* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Water pollution wikipedia , lookup
Anoxic event wikipedia , lookup
Secondary treatment wikipedia , lookup
Agroecology wikipedia , lookup
Freshwater environmental quality parameters wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable architecture wikipedia , lookup
Climate change feedback wikipedia , lookup
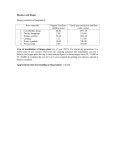
Introduction to Environment Renewable and Non Renewable resources Conventional Fuels Environmental Impacts of Conventional fuels Modern Fuels and their Environmental Impacts Methanogenic bacteria and biogas Microbial Hydrogen Production Conversion of sugars to ethanol The gasohol exp ,Solar energy Converters –Hopes from photosynthetic pigments Treatment of municipal waste and industrial effluents ucla genomics Methanogens are bacteria that produce methane gas They can be used as sources of biogas gas This would be a renewable source of energy Methanogens require anaerobic conditions In the digestive systems of herbivores, marshes or lake bottoms. Many require warm conditions to work best. They are associated with a source of organic matter (e.g. plant remains or sewage) and with heterotrophic bacteria The heterotrophs break down this organic matter to release compounds such as ethanoic acid (aka acetic acid or vinegar) and hydrogen The ethanoate ions are a substrate for the methanogens Methanogens belong to the Archaea group of the Prokaryotes Examples Methanococcus jannaschii Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum The prokaryote kingdom has been split into several further kingdoms (e.g. Archaea and Eubacteria) based on the genetics and biochemistry of microbes Methanogens are chemoautotrophs Methanogens use a number of different ways to produce methane Using ethanoate (acetate) that may be derived from the decomposition of cellulose: CH3COO+ + H- CH4 + CO2 +36 kJ mol-1 Or using hydrogen and carbon dioxide produced by the decomposers: 4 H2 + CO2 CH4 + 2 H2O +130.4 kJ mol-1 From the decomposition of wastes in farming sewage treatment A bi-product of the cleaning up of waste water Biogas consists of about 40% CO2 and 60% CH4 BEA Dithmarschen a fermenter, which is supplied with an innoculum of bacteria (methanogens and decomposers) anaerobic conditions an optimum temperature of 35°C an optimum pH of 6.5 to 8 This needs to be monitored as the decomposers produce acids and they work faster than the methanogens consume the acids organic waste (biomass) e.g. sewage, wood pulp Half of the methane produced by methanogens is used up as an energy source by other bacteria Half is lost to the atmosphere (600 M tonnes y-1) where it acts as an important greenhouse gas As more land is converted to rice paddy fields and pasture for grazing animals more methane will be produced DAF Shiga Pref. As global warming progresses the permafrost with thaw in the regions covered by tundra Tundra contains extensive reserves of frozen peat As the peat warms and melts, it will provide a source of material for methanogens The amount of methane release into the atmosphere will accelerate. This in turn will drive global warming even further Peatlands form 2030% of organic C in N. Hemisphere UNEP Formation First stage consists into making the waste dissolvable by the enzymes secreted from micro organisms. Then, the acid forming bacteria takes action and transforms these substances into small-structured substances like acetic acid. After that the methane forming bacteria converts these substances into biogas. Hydrolysis stage: Long chained complex carbohydrates proteins oils and lipids are transmuted into short chained forms. The first step known as hydrolysis is completed after this transmutation into basic organics. Acid formation stage: The dissolvable organic materials are transformed into small-structured materials as acetic acid volatile fatty acids hydrogen and carbon dioxide. Methane formation: The stage of acetic acid disintegration or hydrogen and carbon dioxide synthesis to acquire biogas by bacteria. Factors that effect biogas production The effects of heat: Methanogenic bacteria are inactive at very high or very low temperatures. That’s why the reactor heat effects the biogas production or its speed directly. The effects of PH: The most suitable PH levels for methane producing bacteria are neutral or have slightly alkali rates. The effects of toxicity: Antibiotic addition to foods in chicken farming has a toxicity effect in chicken compost using systems in biogas production. The effects of organic load speed: Organic load speed is daily organic material supply amount to bioreactors. Advantages of Biogas In our country animal and herbal wastes are burned directly or they are used as compost agricultural soil. But it is more common to burn wastes for heat production. Biogas production provides storage or organic wastes under controllable-suitable conditions. The uncontrolled storage of farm originated organic wastes-composts pollutes water earthy and the air. Benefits of biogas production Biogas is a clean and high heat-capacited energy source. Wastes do not perish. Instead of that, they become a more valuable compost. The weeds in animal compost cannot germinate. Biogas has especially positive health effects in rural areas. Smell of animal compost disappears widely after biogas production. Also, disease agents threatening human health coming from animal waste become inactive. Areas where Biogas is used in Usage In Heating: acquired biogas is burned by a burner and the gained heat is used in houses, animal stables, greenhouses and inside the facility. Biogas stoves, hot water cauldrons or steam cauldrons are generally used in this systems. The biogas purification before usage is important to eliminate corroding hydrogen sulphur (H2S) and carbon dioxide. Usage In Cooking: Biogas can be used in kitchens, as fuel for ovens and stoves using LPG. Usage In Lighting: Biogas can be used in LPG-using lamps by burning directly and also by transforming into electricity. The efficiency level is low like 3% when burning. Preparing Hot Water: We can use biogas to provide hot water at home and industrial need and also for geyser and other water heater systems. Usage In Internal Combustion Engine: Biogas can be used in vehicles as an alternative fuel to common energy sources. Especially in Europe, this kind of applications is encouraged by several projects. Electricity Production: Espacially in medium and large facilities, biogas is used in electric generators. The electric transformation efficiency of biogas is about 22%- 40%. THANKS
























![Bio slurry []](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/004279051_1-54879b7d9c40b09c5c8eed8423d4d6d8-150x150.png)

