* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Reader 1 - Development of Civilizations
Discovery of human antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Potential cultural impact of extraterrestrial contact wikipedia , lookup
Human variability wikipedia , lookup
Nutritional anthropology wikipedia , lookup
Anarcho-primitivism wikipedia , lookup
Environmental determinism wikipedia , lookup
Cultural anthropology wikipedia , lookup
Cradle of civilization wikipedia , lookup
Post-excavation analysis wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary origin of religions wikipedia , lookup
Hunter-gatherer wikipedia , lookup
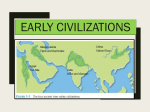
ORIGINS CIVILIZATION OF Due: 8/2/2016 Vocabulary Using a dictionary or the textbook, write the word with its corresponding definition in your notebook. 1. artifact 2. archeology 3. anthropology 4. homo sapien 5. nomad 6. domestication 7. civilization 8. Paleolithic 9. Neolithic 10.artisan Culture. Community. Civilization. All of these describe certain people-groups, but what is the difference between each of these ideas? And what does a people-group have to become in order to be considered a civilization? As we study the history of the World, we must determine the make-up of different lands and people-groups in order to determine the level of influence each has had on the development of the world. Anthropologists disagree with the definition of each of these ideas, however, there are certain markers that help us categorize differing people-groups. At the first level, we define society as “a structured community of people bound together by similar traditions, institutions, or nationality.” This is broad, and could include large nations or even groups of just a few people. Hunter-Gatherers, nomadic groups of early humans who A BEHAVIOUR traveled in order to find and gather food, could be CONSIDERED considered a society. However, just because groups of people have something in common does not "CIVILIZED"BY automatically make them a civilization. A PARTICULAR Certain elements must come together before a human CULTURE MAY community develops to the level of sophistication BE JUDGED commonly referred to as civilization. The meaning of the SENSELESS OR term civilization is commonly used to describe human societies "with a high level of cultural and technological EVEN SEEN development", as opposed to what many consider to be WITH HORROR less "advanced" societies like a jungle tribe. This definition, however, is unclear, subjective, and it carries with it assumptions no longer accepted by modern scholarship on how human societies have changed during their BY ANOTHER long past. CULTURE. In the broader sense, "civilization" often refers to any distinct society. Every society, civilization or not, has a specific set of ideas and customs, and a certain set of items and arts, that make it unique. But true civilizations have more complex cultures, including literature, professional art, architecture, organized religion, and complex customs associated with the elite. Primary characteristics of a Civilization 1. Urban settlements 2. Specialists (or artisans) not involved in agricultural activities 3. Stable food supply 4. Class structure 5. State-level organization (government) Secondary characteristics of a Civilization 6. Monumental public building 7. Extensive trading networks 8. Standardized monumental artwork 9. Writing 10. Development of exact sciences How Do We Know About Early Civilizations? Scientists called anthropologists have studied anthropology, or the study of humankind, for many years. Archeologists are specially trained scientists who work like detectives to uncover the story of prehistoric peoples. They sift through dirt and rock to uncover and analyze any existing evidence such as bones and artifacts. Even though scientists were not there to actually observe or record the history of mankind, the evidence they find helps create the stories of different civilizations and historic events. These scientists have discovered a wealth of evidence concerning human progress which tells us how homo-sapiens developed from wandering nomads into permanent members of communities. Thousands of human fossils enable researchers and students to study the changes that occurred in brain and body size, locomotion, diet, and other aspects regarding the way of life of early human species. Millions of stone tools, figurines and paintings, footprints, and other traces of human behavior in the prehistoric record tell about where and how early humans lived and when certain technological innovations were invented. What Do We Know About Early Man? The earliest homo-sapiens were nomads, moving from place to place to forage (search) for new sources of food. Humans migrated across land masses looking for food supply, eventually wandering into new continents. Nomad groups whose food supply depended on hunting animals and collecting plant foods are called hunter-gatherers. For thousands of years, humans survived by traveling together in groups of 2570, hunting game and gathering edible plants. Their tools were crudely made from bones or stone. This era is called the Paleolithic era, and was the earliest part of the Stone Age. Neolithic or Agricultural Revolution The Neolithic Revolution was the last part of the Stone Age, and describes the era when the use of metal tools, weapons and farming was discovered. About 10,000 years ago, people in the Mesopotamia region began to realize they could domesticate plants, allowing them to plant crops that could provide a permanent food source. This caused early man to stop wandering and Agricultural economies settle down in one area or region, always developed while hunting around a large fresh water source such as a river. About the same time, they also and gathering activities began domesticating animals for meat, were reduced. milk, and skins. The skins of animals were used for clothing, storage, and to build tent shelters. Larger animals were used for working in the fields. The Neolithic (or Agricultural) Revolution is considered a major turning point in human history. Once humans settled into permanent communities, humans were able to develop new technologies and skills. Artisans became important to the growth of the community as they developed a specialization of trades such as art or weapons. Social structures, common religious beliefs and trading systems developed, and with them, the eventual rise of civilizations. The earliest civilizations such as the Indus Valley civilizations and Mesopotamia are no longer in existence as they were then, but we can see the development of entire ethnicities and nations that sprung forward from these early civilizations. As archeologists continue to uncover ancient ruins and artifacts, we discover more amazing evidence about our early ancestors and their ability to evolve and progress from simple hunters into powerful and productive civilizations.