* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Testicular Cancer Prevention
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
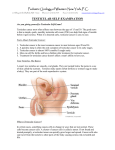
What You Need to Know About: Testicular Cancer While testicular cancer is a rare type of cancer, it is the most common cancer found in men age 15 to 35. Fortunately, most forms of testicular cancer are curable if they can be detected early. What is testicular cancer? Testicular cancer occurs when abnormal cells grow uncontrollably in the testicles. Who is at the highest risk for developing this cancer? The following conditions increase the risk of developing this cancer: Undescended testicle Abnormal testicular development Klinefelter syndrome (a genetic disorder) Previous diagnosis of testicular cancer Infertility from sperm problems Testicular cancer is more common in Caucasians than African-Americans. What are the symptoms? The most common symptoms of testicular cancer include: Heavy feeling in the scrotum Change in size or shape of one or both of the testes, which may or may not be painful Dull lower back, groin, and/or belly pressure How is testicular cancer diagnosed? Many men find it themselves during a self-exam, so it’s important to perform regular self-exams. Your physician may also find testicular cancer during a routine physical exam. If cancer is suspected, your physician will likely order imaging tests, such as an ultrasound or a CT (CAT) scan, to find out if the cancer is spreading. How is this cancer treated? A physician will perform surgery to remove the cancerous testicle. A biopsy of the testicle will reveal what type of cancer cells you have, which will help your physician devise a treatment plan. Treatment after surgery may include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and/or removal of lymph nodes. Visit PacificSource.com for free online tools and resources As a PacificSource member, you can access CaféWell, an online health engagement portal. To get started, go to PacificSource.com, log into InTouch, and then click on the CaféWell button. Visit CaféWell to: Complete the health assessment to identify your potential health risks. Get your health and wellness questions answered by an expert health coach. Connect with family, friends, and others with similar health goals. Access helpful tips and articles on health and wellness. If you have questions about your coverage, a claim, or any benefit or service, please visit PacificSource.com and log in to InTouch for Members to access information, or contact our Customer Service team: Email: [email protected] Phone: Idaho: 208.333.1596 or 800.688.5008 Montana: 406.442.6589 or 877.590.1596 Oregon: 541.684.5582 or 888.977.9299 En Español: 541.684.5456 or 800.624.6052, ext. 1009 © 2009