* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Geometry 1
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Riemannian connection on a surface wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Duality (projective geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Perspective (graphical) wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
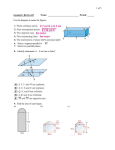
Geometry 1 – Unit 3 Review Name________________________________ 1. Identify alternate interior angles, consecutive interior angles, alternate exterior C angles, corresponding angles, vertical angles, and linear pairs. 2. When two parallel lines are cut by a transversal, compute the A E measures of the angles created. B a. Example 1: ABC = 120°. What is the measure of the other angles? b. Example 2: ABC = (3x + 75)° and FEG = (2x + 85)°. H G Find x. 3. Identify the converse used to determine that two lines are parallel given the measures of alternate interior angles, consecutive interior angles, alternate exterior angles, or corresponding angles. 4. Determine which lines are parallel when given a pair of congruent angles. a b c D F d 5. Find the slope of a line passing through two given points. a. From a Graph b. From an Equation: 3x + 2y = 7 c. From 2 Points: (6, 2) and (3, -5) Geometry 1 – Unit 3 Review Name________________________________ 1. Identify alternate interior angles, consecutive interior angles, alternate exterior C angles, corresponding angles, vertical angles, and linear pairs. 2. When two parallel lines are cut by a transversal, compute the A E measures of the angles created. B a. Example 1: ABC = 120°. What is the measure of the other angles? b. Example 2: ABC = (3x + 75)° and FEG = (2x + 85)°. H G Find x. 3. Identify the converse used to determine that two lines are parallel given the measures of alternate interior angles, consecutive interior angles, alternate exterior angles, or corresponding angles. 4. Determine which lines are parallel when given a pair of congruent angles. a b c d 5. Find the slope of a line passing through two given points. a. From a Graph b. From an Equation: 3x + 2y = 7 c. From 2 Points: (6, 2) and (3, -5) D F 6. Define. a. Transversal b. Parallel Lines c. Perpendicular Lines d. Slope e. Skew Lines f. Inverse of a Statement g. Converse of a Statement h. Contrapositive of a Statement 7. Write the equation of a line parallel or perpendicular to a given line through a given point. 8. Use Angle Addition to find x when given the measure of two adjacent angles K and their combined sum. J H 9. Use Segment Addition to find x and in a proof. 10. Write a two column proof proving 2 lines parallel. I Q R S Exam has 25 questions, approximately half are multiple choice. There are proofs on the test. 6. Define. a. Transversal b. Parallel Lines c. Perpendicular Lines d. Slope e. Skew Lines f. Inverse of a Statement g. Converse of a Statement h. Contrapositive of a Statement 7. Write the equation of a line parallel or perpendicular to a given line through a given point. 8. Use Angle Addition to find x when given the measure of two adjacent angles K and their combined sum. J H 9. Use Segment Addition to find x and in a proof. 10. Write a two column proof proving 2 lines parallel. I Q R S Exam has 25 questions, approximately half are multiple choice. There are proofs on the test.