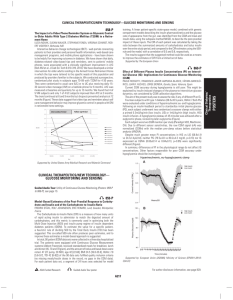
Glycemic Management in T2DM
... Note: benefits for trials often given in relative numbers for multiple years (~10years in the case of the UKPDS); however adverse events often only reported in absolute numbers over one year. This has the effect of minimizing the quantification of harms and exaggerating the benefits. Drug-induced Hy ...
... Note: benefits for trials often given in relative numbers for multiple years (~10years in the case of the UKPDS); however adverse events often only reported in absolute numbers over one year. This has the effect of minimizing the quantification of harms and exaggerating the benefits. Drug-induced Hy ...
Pharmacokinetics of Metformin during Pregnancy
... of the mother’s weight-adjusted dose. Our results indicate that metformin pharmacokinetics are affected by pregnancy-related changes in renal filtration and net tubular transport and can be roughly estimated by the use of creatinine clearance. At the time of delivery, the fetus is exposed to metform ...
... of the mother’s weight-adjusted dose. Our results indicate that metformin pharmacokinetics are affected by pregnancy-related changes in renal filtration and net tubular transport and can be roughly estimated by the use of creatinine clearance. At the time of delivery, the fetus is exposed to metform ...
Pharmacokinetics of Metformin during pregnancy (2010)
... of the mother’s weight-adjusted dose. Our results indicate that metformin pharmacokinetics are affected by pregnancy-related changes in renal filtration and net tubular transport and can be roughly estimated by the use of creatinine clearance. At the time of delivery, the fetus is exposed to metform ...
... of the mother’s weight-adjusted dose. Our results indicate that metformin pharmacokinetics are affected by pregnancy-related changes in renal filtration and net tubular transport and can be roughly estimated by the use of creatinine clearance. At the time of delivery, the fetus is exposed to metform ...
standardofcare2017fulldeckfinal - Diabetes Pro
... BMI ≥25 kg/m2 or ≥23 kg/m2 in Asian Americans who have 1 or more add’l dm risk factors. B • For all patients, testing should begin at age 45 years. B • If tests are normal, repeat testing carried out at a minimum of 3-year intervals is reasonable. C American Diabetes Association Standards of Medical ...
... BMI ≥25 kg/m2 or ≥23 kg/m2 in Asian Americans who have 1 or more add’l dm risk factors. B • For all patients, testing should begin at age 45 years. B • If tests are normal, repeat testing carried out at a minimum of 3-year intervals is reasonable. C American Diabetes Association Standards of Medical ...
Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes - Diabetes Care
... large portion of the diabetic population remains unaware of its condition. Thus, the lower sensitivity of A1C at the designated cut point may well be offset by the test’s greater practicality, and wider application of a more convenient test (A1C) may actually increase the number of diagnoses made. A ...
... large portion of the diabetic population remains unaware of its condition. Thus, the lower sensitivity of A1C at the designated cut point may well be offset by the test’s greater practicality, and wider application of a more convenient test (A1C) may actually increase the number of diagnoses made. A ...
PRODUCT MONOGRAPH HUMALOG HUMALOG 200 units/mL
... Pregnant Women HUMALOG can be used in pregnancy if clinically indicated. Data on a large number of exposed pregnancies do not indicate any adverse effect of HUMALOG 100 units/mL on pregnancy or on the health of the foetus/newborn. It is essential to maintain good glucose control in both gestational ...
... Pregnant Women HUMALOG can be used in pregnancy if clinically indicated. Data on a large number of exposed pregnancies do not indicate any adverse effect of HUMALOG 100 units/mL on pregnancy or on the health of the foetus/newborn. It is essential to maintain good glucose control in both gestational ...
Humalog® 200 units/mL KwikPen
... Pregnant Women HUMALOG can be used in pregnancy if clinically indicated. Data on a large number of exposed pregnancies do not indicate any adverse effect of HUMALOG 100 units/mL on pregnancy or on the health of the foetus/newborn. It is essential to maintain good glucose control in both gestational ...
... Pregnant Women HUMALOG can be used in pregnancy if clinically indicated. Data on a large number of exposed pregnancies do not indicate any adverse effect of HUMALOG 100 units/mL on pregnancy or on the health of the foetus/newborn. It is essential to maintain good glucose control in both gestational ...
The Underdiagnosis of Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome in
... Because of the metabolic abnormalities associated with PCOS, a 75g oral glucose-tolerance test (OGTT) is suggested to evaluate for insulin resistance (IR) and diabetes mellitus (DM) (Cowan, 2009). It is recommended to obtain a baseline fasting glucose level followed by a 2-hour glucose level (Emans ...
... Because of the metabolic abnormalities associated with PCOS, a 75g oral glucose-tolerance test (OGTT) is suggested to evaluate for insulin resistance (IR) and diabetes mellitus (DM) (Cowan, 2009). It is recommended to obtain a baseline fasting glucose level followed by a 2-hour glucose level (Emans ...
Part 4 – ToR 8 Benefits and safety of insulin pump therapy
... and reduced rates of severe hypoglycaemia and hospitalisation for ketoacidosis (Johnson 2013). Before-and-after studies showed statistically significant reductions in HbA1c of 0.4–2.6% in adults using insulin pump therapy at 2–6 years follow-up, with the majority showing reductions of 0.4-0.7%. The ...
... and reduced rates of severe hypoglycaemia and hospitalisation for ketoacidosis (Johnson 2013). Before-and-after studies showed statistically significant reductions in HbA1c of 0.4–2.6% in adults using insulin pump therapy at 2–6 years follow-up, with the majority showing reductions of 0.4-0.7%. The ...
