* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Overview of Cells and Body Systems - Moodle
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
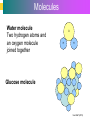
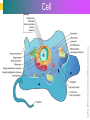
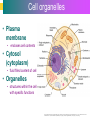
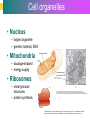
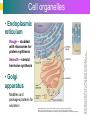
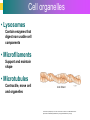
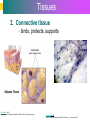
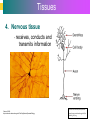
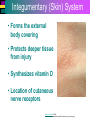
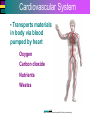
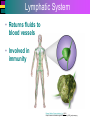
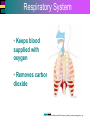
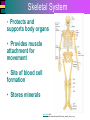
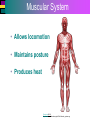
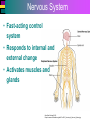
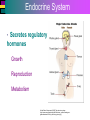
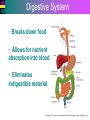
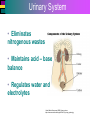
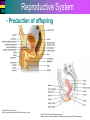
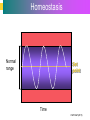
Introduction to Cells, Tissues and Body Systems Life Science FLSS All images used are taken from copyright-free sources e.g. Wikicommons Media or produced by UWS staff and are for illustrative purposes. The human body • Many interdependent parts acting together as an integrated whole • Many structural levels of organisation • Atoms / molecules complex organ systems Levels of organisation • chemical – atoms/molecules • cell Systems – smallest living unit • tissue – aggregates of similar cells • organ – Specific function/ several tissue types • system – many organs/ tissues – specific survival needs Organs Tissues Cellular Chemical Atoms and molecules Atoms eg. Hydrogen (H), Oxygen (O), Carbon (C) Molecules e.g. oxygen molecule (O2) H C O O O Molecules Water molecule Two hydrogen atoms and an oxygen molecule joined together O H H Glucose molecule Uws Staff (2015) Cells • Small community with all component parts essential to maintain life • Cells have certain common features LadyofHats: (2006) http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Animal_cell_structure_en.svg Cell Cell organelles • Plasma membrane • encloses cell contents • Cytosol (cytoplasm) • fluid filled content of cell • Organelles • structures within the cell with specific functions "0312 Animal Cell and Components" by OpenStax College - Anatomy & Physiology, Connexions Web site. http://cnx.org/content/col11496/1.6/, Jun 19, 2013.. Licensed under CC BY 3.0 via Wikimedia Commons - https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:0312_Animal_Cell_and_Components.jpg#/media/File:0312_Animal_Cell_and_Components.jpg Cell organelles • Nucleus • largest organelle • genetic material, DNA • Mitochondria • sausage-shaped • energy supply • Ribosomes • small granular structures • protein synthesis "0315 Mitochondrion new" by OpenStax College - Anatomy & Physiology, Connexions Web site. http://cnx.org/content/col11496/1.6/, Jun 19, 2013.. Licensed under CC BY 3.0 via Wikimedia Commons https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:0315_Mitochondrion_new.jpg#/media/File:0315_Mitochondrion_new.jpg "Ribosme symbol" by Jerome Walker - Own work. Licensed under CC BY 2.5 via Wikimedia Commons https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Ribosme_symbol.svg#/media/File:Ribosme_symbol.svg Cell organelles Rough – studded with ribosomes for protein synthesis Smooth – steroid hormone synthesis • Golgi apparatus Modifies and packages proteins for secretion "0313 Endoplasmic Reticulum" by OpenStax College - Anatomy & Physiology, Connexions Web site. http://cnx.org/content/col11496/1.6/, Jun 19, 2013.. Licensed under CC BY 3.0 via Wikimedia Commons https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:0313_Endoplasmic_Reticulum.jpg#/media/File:0313_Endoplasmic_Reticulum.jpg "0314 Golgi Apparatus" by OpenStax College - Anatomy & Physiology, Connexions Web site. http://cnx.org/content/col11496/1.6/, Jun 19, 2013.. Licensed under CC BY 3.0 via Wikimedia Commons https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:0314_Golgi_Apparatus.jpg#/media/File:0314_Golgi_Apparatus.jpg • Endoplasmic reticulum Cell organelles • Lysosomes Contain enzymes that digest non usable cell components • Microfilaments Support and maintain shape • Microtubules Contractile, move cell and organelles "Actin strand" by Boumphreyfr - Own work. Licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0 via Wikimedia Commons https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Actin_strand.png#/media/File:Actin_strand.png "Erythrocyte" by Jerome Walker - Own work. Licensed under CC BY 2.5 via Wikimedia Commons https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Erythrocyte.svg#/media/File:Erythrocyte.svg Variety of cells types "Derived Neuron schema with no labels" by Dhp1080, svg adaptation by Actam - Image:Neuron.svg. Licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0 via Wikimedia Commons https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Derived_Neuron_schema_with_no_labels.svg#/media/File:Derived_Neuron_schema_with_no_labels.svg "Anatomy and physiology of animals A sperm" by Original uploader was Sunshineconnelly at en.wikibooks - Transferred from en.wikibooks; transferred to Commons by User:Adrignola using CommonsHelper.. Licensed under CC BY 3.0 via Wikimedia Commons https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Anatomy_and_physiology_of_animals_A_sperm.jpg#/media/File:Anatomy_and_physiology_of_animals_A_sperm.jpg Genes & enzymes Enzyme 2 Enzyme 3 Enzyme 1 Lipid molecules oestrogen • Genes – carry a unique molecular code – instruct ribosomes to make specific enzymes • Enzymes – – control chemical reactions in cell THEREFORE GENES CONTROL THE CELL CC0 (2012) https://pixabay.com/en/factory-plant-assembly-line-35081/ Tissues • Cells of similar structure organised to carry out one or more functions • 4 main types of tissue