* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electrons and Photons
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Bohr–Einstein debates wikipedia , lookup
Franck–Condon principle wikipedia , lookup
Particle in a box wikipedia , lookup
Delayed choice quantum eraser wikipedia , lookup
Double-slit experiment wikipedia , lookup
Electron configuration wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Matter wave wikipedia , lookup
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Ultrafast laser spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Population inversion wikipedia , lookup
Wave–particle duality wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
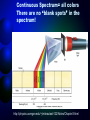
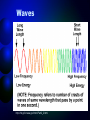
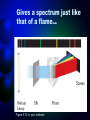
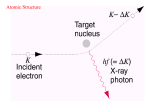
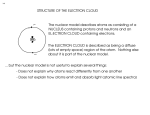
How atoms produce light http://www.wbateman.demon.co.uk/asa2sums/sum3.1B/topic3.1B.htm What is Light? • LIGHT is a form of energy • Light can be considered as a bunch of individual light “packets” called PHOTONS • Each packet has its own set of properties (wavelength, etc) • A bunch of these packets traveling together is like a ray of light. Continuous Spectrum= all colors There are no “blank spots” in the spectrum! http://physics.uoregon.edu/~jimbrau/astr122/Notes/Chapter3.html Why continuous spectrum? • A solid is heated…all of its atoms/molecules and their parts move really fast • Energy is given off as the atoms constantly vibrate. • Photons of all colors can be emitted. • All colors blend into “white light” Brightline Spectrum When only certain photons are observed, it means that only light packets of a particular type are being emitted! • Each photon has a specific energy value. • So only certain energy exchanges are happening within the heated substance. • So there must only be certain ways of changing the energy in the substance! How? • This can be explained by the movement of electrons! • We know from middle school that atoms have “layers” of electrons called energy levels. • Each energy level has electrons with a certain amount of energy in them that matches the level. • When the electrons change levels, they have to gain or lose energy to do so. • Each time they lose energy, they emit a bundle of energy. • We see that bundle as a photon! Conclusion • Atoms only emit photons of specific energies • WHY?? All about… LIGHT LIGHT • A form of energy! • Travels in waves • Wave properties are all related • All light is part of the electromagnetic spectrum (like energy from the sun) • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=R VyHkV3wIyk Wave properties • Speed • Wavelength • Frequency • Energy http://web.chemistry.gatech.edu/~williams/bCour se_Information/6582/problem_sets/waves/index. html Speed • Light travels at the speed of light (duh!) • The speed of light = 2.998 x 108 m/s • The symbol “c” stands for the speed of light – c = 2.998 x 108 m/s • All light waves will have the same speed, so speed is a constant Waves http://rst.gsfc.nasa.gov/Intro/Part2_2.html Quantum • A specific quantity of light • Bohr said that when energy is added to atoms, the electrons gain a “quantum” of energy to move to a higher level. • When electrons relax back to their normal state, they emit a quantum of energy to go back to the lowest level. Quantum…photon • Photon is just the name for a quantum of light • Electron Transition – when an electron moves from one level to another – When an electron transitions to a higher energy level, a photon is absorbed. – When an electron transitions to a lower energy level, a photon is emitted. Quantum…photon • The emitted photon is just a “piece” of light. • It has a specific energy value, so it has a specific wavelength, frequency and color • If you can measure the wavelength of the photon, you can calculate its energy. Gas Discharge Tubes • Another way to give energy to the atom is using electricity http://www.physics.lsa.umich.edu/demolab/graphics2/7b10_10.jpg Gives a spectrum just like that of a flame… Figure 5.12 in your textbook Ta-daa • This is why scientists can calculate the energy values of the levels within an atom even though they can’t see them!