* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The buoyant force on an object totally submerged in a fluid depends
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
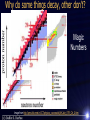
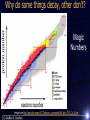
Discussion question: If a nucleus undergoes radioactive decay it must be older than the other nuclei in the sample that haven’t decayed. A. B. True False Types of radioactive decay Gamma Beta (+,-, e.c.) Alpha Neutron emission Fission Fusion Gamma Decay Nucleus in excited state gives off energy as a photon 14 6𝐶 ∗ → 14 6𝐶 +𝛾 Beta Decay – electron and positron decay Changes a proton to a neutron or a neutron to a proton β- 14 β+ 141 Sm 62 e.c. 6C 18 F 9 +e Alpha Decay--42He given off Alpha particle is a very low energy system / very tightly bound 226 88Ra 238 A. B. C. D. E. U 92 alpha beta + beta – e.c. gamma 234 Th + ? 90 T1/2 = 4.5 Gy 234 A. B. C. D. E. 90Th alpha beta + beta – e.c. gamma 234 91Pa + ? T1/2 = 24 days Why do some things decay, other don’t? Magic Numbers Image from http://pms.iitk.ernet.in/ICT/physics_courses/akj/AKJain_IITR_Ch_2.htm Why do some things decay, other don’t? Magic Numbers Image from http://pms.iitk.ernet.in/ICT/physics_courses/akj/AKJain_IITR_Ch_2.htm Small nuclei – N ~ Z Large nuclei – N > Z Radiometric Dating Carbon Dating – Cosmic rays release neutrons – 14N + n → 14C + 1H Half life of ~5760 years – Compare carbon-12 to carbon-14 ratio – Limitations Must be organic Has the ratio of C-12 to C-14 always been the same? – Calibration 50,000 years limit (not much C-14 left) 2 Nephi 2:26 And the Messiah cometh in the fulness of time, that he may redeem the children of men from the fall. And because that they are redeemed from the fall they have become free forever, knowing good from evil; to act for themselves and not to be acted upon, save it be by the punishment of the law at the great and last day, according to the commandments which God hath given. More Proof 226 Ra 88 eventually becomes 20682Pb. What is released in this process? A. B. C. D. E. only alphas only betas both but more alphas than betas both but the same number of alphas and betas both but more betas than alphas 232 90 Th 237 93 238 92 Np 235 92 U U N 238 92 234 90 U Th 145 234 91 234 92 230 90 Th 140 226 90 80 85 Pa U Ra 90 Z http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Decay_chain Penetration Depth Alpha– only a few cm through air Beta—only through air—blocked by paper or sheet of metal Gamma rays—short wavelength light— penetrate several cm lead or a meter of concrete. Easily penetrates the skin and interacts with human cells—these are the dangerous ones. What has to be true for a particular type of nuclear decay to happen? Conservation of . . . – Energy, momentum, angular momentum Compare rest energy OK if we go down in energy – turn into kinetic – Lepton number, Baryon number, … Force to make it happen For radioactive decay where No is the number of nuclei you start with and N is the number of nuclei after a time t N Noe t How do I solve for λ? Discussion question: Over the course of 3 hours, 15% of a radioactive material decays. What is its half-life? A. B. C. D. E. 4.1 hrs 12.8 hrs 24.0 hrs 68.6 hrs 84.2 hrs #decays/sec=λN 1 Ci = 3.7x1010 decays/sec Fission: Heavy Elements can reduce energy (i.e. increase binding energy per nucleon) by splitting roughly in half.