Tissues 1. Epithelial tissue (epithelium) – covers and lines body cavities & surfaces Ruth Lawson. (2007) http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Anatomy_and_physiology_of_animals_cuboidal_epithelium.jpg Tissues 2. Connective tissue - binds, protects, supports BruceBlaus. (2013) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Blausen_0012_AdiposeTissue.png Ganímedes (2013) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Conjuntivo_-_bola_edema.JPG Tissues 3. Muscle tissue - Specialised contractile cells; may be skeletal, cardiac, or smooth OpenStax College (2013) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:1021_Smooth_Muscle_new.jpg Tissues 4. Nervous tissue - receives, conducts and transmits information Pearson Scott Foresman (2012) dendrite: Cahass (2006) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:GolgiStainedPyramidalCell.jpg https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File: Dendrite_(PSF).svg Organs and Body Systems • Organ – body part specialised to perform one or a number of functons • Body system – group of organs working closely together Integumentary (Skin) System • Forms the external body covering • Protects deeper tissue from injury • Synthesizes vitamin D • Location of cutaneous nerve receptors CommonismNow (2006) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Human_skin_structure.jpg Cardiovascular System • Transports materials in body via blood pumped by heart Oxygen Carbon dioxide Nutrients Wastes Sansculotte (2005) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Grafik_blutkreislauf.jpg Lymphatic System • Returns fluids to blood vessels • Involved in immunity Blausen Medical Communications, Inc. (2013) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Blausen_0626_lymphoma.png Respiratory System • Keeps blood supplied with oxygen • Removes carbon dioxide Michka B (2014) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Human_respiratory_system_pedagogical_fr.svg Skeletal System • Protects and supports body organs • Provides muscle attachment for movement • Site of blood cell formation • Stores minerals LadyofHats (2007) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Human_skeleton_front_en.svg Muscular System • Allows locomotion • Maintains posture • Produces heat Termininja (2012) http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Muscular_system.svg Nervous System • Fast-acting control system • Responds to internal and external change • Activates muscles and glands OpenStax College (2013) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:1201_Overview_of_Nervous_System.jpg Endocrine System • Secretes regulatory hormones Growth Reproduction Metabolism United States Governemnt (2005) The endocrine system http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Endocrine_system?uselang=engb#mediaviewer/File:Illu_endocrine_system.jpg Digestive System • Breaks down food • Allows for nutrient absorption into blood • Eliminates indigestible material LadyofHats (2007) : http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Digestive_system_simplified_az.png Immune System • Protects body from infection United States Government (2006) Lymphatic System https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Illu_lymphatic_system.jpg Urinary System • Eliminates nitrogenous wastes • Maintains acid – base balance • Regulates water and electrolytes United States Government (2006) Urinary system https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Illu_urinary_system.jpg Reproductive System • Production of offspring Tsaitgaist (2009) male anatomy https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Male_anatomy_en.svg http://CFCF (2013) Female Reproductive Lateral https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Female_Reproductive_Lateral.JPG?uselang=en-gb Survival Needs • What do cells (and tissues/organs) need to survive ? – nutrients and oxygen – waste removal • Which systems are involved in these processes? Survival needs • Intake Water & nutrients - Digestive system Oxygen - Respiratory system • Elimination Carbon dioxide - Respiratory system Urine - Urinary system Faeces – Digestive system Survival needs • In humans (complex organism), tissues and organs are both: – Highly specialised – Interdependent • Communication is essential! Communication systems • Transport – Blood, circulatory system – lymphatic system • Communication with internal environment – nervous system – endocrine system • Communication with external environment – special senses – verbal/ non-verbal communication Survival needs • Generally, a number of body activities are involved in protection /survival of the body as a whole … Protection and Survival • Protection against external environment – Mainly Integumentary (skin) system: • • • • • invasion by microbes chemicals dehydration reflex action (e.g. in response to pain) regulation of body temperature Internal environment • Human body, millions of cells bathed in tissue fluid = internal environment • must be maintained within narrow limits • Conditions may fluctuate, e.g. – Water content of blood / fluid intake – Blood sugar levels / food intake – Temperature / external environment Homeostasis Normal range Set point Time UWS Staff (2015) Homeostasis • Homeostasis is maintenance of stable internal environment despite changes in external environment • Maintained by control systems 3 basic components: • Receptor (sensor) – detects the change • Control centre – determines set point, analyzes information and determines appropriate response • Effector – Provides a means for response to the stimulus Homeostasis • Disturbance of homeostasis = disease • First become familiar with normal healthy body systems! Steven Rasmussen (2013) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Lauren_Mitchell,_41st_AG_World_Championship_2009 _(tone).jpg