Novolin®ge – Product Monograph Page 1 of 54 PRODUCT
... There is no information available on teratogenicity of human insulin products. Special Populations Pregnant Women During pregnancy and lactation, diabetes may become more difficult to manage. However, optimal metabolic control not only during pregnancy, but also prior to conception has proven to be ...
... There is no information available on teratogenicity of human insulin products. Special Populations Pregnant Women During pregnancy and lactation, diabetes may become more difficult to manage. However, optimal metabolic control not only during pregnancy, but also prior to conception has proven to be ...
The national system for monitoring diabetes in Australia
... Diabetes has become one of the leading threats to the health of Australians. It has been estimated that around one million Australians (7.6% of the population) have diabetes, with 85–90% of these people having Type 2 diabetes (ABS 1997, p.19; Dunstan et al. 2002). Evidence suggests that up to half o ...
... Diabetes has become one of the leading threats to the health of Australians. It has been estimated that around one million Australians (7.6% of the population) have diabetes, with 85–90% of these people having Type 2 diabetes (ABS 1997, p.19; Dunstan et al. 2002). Evidence suggests that up to half o ...
I N T E R N A T I O...
... years) was estimated to be 1.8 billion, of whom 0.02% have diabetes. This means that approximately 440,000 children around the world have diabetes with 70,000 new cases diagnosed each year (1). This very large number of children needs help to survive with injections of insulin to live a full life wi ...
... years) was estimated to be 1.8 billion, of whom 0.02% have diabetes. This means that approximately 440,000 children around the world have diabetes with 70,000 new cases diagnosed each year (1). This very large number of children needs help to survive with injections of insulin to live a full life wi ...
SELF EFFICACY, SELF RELIANCE, ADHERENCE TO SELF CARE
... Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of a group of metabolic disorders that is characterized by high blood glucose levels resulting from defects in the body's ability to produce or use insulin. The body either does not produce enough insulin or is unable to efficiently utilize insulin to convert ...
... Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of a group of metabolic disorders that is characterized by high blood glucose levels resulting from defects in the body's ability to produce or use insulin. The body either does not produce enough insulin or is unable to efficiently utilize insulin to convert ...
2013 ADA Posters 386-1338.indd - American Diabetes Association
... patients and their healthcare providers (HCPs). Tools that allow rapid evaluation of blood glucose (BG) patterns by HCPs during short office visits and provide insight to patients between visits to enable positive changes may support these efforts. This study evaluated HCP experience with a BG meter ...
... patients and their healthcare providers (HCPs). Tools that allow rapid evaluation of blood glucose (BG) patterns by HCPs during short office visits and provide insight to patients between visits to enable positive changes may support these efforts. This study evaluated HCP experience with a BG meter ...
Practical Guide Insulin Therapy
... Numerous randomised controlled trials and large observational studies have shown that good glycemic control can be achieved in patients with T2DM who are treated with insulin or insulin analogues using treatment algorithms5,6. As most people with T2DM will ultimately require long-term insulin therap ...
... Numerous randomised controlled trials and large observational studies have shown that good glycemic control can be achieved in patients with T2DM who are treated with insulin or insulin analogues using treatment algorithms5,6. As most people with T2DM will ultimately require long-term insulin therap ...
Curriculum - International Diabetes Federation
... slides and teaching notes, are available at the ...
... slides and teaching notes, are available at the ...
The effects of aerobic and resistance exercise on inflammatory
... 4.4.1. Acute exercise (one session) ........................................................................ 157 4.4.2. Chronic exercise (12sessions) ...................................................................... 161 ...
... 4.4.1. Acute exercise (one session) ........................................................................ 157 4.4.2. Chronic exercise (12sessions) ...................................................................... 161 ...
General practice management of type 2 diabetes
... Those with BMI >35 kg/m2 and comorbidities, or BMI >40 kg/m2, greater weight loss measures should be considered Note that BMI is a difficult parameter to standardise between different population groups ...
... Those with BMI >35 kg/m2 and comorbidities, or BMI >40 kg/m2, greater weight loss measures should be considered Note that BMI is a difficult parameter to standardise between different population groups ...
Gestational diabetes
Gestational diabetes (or gestational diabetes mellitus, GDM) is a condition in which women without previously diagnosed diabetes exhibit high blood glucose (blood sugar) levels during pregnancy (especially during their third trimester). Gestational diabetes is caused when insulin receptors do not function properly. This is likely due to pregnancy-related factors such as the presence of human placental lactogen that interferes with susceptible insulin receptors. This in turn causes inappropriately elevated blood sugar levels.Gestational diabetes generally has few symptoms and it is most commonly diagnosed by screening during pregnancy. Diagnostic tests detect inappropriately high levels of glucose in blood samples. Gestational diabetes affects 3-10% of pregnancies, depending on the population studied.As with diabetes mellitus in pregnancy in general, babies born to mothers with untreated gestational diabetes are typically at increased risk of problems such as being large for gestational age (which may lead to delivery complications), low blood sugar, and jaundice. If untreated, it can also cause seizures or stillbirth. Gestational diabetes is a treatable condition and women who have adequate control of glucose levels can effectively decrease these risks. The food plan is often the first recommended target for strategic management of GDM.Women with unmanaged gestational diabetes are at increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes mellitus (or, very rarely, latent autoimmune diabetes or Type 1) after pregnancy, as well as having a higher incidence of pre-eclampsia and Caesarean section; their offspring are prone to developing childhood obesity, with type 2 diabetes later in life. Most women are able to manage their blood glucose levels with a modified diet and the introduction of moderate exercise, but some require antidiabetic drugs, including insulin.