* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Welcome to Physics 112N
Copenhagen interpretation wikipedia , lookup
Bell's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Bell test experiments wikipedia , lookup
Particle in a box wikipedia , lookup
Wheeler's delayed choice experiment wikipedia , lookup
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
EPR paradox wikipedia , lookup
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
Canonical quantization wikipedia , lookup
Electron configuration wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization group wikipedia , lookup
Bohr–Einstein debates wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Hidden variable theory wikipedia , lookup
Matter wave wikipedia , lookup
Double-slit experiment wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
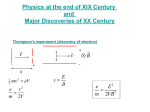
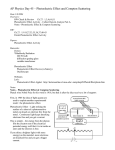
How I learned to stop worrying and love physics The Course So Far… • Introduction to the debates • General Epistemology • Epistemology of Science • Epistemology of Religion From here on …… • The big debates • Physics • • • • – Quantum Mechanics, Thermodynamics & Relativity – Astronomy & Cosmology Evolution, Creationism and Intelligent Design Mind and Cognition Morality, Ethics and Sociobiology Process thought Physics – The Beginnings • Assyrians, Babylonians, Egyptians • • • • • – Astronomy (Agrarian Societies) – Astrology Mayans, Aztecs Greeks – Systematized Scientific Thought Democritus vs. Aristotle (Two World Views) Astronomy, Mechanics, Optics……. Ptolemy vs. Aristarchus 9 14 16 28 30 Q/M Physics Q/M Philosophical Issues Implications Discussion Quiz Relativity Thermodynamics Implications Discussion 4 6 9 11 13 18 20 Astronomy/ Cosmology Religious Cosmologies Implications Discussion Quiz Evolution The Science Creationism Intelligent Design Implications Discussion Summary Discussion Quiz Essay Due Greek Physics • Aristotle – Four Elements (earth, Water, Air, fire) • Democritus – Atomistic View • Ptolemy – Geo-centric Universe • Aristarchus of Samos – Heliocentric Universe Ideas that prevailed in antiquity…. • Infinitely divisible matter, geocentric universe, ‘natural state’ of objects • Aristotle and Ptolemy • Dominated thought through the middle ages • Completely incorrect astronomy and mechanics • Alternate views present • Why did they not prevail? The Middle Ages • Rise of the Islamic empire • Translations from Greek • Developments in Astronomy, Optics, Mechanics • Did the ‘scientific method’ develop? The Scientific Revolution • Astronomy – Copernicus • Heliocentric Universe • Explains rotation of stars etc. in terms of earth’s movement around the sun – Galileo • Observations using telescope • Laws of motion – Kepler’s Laws • Tycho Brahe carefully collected data • Formulated mathematical laws The Scientific Revolution • Huygens – Wave theory of light – Astronomical observations • Boyle - Boyle’s Law - Steps towards Atomic Theory • Pascal – Fluid flows – Pascal’s Law The Scientific Revolution • Newton – Laws of Motion – Law of Gravitation – Kepler’s Laws follow from these general principles – Corpuscular Theory of Light – Development of Calculus to aid in understanding physics Philosophical Underpinnings • Realism – Theories describe the world as it is in itself • Determinism – Present state predicts future state • Reductionism – Whole is the sum of its parts Demise of Classical Physics • Ultraviolet Catastrophe – Quantization of energy • Nature of Light (Newton or Huygens) – Photoelectric Effect • Nature of Electrons – Double Slit Experiment The Ultraviolet Catastrophe Classical physics can describe the shape of the blackbody spectrum only at long wavelengths. At short wavelengths there is complete disagreement. This disagreement between observations and the classical theory is known as the ultraviolet catastrophe. Planck’s Solution In 1900, Max Planck was able to explain the observed blackbody spectrum by assuming that it originated from oscillators on the surface of the object and that the energies associated with the oscillators were discrete or quantized: En = nhf n = 0, 1, 2, 3… n is an integer called the quantum number h is Planck’s constant: 6.62 10-34 J·s f is the frequency The PhotoElectric Effect When light is incident on a surface (usually a metal), electrons can be ejected. This is known as the photoelectric effect. Around the turn of the century, observations of the photoelectric effect were in disagreement with the predictions of classical wave theory. Photoelectric Effect Observations of the Photoelectric Effect • No electrons are emitted if the frequency of the incident photons is below some cutoff value, independent of intensity. • The maximum kinetic energy of the emitted electrons does not depend on the light intensity. • The maximum kinetic energy of the emitted electrons does depend on the photon frequency. • Electrons are emitted almost instantaneously from the surface. The Photoelectric Effect Explained The photoelectric effect can be understood as follows: • Electrons are emitted by absorbing a single photon. • A certain amount of energy is required to remove the electron from the material. • The maximum observed kinetic energy is the difference between the photon energy and this energy. Double Slit Experiment • Electrons through a single slit act as particle • If we now have two slits close by a diffraction pattern is observed i.e wave like behavior • If we try and detect which slit the electron goes through the diffraction pattern disappears Double Slit Experiment The Strange Quantum World • Wave Particle Duality • How to describe systems? • Wave Function describes the state of a system in a probabilistic sense • Systems exist a superposition of states • Observation collapses to a particular state Schrodinger’s Cat Philosophical Underpinnings • Classical Realism – Physical theories describe nature as it is in itself • Instrumentalism – Theories a human constructs for correlating observations and making predictions • Critical Realism – Physical theories are a partial representation of limited aspects of the world as it interacts with us EPR Paradox • Two particles separate with zero initial momentum • Measure component of momentum of one • Automatically component of momentum of second is determined !!!! – Action at a distance? – Hidden Variables? – Holistic World? Two Views • Complementarity (Critical Realism?) – Must consider interaction between subject and object in an experiment – Conceptual limitation of understanding • Realism – Theories are description of nature in itself – Hidden Variables to explain away apparent indeterminacy? Points to Ponder • Does Complementarity imply instrumentalism? • Complementarity a good paradigm for science and religion? • Indeterminacy – temporary ignorance? – measurement or conceptual issue? – inherent to nature? • Parts and Wholes – A new paradigm for understanding the world?