* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Questions on Vascular System
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
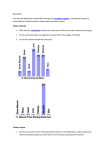
1. Following the release of oxygen at the tissues the blood is returned to the heart. Identify four mechanisms that aid venous return during exercise. (4) 2. Describe the changes that occur in the distribution of cardiac output as a performer moves from rest to exercise. (4) 3. Identify two changes to the vascular system during a warm up. (2) 4. Describe how conduction system of heart controls cardiac cycle to ensure enough blood is ejected from heart during a training run. (4 ) 5. During a game of football, a player’s heart rate will vary. Explain how changes in the acidity of the blood cause the heart rate to increase during a game of football. (4) Mark scheme: 1. 1 Valves 2 Skeletal muscular pump 3 Respiratory pump 4 Venoconstriction/venomotor control/smooth muscle 5 Gravity for blood from above heart 2. Describe the changes that occur in the distribution of cardiac output as a performer moves from rest to exercise. (Describe) 1. More blood is distributed to the working muscles 2. Less blood is distributed to non essential organs 3. Vasodilation of arteries/arterioles supplying working muscles/Vascular shunt 4. Opening of precapillary sphincters supplying working muscles 5. Vasodilation of arteries/arterioles supplying non essential organs 6. Closing of precapillary sphincters supplying non essential organs. 3. 1. Increases blood flow/cardiac output/stroke volume/oxygen delivery to working muscles/delays OBLA 2 Blood vessels/arterioles within the muscle dilate/vasodilatation/ vascular shunt 3 Pre capillary sphincters/capillaries dilate at muscle 4 Blood vessels/arterioles at non-essential organs constrict/vasoconstriction 5 Pre capillary sphincters/capillaries constrict at organs 6 Decreases blood viscosity 7 Blood transports heat to be released at skin/increased temperature 8 Increased hormonal/nutrient/enzyme transport/activity 9 Increase in venous return/blood pressure 4. 1 Impulse initiates from SA (sino atrial) node 2 This causes atria to contract/atrial systole/blood ejected from the right and left atria/atrial depolarisation. 3 Impulse received by AV (atrioventricular) node 4 Impulse conducted down Bundle of His 5 Up the Purkinje fibres 6 This causes ventricles to contract/ventricular systole/blood ejected out of right and left ventricles/ventricular depolarisation 7 The atria/ventricles relax to allow the heart to refill with blood. 5. A. Blood’s acidity increases/pH lowers; B. Caused by more carbon dioxide being produced; C. This is detected by chemoreceptors; D. Nerve messages are sent to the medulla (oblongata)/cardiac (control) centre; E. Sympathetic nervous impulses are sent; F. To the Sino-Atrio node/SAN/SA node; G. Decrease in parasympathetic/vagus nerve impulses; Vascular System - Answers 1. Following the release of oxygen at the tissues the blood is returned to the heart (venous return). i) Identify four mechanisms that aid venous return during exercise. 1 Valves 2 Skeletal muscular pump 3 Respiratory pump 4 Venoconstriction/venomotor control/smooth muscle 5 Gravity for blood from above heart (4) May 04 2. Describe the changes that occur in the distribution of cardiac output as a performer moves from rest to exercise. Explain how the vasomotor centre controls this distribution. (Describe) 7. More blood is distributed to the working muscles 8. Less blood is distributed to non essential organs (Explanation) 9. Vasodilation of arteries/arterioles supplying working muscles/Vascular shunt 10. Opening of precapillary sphincters supplying working muscles 11. Vasodilation of arteries/arterioles supplying non essential organs 12. Closing of precapillary sphincters supplying non essential organs. (4) Jan 04 3. Identify two changes to the vascular system during a warm up. 2 marks max 1. Increases blood flow/cardiac output/stroke volume/oxygen delivery to working muscles/delays OBLA 2 Blood vessels/arterioles within the muscle dilate/vasodilatation/ vascular shunt 3 Pre capillary sphincters/capillaries dilate at muscle 4 Blood vessels/arterioles at non-essential organs constrict/vasoconstriction 5 Pre capillary sphincters/capillaries constrict at organs 6 Decreases blood viscosity 7 Blood transports heat to be released at skin/increased temperature 8 Increased hormonal/nutrient/enzyme transport/activity 9 Increase in venous return/blood pressure 4. What effects will a cool down have on the vascular system of a performer? 2 marks max 1. Flushes out lactic acid/waste products/repays oxygen debt 2. Keeps capillaries dilated/maintains blood flow/oxygen to muscles 3. Maintains skeletal muscle pump/respiratory pump 4. Prevents blood pooling 5. Maintains venous return 6. Maintains stroke volume/cardiac output 7. Maintains blood pressure 8. Keeps metabolic activity elevated/gradually decreases heart rate 5. Describe how oxygen and carbon dioxide are transported in the blood. 4 marks max (3 max for any one gas) Oxygen – 1. Dissolves in the plasma 2. Combines with haemoglobin 3. To form oxyhaemoglobin Carbondioxide 4. Dissolves in the plasma 5. Combines with haemoglobin 6. Forms carbaminohaemoglobin 7. Dissolves in water/forms carbonic acid 8. in plasma dissociates to hydrogen ions/bicarbonate ions